I recently signed up for the AI Partner Catalyst: Accelerate Innovation hackathon — an initiative focused on accelerating innovation through the Google Cloud partner ecosystem.
For this submission, I built VoiceDoc-Agent : a voice‑native document intelligence system that transforms static text documents into spoken, conversational experiences. The system is powered by Gemini on Vertex AI, ElevenLabs Speech‑to‑Text and Text‑to‑Speech, and Datadog observability, demonstrating how partner AI services can be composed into a cohesive, production‑grade architecture.
VoiceDoc Agent allows users to upload text‑based documents and interact with them entirely through speech. Beyond basic Q&A, the agent supports narration, expressive voice output, persona‑aware responses, and end‑to‑end observability — all deployed serverlessly on Google Cloud.
This project was created specifically for AI Partner Catalyst: Accelerate Innovation, showcasing how Google Cloud partners can collaborate to deliver voice‑first AI systems with real‑time insight into performance, cost, and user experience.
Setup
Firestore
Firestore is used as a serverless document database for ingestion, deduplication, and retrieval‑augmented generation (RAG).
Create a new Firestore database named voicedoc-fs. Two collections are required:
- documents — Used for smart ingestion and deduplication. Before processing a file, the system checks whether its content hash already exists.
- document_chunks" — Stores chunked document text and embeddings used for retrieval.

Service Account
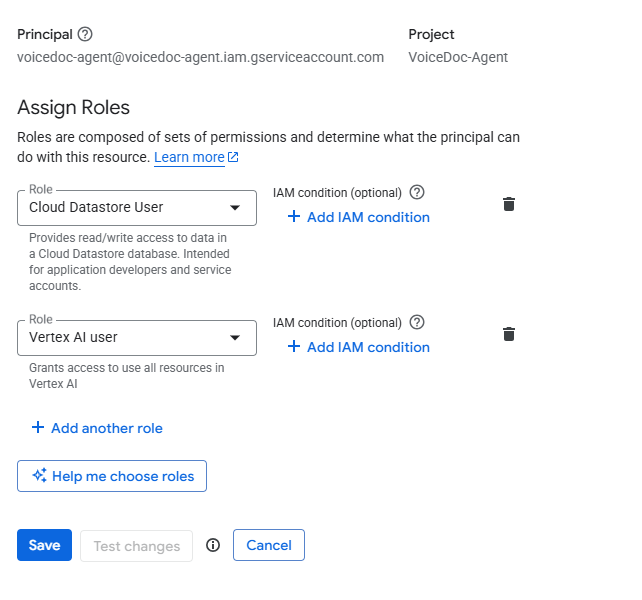
VoiceDoc Agent follows the principle of least privilege. Only the following IAM roles are required:
- Vertex AI User — Gemini API calls, embeddings generation, and document classification
- Cloud Datastore User — Firestore read/write access for document chunks and metadata
Datadog Dashboard
To visualize system‑wide metrics:
- Navigate to Dashboards → New Dashboard in Datadog
- Click Configure → Import dashboard JSON
- Paste the contents of
setup/datadog-dashboard.json

Datadog Monitors
To enable proactive alerting:
- Go to Monitoring → New Monitor
- Select Import From JSON
- Import each monitor defined in
setup/datadob-monitors.json

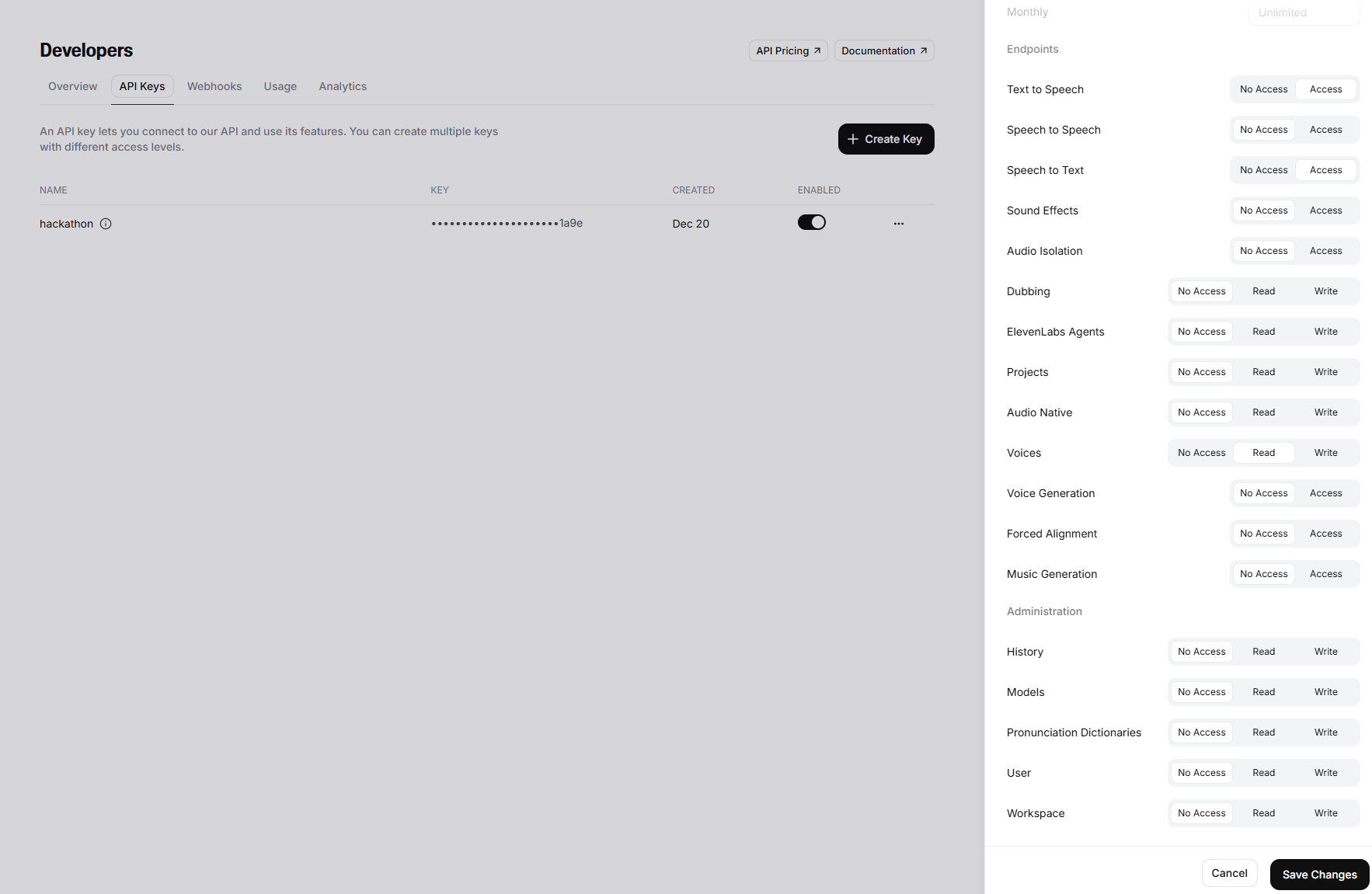
ElevenLabs API Key
Configure the ElevenLabs API key with least‑privilege access:
- ✅ Text to Speech → Access
- ✅ Voices → Read
- ✅ Speech to Text → Access
- ❌ Everything else → Disabled
Code Walkthrough
1. Gemini AI Integration
The Gemini integration lives in src/lib/vertex.ts and is structured as a three‑stage pipeline:
- Retrieve the raw LLM response
- Optionally enrich the response with emotion tags (Expressive Mode)
- Stream the final response back to the client
This design keeps narration, expressive speech, and observability concerns cleanly separated.
1.1 Get the raw response from Gemini
The first call retrieves a strictly grounded response from Gemini, instrumented with Datadog tracing and token‑level metrics.
// ============================================================================
// CALL 1: Get the raw response from Gemini (WITH METRICS)
// ============================================================================
async function getGeminiRawResponse(
history: any[],
query: string,
context: string,
isNarrationRequest: boolean,
voiceMode: 'standard' | 'expressive' = 'standard',
trafficType: string = 'user'
): Promise<string> {
const startTime = Date.now();
return tracer.trace('gemini.request', { resource: 'getGeminiRawResponse' }, async (span) => {
span?.setTag('voice_mode', voiceMode);
console.log('[Call1:getGeminiRawResponse] Getting raw response from Gemini');
const model: GenerativeModel = getVertexAI().getGenerativeModel({
model: modelName,
generationConfig: {
maxOutputTokens: 8192,
temperature: 0.7,
}
});
const validHistory: Content[] = history.map((h: any) => ({
role: h.role,
parts: h.parts || [{ text: h.text }]
}));
let systemPrompt: string;
let textToRead = context;
if (isNarrationRequest) {
const extracted = extractSection(context, query);
if (extracted) {
textToRead = extracted;
console.log('[Call1] Extracted chapter/section');
}
systemPrompt = `You are a professional audiobook narrator. Read the following text aloud EXACTLY as written, word-for-word.
CRITICAL RULES:
1. Do NOT summarize.
2. Do NOT paraphrase.
3. Do NOT skip any words.
4. Output the spoken text ONLY.
5. Do NOT include narration notes, stage directions, or descriptions of tone (e.g., (softly), (muttering), (friendly)).
6. Do NOT include speaker labels.
TEXT TO READ:
${textToRead}`;
} else {
systemPrompt = `You are a voice assistant answering questions about a document. Answer based STRICTLY on the provided context. Do NOT use training data to fill gaps.
CONTEXT:
${context}`;
}
span?.setTag('llm.model', modelName);
span?.setTag('llm.is_narration', isNarrationRequest);
const chat = model.startChat({
history: validHistory,
systemInstruction: {
role: 'system',
parts: [{ text: systemPrompt }]
}
});
const message = isNarrationRequest && extractSection(context, query)
? `Please begin reading.`
: query;
try {
const result = await chat.sendMessage(message);
const response = await result.response;
const rawText = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts[0].text || '';
const usage = response.usageMetadata;
if (usage && usage.promptTokenCount && usage.candidatesTokenCount) {
span?.setTag('llm.prompt_tokens', usage.promptTokenCount);
span?.setTag('llm.completion_tokens', usage.candidatesTokenCount);
span?.setTag('llm.total_tokens', usage.totalTokenCount);
// 📊 RECORD METRICS
MetricsCollector.recordTokens(
usage.promptTokenCount,
usage.candidatesTokenCount,
voiceMode,
trafficType
);
MetricsCollector.recordLLMCost(
usage.promptTokenCount,
usage.candidatesTokenCount,
voiceMode,
trafficType
);
}
console.log('[Call1] Got raw response, length:', rawText.length);
return rawText;
} catch (error: any) {
span?.setTag('error', true);
span?.setTag('error.message', error.message);
// 📊 RECORD ERROR METRIC
MetricsCollector.recordError('call1_error', voiceMode, trafficType);
throw error;
}
});
}Key characteristics:
- Supports both narration and Q&A modes
- Enforces strict grounding against provided document context
- Records token usage and estimated cost
- Emits latency and error metrics for observability
1.2 Add emotion tags using few-shot learning
When Expressive Mode is enabled, a second Gemini call augments the text with ElevenLabs V3 emotion tags using few‑shot examples.
// ============================================================================
// CALL 2: Add emotion tags using few-shot learning (WITH METRICS)
// ============================================================================
async function addEmotionTagsWithFewShot(
rawText: string,
persona: string,
contextHint?: string,
voiceMode: 'standard' | 'expressive' = 'expressive',
trafficType: string = 'user'
): Promise<string> {
return tracer.trace('gemini.request', { resource: 'addEmotionTagsWithFewShot' }, async (span) => {
span?.setTag('voice_mode', voiceMode);
console.log('[Call2:addEmotionTagsWithFewShot] Starting with text length:', rawText.length);
const model: GenerativeModel = getVertexAI().getGenerativeModel({
model: modelName,
generationConfig: {
temperature: 0.2,
topP: 0.7,
}
});
const fewShotExamples = getFewShotExamples(persona);
const history: Content[] = [];
for (const example of fewShotExamples) {
history.push({
role: 'user',
parts: [{ text: example.userInput }]
});
history.push({
role: 'assistant',
parts: [{ text: example.expectedOutput }]
});
}
const systemPrompt = `SYSTEM: You add emotion tags to text ONLY. Nothing else.
TAGS ONLY: [excited] [nervous] [frustrated] [sorrowful] [calm] [sigh] [laughs] [gulps] [gasps] [whispers] [pauses] [hesitates] [wearily] [warmly] [playfully] [stunned] [intrigued] [reflectively] [passionately] [poetically]
YOUR JOB:
1. Take input text
2. Add [tag] BEFORE words - no parentheses, no narration notes
3. Keep EVERY word exactly the same
4. Return ONLY the tagged text
NEVER add: (notes), descriptions, or stage directions.
ONLY add: [emotion_tag] tags in square brackets.`;
span?.setTag('llm.model', modelName);
span?.setTag('llm.persona', persona);
const chat = model.startChat({
history,
systemInstruction: {
role: 'system',
parts: [{ text: systemPrompt }]
}
});
const userMessage = `Add ONLY emotion tags [like this] to this text. Do NOT add parentheses or narration notes. PRESERVE ALL WORDS:
${rawText}`;
console.log('[Call2] Sending to Gemini...');
try {
const result = await chat.sendMessage(userMessage);
const response = await result.response;
let taggedText = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts[0].text || rawText;
const usage = response.usageMetadata;
if (usage && usage.promptTokenCount && usage.candidatesTokenCount) {
span?.setTag('llm.prompt_tokens', usage.promptTokenCount);
span?.setTag('llm.completion_tokens', usage.candidatesTokenCount);
span?.setTag('llm.total_tokens', usage.totalTokenCount);
// 📊 RECORD METRICS
MetricsCollector.recordTokens(
usage.promptTokenCount,
usage.candidatesTokenCount,
voiceMode,
trafficType
);
MetricsCollector.recordLLMCost(
usage.promptTokenCount,
usage.candidatesTokenCount,
voiceMode,
trafficType
);
}
taggedText = taggedText.replace(/\([^)]*?\)/g, '').trim();
console.log('[Call2] After cleanup, length:', taggedText.length);
return taggedText;
} catch (error: any) {
span?.setTag('error', true);
span?.setTag('error.message', error.message);
// 📊 RECORD ERROR METRIC
MetricsCollector.recordError('call2_error', voiceMode, trafficType);
throw error;
}
});
}Design goals:
- Preserve every word of the original text
- Insert emotion tags only in square‑bracket format
- Prevent narration notes or paraphrasing
- Keep expressive behavior deterministic and auditable
1.3 Stream response from LLM
The streaming function orchestrates the two‑call pipeline and yields the final text for downstream TTS processing.
// ============================================================================
// STREAMING RESPONSE (WITH METRICS)
// ============================================================================
export async function* getGeminiStream(
history: Content[],
query: string,
context: string,
isNarrationRequest: boolean = false,
expressiveMode: boolean = false,
persona: string = 'narrative',
trafficType: string = 'user'
) {
const startTime = Date.now();
console.log('[getGeminiStream] 🚀 Starting two-call process', { expressiveMode, persona, trafficType });
try {
console.log('[getGeminiStream] Is narration request:', isNarrationRequest);
// CALL 1: Get raw response
console.log('[getGeminiStream] ========== CALL 1: RAW RESPONSE ==========');
const voiceMode = expressiveMode ? 'expressive' : 'standard';
const rawResponse = await getGeminiRawResponse(history, query, context, isNarrationRequest, voiceMode, trafficType);
console.log('[getGeminiStream] CALL 1 OUTPUT (length:', rawResponse.length, ')');
if (!rawResponse.trim()) {
yield 'No response generated.';
// 📊 RECORD METRICS
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
return;
}
// CALL 2: Add emotion tags if expressive mode
let finalResponse: string;
if (expressiveMode) {
console.log('[getGeminiStream] ========== CALL 2: ADD EMOTION TAGS ==========');
finalResponse = await addEmotionTagsWithFewShot(rawResponse, persona, undefined, voiceMode, trafficType);
console.log('[getGeminiStream] CALL 2 OUTPUT (length:', finalResponse.length, ')');
} else {
// Cleanup any hallucinations like (narrative tone) or [pauses] that might leak in Standard mode
finalResponse = rawResponse.replace(/\([^)]*?\)/g, '').replace(/\[[^\]]*?\]/g, '').trim();
console.log('[getGeminiStream] Standard mode - cleanup applied and Call 2 skipped');
}
console.log('[getGeminiStream] ✅ Complete, yielding final response');
yield finalResponse;
} catch (error) {
console.error('[getGeminiStream] ❌ Fatal error:', error);
// 📊 RECORD ERROR
MetricsCollector.recordError('fatal_error', expressiveMode ? 'expressive' : 'standard', trafficType);
if (error instanceof Error) {
console.error('[getGeminiStream] Message:', error.message);
console.error('[getGeminiStream] Stack:', error.stack);
}
yield `\n\nERROR: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}\n`;
throw error;
}
}Highlights:
- Expressive Mode triggers a controlled second LLM call
- Standard Mode performs defensive cleanup of stray tags
- All errors and latency are captured via Datadog metrics
2. ElevenLabs API
ElevenLabs is used for both speech transcription and voice generation, with dynamic model selection based on document persona and expressive intent.
2.1 Transcribe API
Speech‑to‑Text is implemented in src/app/api/transcribe/route.ts:
export async function POST(req: NextRequest) {
try {
console.log('=== Transcribe API Called ===');
const formData = await req.formData();
const audioFile = formData.get('audio') as File;
if (!audioFile) {
console.error('No audio file provided');
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: 'No audio file provided' },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
console.log(`📦 Received audio file: ${audioFile.name}, size: ${audioFile.size} bytes, type: ${audioFile.type}`);
// Convert File to Blob
const arrayBuffer = await audioFile.arrayBuffer();
const audioBlob = new Blob([arrayBuffer], { type: audioFile.type || 'audio/webm' });
console.log('🎙️ Calling ElevenLabs speechToText.convert()...');
const transcription = await getClient().speechToText.convert({
file: audioBlob,
modelId: 'scribe_v1',
tagAudioEvents: true,
languageCode: 'eng',
diarize: true,
});
console.log('✅ Transcription successful:', JSON.stringify(transcription, null, 2));
// Handle different response structures
let transcribedText = '';
// Check various possible response structures
if ((transcription as any).text) {
transcribedText = (transcription as any).text;
} else if ((transcription as any).transcription) {
transcribedText = (transcription as any).transcription;
} else if ((transcription as any).result) {
transcribedText = (transcription as any).result;
} else if ((transcription as any).chunks && Array.isArray((transcription as any).chunks)) {
// If it's multichannel with chunks
transcribedText = (transcription as any).chunks
.map((chunk: any) => chunk.text || chunk.transcript || '')
.join(' ');
} else if (Array.isArray(transcription)) {
// If it's an array response
transcribedText = transcription
.map((item: any) => item.text || item.transcript || '')
.join(' ');
}
console.log('📝 Extracted text:', transcribedText);
return NextResponse.json({
text: transcribedText,
success: true,
transcription: transcription,
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ Transcription error:', error);
// Log detailed error info
if (error instanceof Error) {
console.error('Error message:', error.message);
console.error('Error stack:', error.stack);
}
const errorMessage = error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error);
return NextResponse.json(
{
error: 'Transcription failed',
details: errorMessage,
},
{ status: 500 }
);
}
}The implementation:
- Accepts streamed audio input
- Handles multiple response formats defensively
- Supports diarization and audio event tagging
- Emits structured logs for debugging and traceability
2.2 Speak API
Text‑to‑Speech is implemented in src/app/api/speak/route.ts:
export async function POST(req: NextRequest) {
try {
const {
text,
persona,
expressiveMode = false, // 🔑 mirrors Gemini pipeline
}: {
text: string;
persona?: Persona;
expressiveMode?: boolean;
} = await req.json();
if (!text) {
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'Text is required' }, { status: 400 });
}
const voiceId = getVoiceIdForPersona(persona as Persona);
// 🎭 Model selection
const modelId = expressiveMode
? 'eleven_v3'
: 'eleven_flash_v2_5';
const inferredExpressive =
expressiveMode || /\[[^\]]+\]/.test(text);
const finalExpressiveMode = inferredExpressive;
// 🧹 Strip emotion tags in standard mode
const processedText = finalExpressiveMode
? text
: text.replace(/\[[^\]]*?\]/g, '').trim();
console.log(
`🎙️ TTS Request | Persona: ${persona || 'narrative'} | ` +
`Mode: ${expressiveMode ? 'expressive' : 'standard'} | ` +
`Model: ${modelId} | VoiceID: ${voiceId}`
);
const audio = await getClient().textToSpeech.convert(voiceId, {
text: processedText,
modelId,
outputFormat: 'mp3_44100_128',
});
return new NextResponse(audio as any, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'audio/mpeg',
},
});
} catch (error: any) {
console.error('❌ TTS Error:', {
message: error.message,
statusCode: error.statusCode,
body: error.body,
});
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: error.message || 'TTS failed', details: error.body || '' },
{ status: error.statusCode || 500 }
);
}
}Notable behaviors:
- Automatically selects Eleven Flash v2.5 or Eleven v3
- Detects emotion tags to infer expressive output
- Strips tags when running in Standard Mode
- Streams MP3 audio optimized for low latency
3. Datadog API
3.1 Core Concept: Agentless Observability
VoiceDoc Agent runs on Google Cloud Run without any Datadog Agent or sidecar containers. All telemetry is sent directly via Datadog’s HTTPS APIs, making it ideal for hackathons and serverless workloads.
3.2 Real User Monitoring (RUM) - Frontend
The frontend captures real user interactions, performance metrics, and session replays.
Implementation: src/components/DatadogInit.tsx:
datadogRum.init({
applicationId,
clientToken,
site,
service: 'voicedoc-agent',
sessionSampleRate: 100,
sessionReplaySampleRate: 20, // 100% for development/testing
trackUserInteractions: true,
trackResources: true,
trackLongTasks: true,
})3.3 Session Replay
Session Replay enables visual debugging by correlating UI behavior with backend traces.
// Start Session Replay Recording
datadogRum.startSessionReplayRecording();3.4 Custom Metrics (Agentless) - Backend
Custom metrics are sent directly to Datadog without StatsD or agents.
// PATH 1: AGENTLESS (HTTPS API) - Best for Hackathons
if (DD_API_KEY) {
const response = await fetch(
`https://api.${DD_SITE}/api/v1/series?api_key=${DD_API_KEY}`,
{
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ series })
}
);
}Key Metrics:
| Metric | Purpose | Voice-Specific Tag |
|---|---|---|
voicedoc.request.latency_ms |
Gemini response latency | voice_mode:* |
voicedoc.llm.total_tokens |
Token usage | voice_mode:* |
voicedoc.llm.cost |
Estimated cost | currency:usd |
voicedoc.request.hits |
Request count | is_narration:* |
voicedoc.request.errors |
Error tracking | error_type:* |
voicedoc.llm.ttft |
Time to First Token | voice_mode:* |
voicedoc.persona.classified |
Persona detection | persona_type:* |
4. Core UI Components
The main Next.js application lives in src/app/page.tsx and provides:
- Document Upload — Text ingestion and persona classification
- Persona Settings — Toggle Standard vs Expressive voice modes
- Mic Test Lab — Standalone microphone testing
- Real-time Metrics — Live visibility into latency and speech performance
- User Input — Speech or text‑based interaction
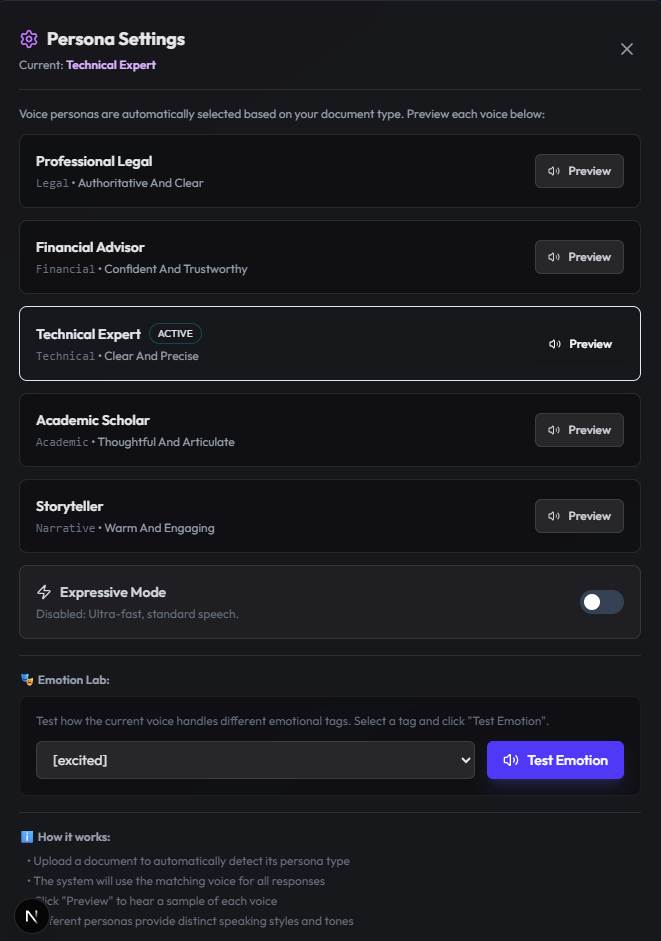
4.1 Persona Settings
Upon upload, src/app/api/upload/route.ts invokes Gemini to classify the document persona. Users can preview voices for:
- Professional Legal
- Financial Advisor
- Technical Expert
- Academic Scholar
- Storyteller
Users can also experiment with ElevenLabs V3 emotion tags directly from the UI.
4.2 Mic Test Lab
The standalone Mic Test Lab allows users to validate microphone input and immediately hear synthesized output.

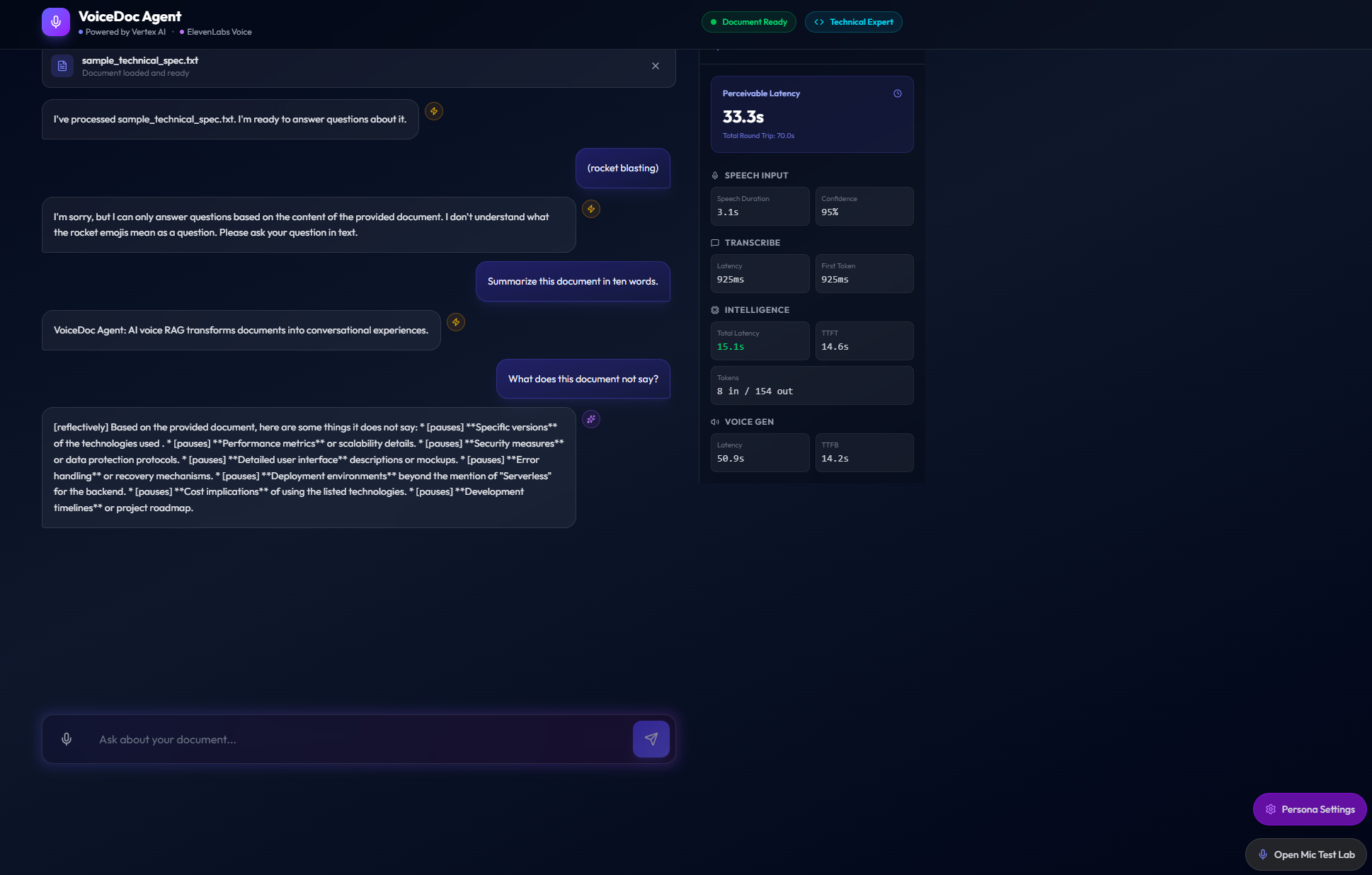
4.3 Real-time Metrics
The metrics sidebar provides transparent, user‑visible performance data, including:
- Perceivable Latency
- Total Round Trip Time
- Speech Duration and Confidence
- STT Latency and First Token
- LLM Latency and TTFT
- Token Usage
- TTS Latency and TTFB
Getting Started
To run VoiceDoc Agent locally, ensure that the following dependencies are provisioned and configured correctly:
- A Firestore database (
voicedoc-fs) with the required collections - A Google Cloud service account with Vertex AI and Firestore access
- Valid API keys for ElevenLabs and Datadog
All required environment variables are documented in env.example. Once configured, the local setup mirrors the production Cloud Run environment used for the hackathon.
Running Locally
Start the VoiceDoc Agent development server with:
npm run devIn Action
To experience Expressive Mode, upload the sample document located at sample/sample_narrative_story.txt, then switch the persona mode to Expressive in the Persona Settings panel.
As a first interaction, try issuing the voice or text command:
“Read Chapter One”
This triggers the full two-stage Gemini pipeline — raw narration followed by emotion tagging — and streams the expressive audio response using ElevenLabs V3 voices.
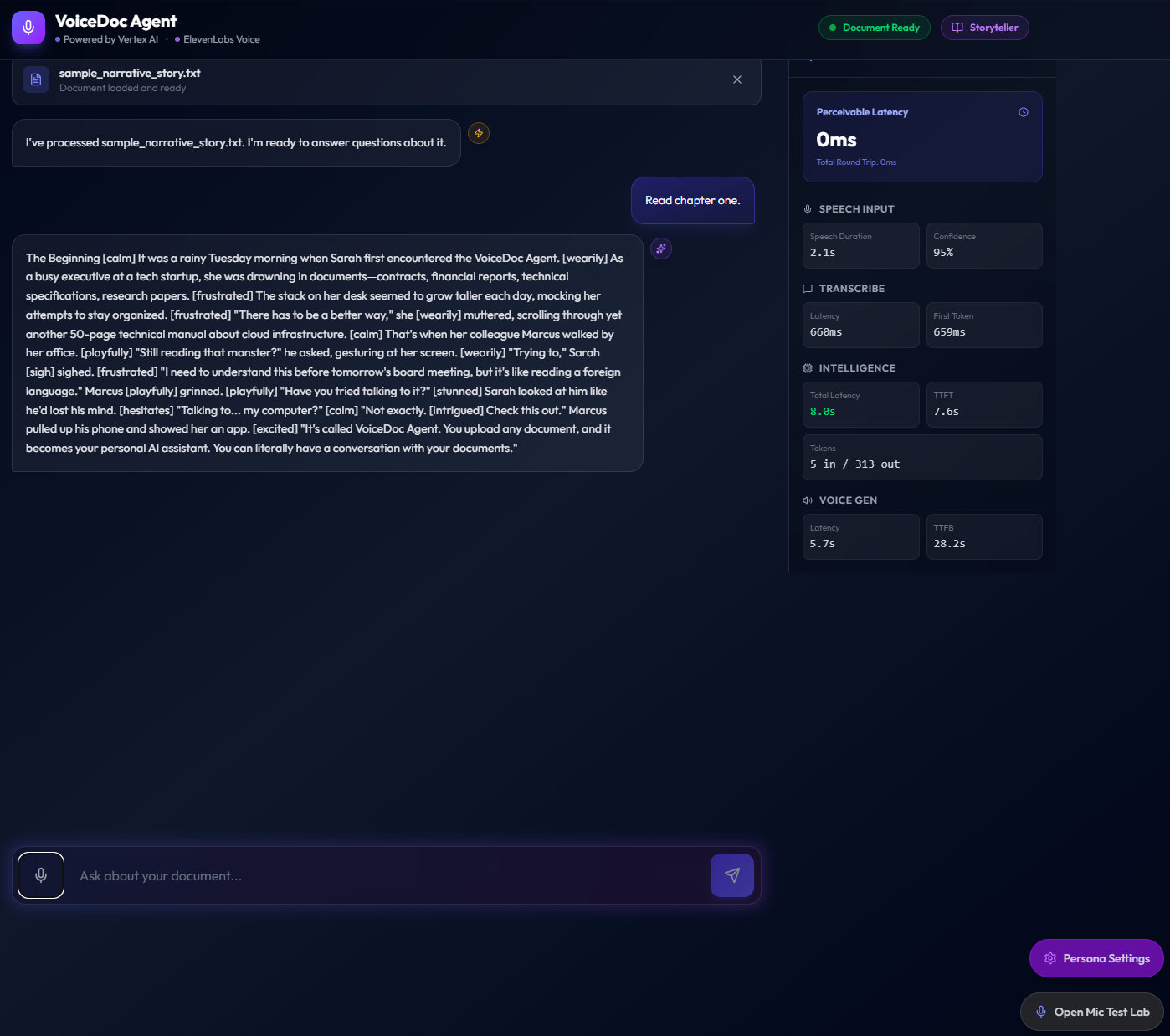
ElevenLabs Narrative Voice
Below is a sample of the generated expressive narration audio:
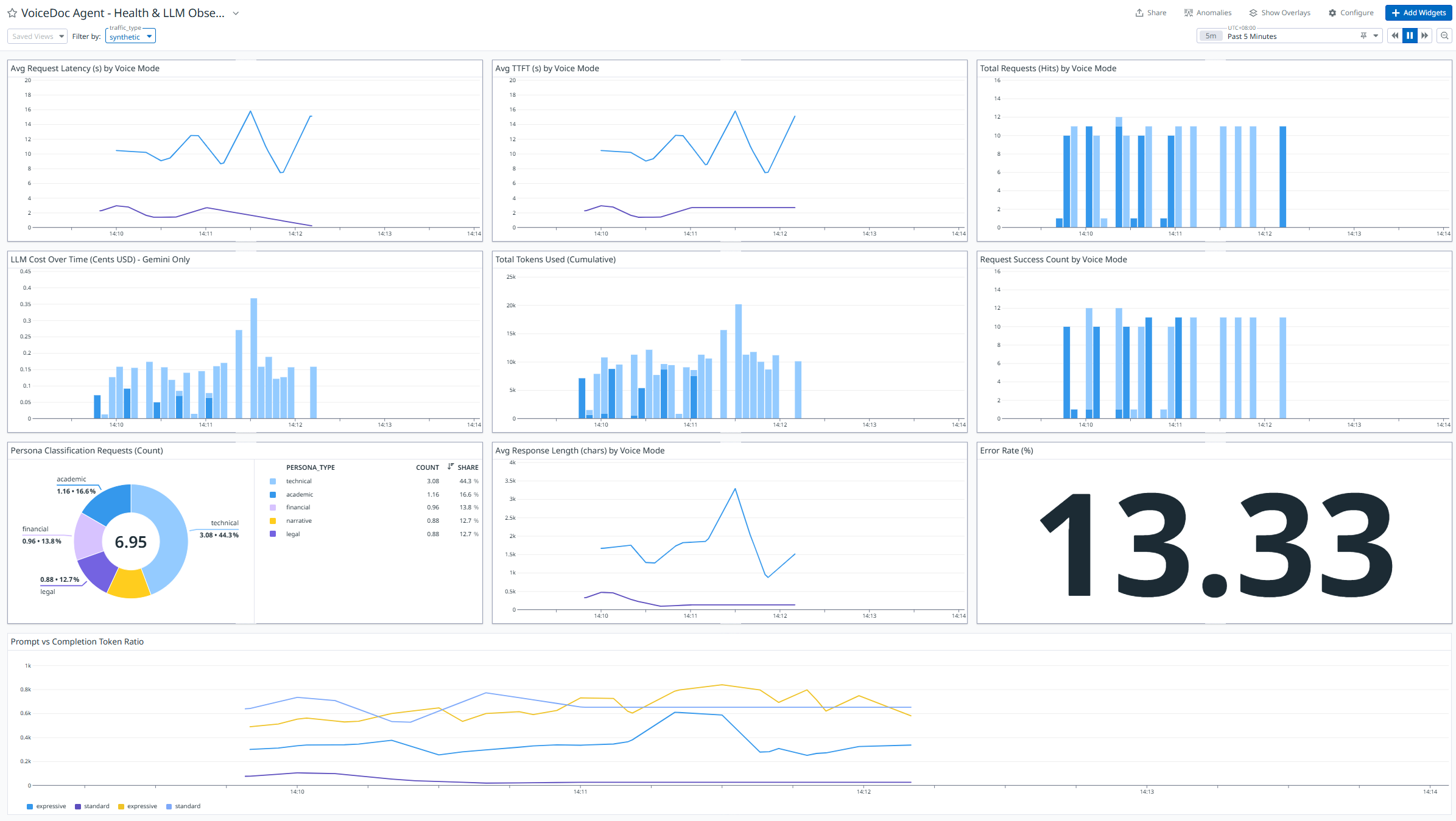
Sample Datadog Dashboard:
The Datadog dashboard provides real-time visibility into latency, token usage, cost estimation, and voice-specific performance metrics across the entire request lifecycle.

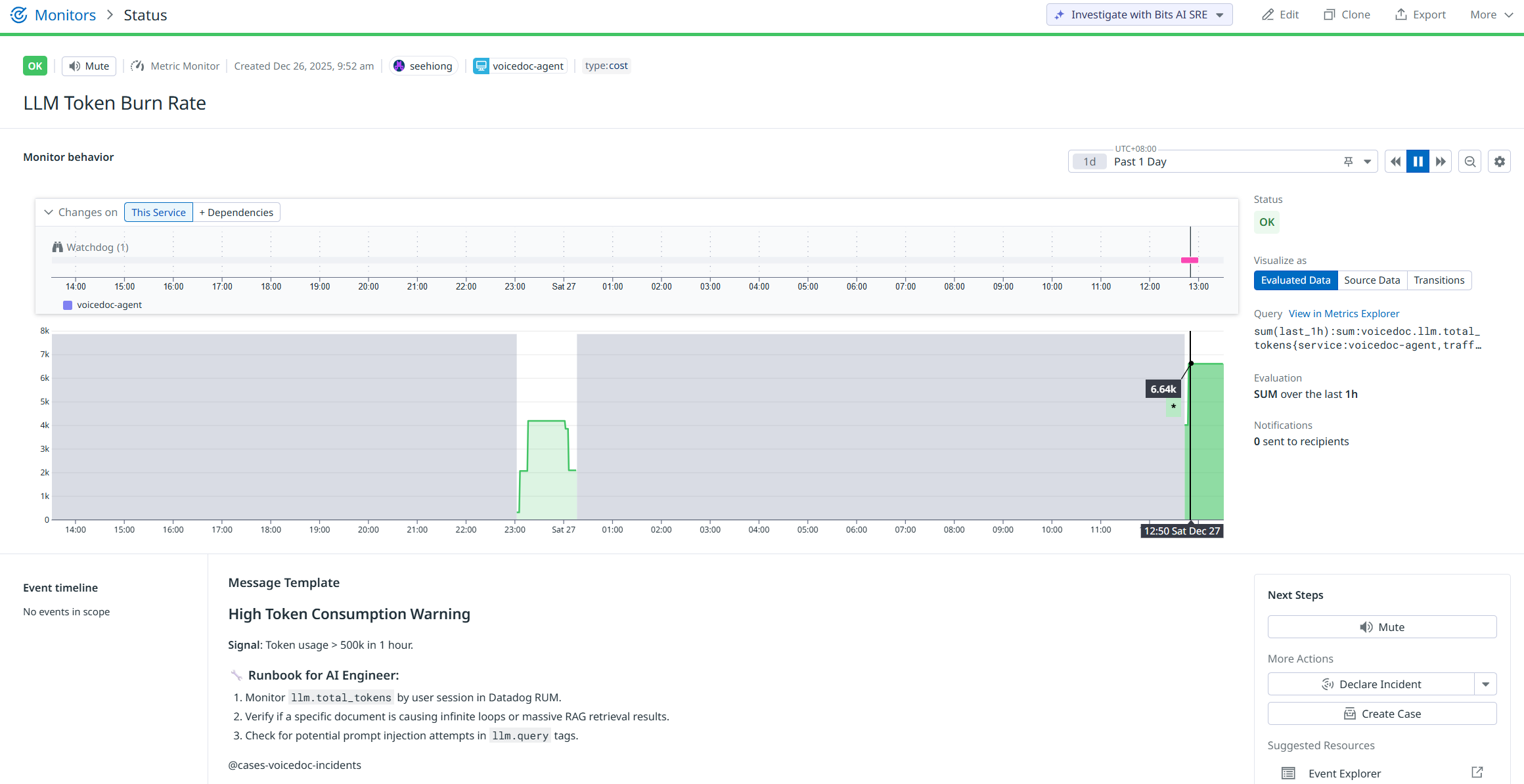
Sample Datadog Monitor:
Monitors are configured to proactively detect anomalies such as LLM token burn rate spikes, elevated latency, or error surges — enabling early intervention before user experience degrades.
Sample Datadog Session Replay
Session Replay ties everything together by correlating frontend user behavior with backend LLM and voice performance, making it easier to debug and optimize real-world voice interactions.
Synthetic Traffic Generator
To validate system behavior under repeatable and controlled conditions, VoiceDoc Agent includes a synthetic traffic generator that simulates real user interactions across different personas, voice modes, and request types.
This tool is especially useful for:
- Load testing expressive vs standard voice paths
- Validating LLM latency, TTFT, and token usage
- Exercising Datadog monitors without real users
- Reproducing edge cases deterministically during development
Trigger the synthetic traffic generator with:
python scripts\traffic-generator.py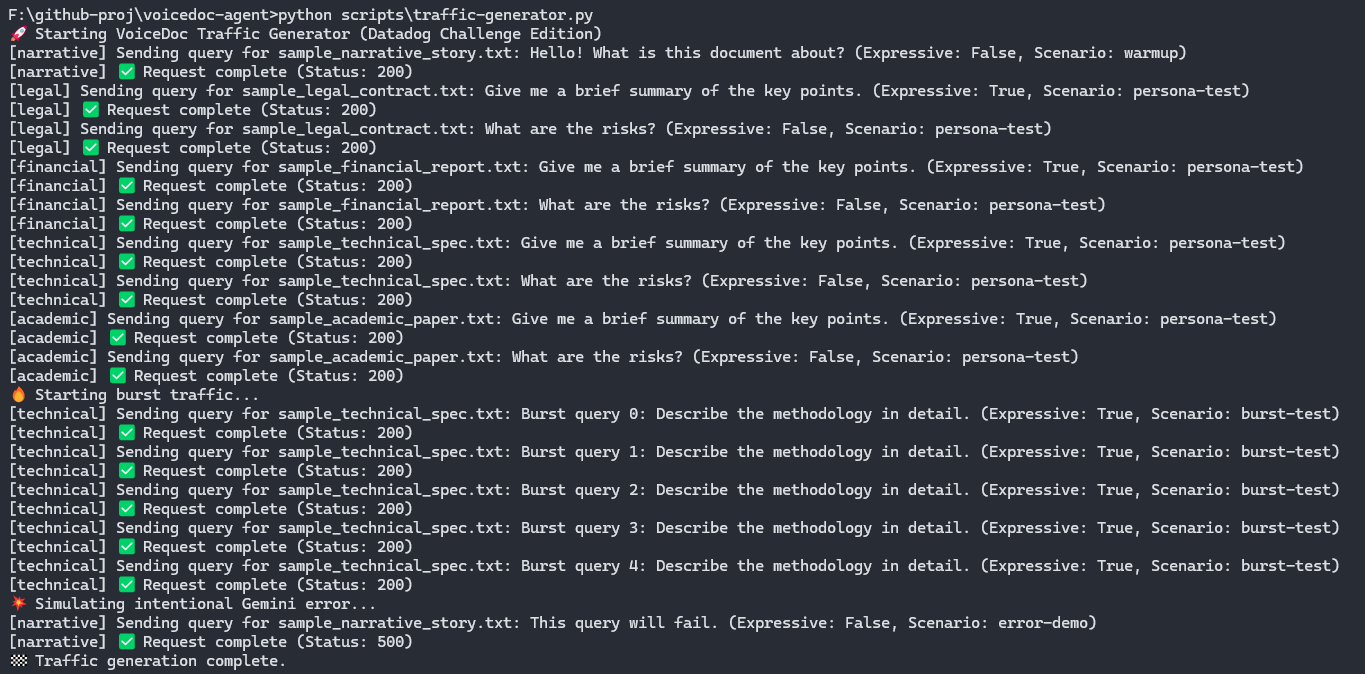
Synthetic traffic is explicitly tagged and can be filtered independently within Datadog dashboards and monitors, ensuring clear separation between test signals and real user behavior.
Conclusion
VoiceDoc Agent demonstrates how voice-first AI systems can be built with production-grade rigor, not just compelling demos. By combining Gemini on Vertex AI for reasoning, ElevenLabs for expressive and real-time voice, and Datadog for end-to-end observability, the project showcases a practical blueprint for deploying conversational, document-aware agents at scale.
More importantly, this project highlights how the Google Cloud partner ecosystem can be composed into a cohesive system where performance, cost, and user experience are first-class concerns. Features such as expressive narration, persona-aware responses, agentless observability, and synthetic traffic testing ensure that the system is not only engaging, but measurable, debuggable, and extensible.
Built for AI Partner Catalyst: Accelerate Innovation, VoiceDoc Agent reflects an approach to AI development that prioritizes clarity, control, and real-world operability — pushing voice-native interfaces beyond novelty and toward production-ready applications.
