Having recently completed Coursera’s Agentic AI with LangChain and LangGraph , I was eager to apply the concepts to a real project. This post walks through the full journey—from building a minimal LangGraph chain, to implementing a ReAct agent, and finally orchestrating a fully automated multi-agent system (MAS) optimized for Singapore HDB data analysis.
Setup
As usual, we begin by initializing a clean Python project using
uv
, an ultra-fast Python package manager and environment tool:
mkdir multi-agent-system-using-langgraph
cd multi-agent-system-using-langgraph
# Initialize project
uv init .
# Create and activate virtual environment
uv sync
.venv\Scripts\activate
# Add dependencies
uv add langgraph langchain langchain_openai langchain_tavily toolbox-langchainUse Case 1: TOTO Generator (Deterministic Chain)
To warm up, let’s start with a fun and simple example: a TOTO number generator.
TOTO is a Singaporean lottery where players choose six numbers from 1 to 49. This use case is perfect for demonstrating a simple LangGraph loop with conditional stopping.
We implement this in a new notebook: toto_generator.ipynb.
1. Define ChainState
import random
from typing import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
class ChainState(TypedDict):
n: int
number: int
used_numbers: set[int]2. Add, dump, and stop-condition functions
def add(state: ChainState) -> ChainState:
used_numbers = state.get("used_numbers", set())
if len(used_numbers) >= 49:
raise ValueError("All numbers from 1-49 have been used")
available = set(range(1, 50)) - used_numbers
random_number = random.choice(list(available))
new_used_numbers = used_numbers.copy()
new_used_numbers.add(random_number)
return {
**state,
"n": state["n"] + 1,
"number": random_number,
"used_numbers": new_used_numbers
}
def dump(state: ChainState) -> ChainState:
print("Current n:", state["n"], "number:", state["number"])
print("Winning numbers:", sorted(state.get("used_numbers", set())))
return state
def stop_condition(state: ChainState) -> bool:
return state["n"] >= 63. Build the graph
graph = StateGraph(ChainState)
graph.add_node("add", add)
graph.add_node("dump", dump)
graph.add_edge("add", "dump")
graph.add_conditional_edges("dump", stop_condition, {
True: END,
False: "add",
})
graph.set_entry_point("add")
app = graph.compile()4. Run the graph
result = app.invoke({"n": 0, "number": ""})
# Sample result
# Current n: 1 number: 43
# Winning numbers: [43]
# Current n: 2 number: 19
# Winning numbers: [19, 43]
# Current n: 3 number: 9
# Winning numbers: [9, 19, 43]
# Current n: 4 number: 36
# Winning numbers: [9, 19, 36, 43]
# Current n: 5 number: 38
# Winning numbers: [9, 19, 36, 38, 43]
# Current n: 6 number: 37
# Winning numbers: [9, 19, 36, 37, 38, 43]Congratulations — you’ve just built your first LangGraph-based deterministic generator!
5. Visualize the chain
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(app.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))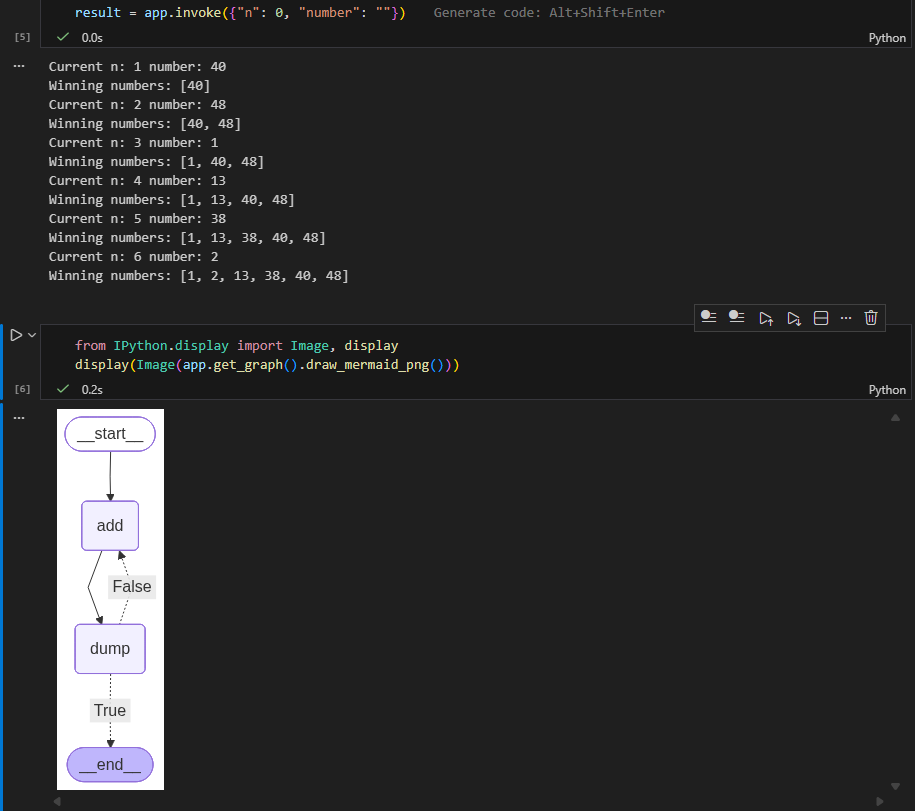
This diagram clearly illustrates the add → dump → add loop until six numbers are generated.
Use Case 2: Full ReAct Agent with MCP, Tavily & SQL
In this section, we significantly expand the system: A ReAct-style agent equipped with:
- MCP Toolbox for Postgres (HDB resale data)
- Tavily for real-world web search
- Custom Python amenities search tool
- LangGraph for orchestration
This uses the same HDB dataset from my previous article: 👉 ADK Web Multi-Agent System
This use case will showcase the full power of your MCP Toolbox SQL suite combined with Tavily + Python tools, inside a ReAct agent powered by LangGraph.
MCP Toolbox – Postgres Configuration
To unify the various HDB resale datasets, I first combine them:
CREATE TABLE hdb_combined_resale_flat_prices AS
SELECT month, town, flat_type, block, street_name, storey_range,
floor_area_sqm, flat_model, lease_commence_date, resale_price
FROM raw_resale_flat_prices_from_jan_2017_onwards
UNION ALL SELECT * FROM raw_resale_flat_prices_from_jan_2015_to_dec_2016
UNION ALL SELECT * FROM raw_resale_flat_prices_from_mar_2012_to_dec_2014
UNION ALL SELECT * FROM raw_resale_flat_prices_2000_to_feb_2012
UNION ALL SELECT * FROM raw_resale_flat_prices_1990_1999;Then I define tools.yaml pointing to my homelab Postgres instance.
sources:
my-pg-source:
kind: postgres
host: postgres.local
port: 5432
database: postgres
user: postgres
password: postgres
tools:
postgres-list-tables:
kind: postgres-list-tables
source: my-pg-source
description: Retrieves schema information for all or specified tables.
execute-sql-tool:
kind: postgres-execute-sql
source: my-pg-source
description: Executes an arbitrary SQL statement.
list-hdb-flats-by-town:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-source
description: Returns the latest 5 resale transaction records for flats in a given town.
parameters:
- name: town
type: string
description: The town to search for.
statement: >
SELECT *
FROM public.hdb_combined_resale_flat_prices t
WHERE t.town ILIKE '%' || $1 || '%'
ORDER BY t.month DESC
LIMIT 5;
count-hdb-flats-by-town:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-source
description: Counts the total number of resale transactions in the given town.
parameters:
- name: town
type: string
description: The town to count transactions in.
statement: >
SELECT COUNT(*) AS count
FROM public.hdb_combined_resale_flat_prices t
WHERE t.town ILIKE '%' || $1 || '%';
percentile-price-by-town:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-source
description: Returns a resale price percentile (median, p90, etc.) for a town.
parameters:
- name: town
type: string
description: The town to compute the percentile for.
- name: percentile
type: float
description: The percentile to compute (0.5 = median).
default: 0.5
statement: >
SELECT
PERCENTILE_CONT($2) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY t.resale_price)
AS percentile_price
FROM public.hdb_combined_resale_flat_prices t
WHERE t.town ILIKE '%' || $1 || '%';
average-price-by-flat-type:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-source
description: Returns the average resale price for a specific flat type, optionally filtered by town.
parameters:
- name: flat_type
type: string
description: The flat type (e.g., '3 ROOM', '4 ROOM').
- name: town
type: string
description: Optional town filter (default = all towns).
default: '%'
statement: >
SELECT AVG(t.resale_price) AS avg_price
FROM public.hdb_combined_resale_flat_prices t
WHERE t.flat_type = $1
AND t.town ILIKE '%' || $2 || '%';
toolsets:
my-toolset:
- postgres-list-tables
- execute-sql-tool
- list-hdb-flats-by-town
- count-hdb-flats-by-town
- percentile-price-by-town
- average-price-by-flat-typeRunning the Toolbox:
$VERSION = "0.18.0"
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://storage.googleapis.com/genai-toolbox/v$VERSION/windows/amd64/toolbox.exe" -OutFile "toolbox.exe"
.\toolboxBuilding the ReAct Agent (LangGraph)
We now construct a full ReAct agent in langgraph_react_agent.ipynb. The flow:
- Load MCP SQL tools
- Load Tavily
- Register all tools
- Create ReAct prompt
- Bind model
- Build LangGraph agent
- Test with streaming
1. Imports
import os
import json
from typing import Annotated, Sequence, TypedDict
from langchain_core.messages import (
HumanMessage, AIMessage, BaseMessage, ToolMessage
)
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain.tools import tool
from toolbox_langchain import ToolboxClient
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages2. Async Load MCP Tools
mcp_client = ToolboxClient("http://127.0.0.1:5000")
async def load_mcp():
return await mcp_client.aload_toolset()
mcp_tools = await load_mcp()
print("Loaded MCP tools:", [t.name for t in mcp_tools])3. Tavily + Amenities Tool
tavily = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
@tool
def search_hdb_amenities(query: str) -> str:
"""
Search for amenities near an HDB block or town using Tavily.
Example queries:
- "amenities near Block 123 Ang Mo Kio"
- "schools near Bukit Panjang"
- "supermarkets near Tampines"
- "parks near Woodlands"
The tool returns summarized search results.
"""
formatted_query = f"amenities around {query}, Singapore HDB, nearby facilities, schools, supermarkets, malls, transport"
results = tavily.invoke(formatted_query)
return results4. Collect all tools
tools = [tavily, search_hdb_amenities] + mcp_tools
tools_by_name = {t.name: t for t in tools}
print("All tools loaded:", list(tools_by_name.keys()))
# Sample output
# All tools loaded: ['tavily_search', 'search_hdb_amenities', 'average-price-by-flat-type', 'count-hdb-flats-by-town', 'execute-sql-tool', 'list-hdb-flats-by-town', 'percentile-price-by-town', 'postgres-list-tables']5. Agent Prompt (ReAct)
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """
You are an intelligent ReAct-style assistant with access to Postgres SQL (via MCP Toolbox)
and real-world web search tools (Tavily + amenities search).
Use SQL tools for:
- HDB transactions
- resale prices
- median / percentile
- flat type analysis
- town or block queries
Use search_hdb_amenities for:
- schools
- malls
- supermarkets
- parks
- hospitals
- amenities around blocks/towns
Use Tavily for general external knowledge.
Always:
1. Think step-by-step
2. Choose the correct tool
3. Call tools with correct arguments
4. Integrate tool output into your answer
"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])6. Bind model and tools
MODEL = "moonshotai/kimi-k2-thinking"
model = ChatOpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("OPENROUTER_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://openrouter.ai/api/v1",
model=MODEL,
)
# Bind tools for ReAct
model_react = chat_prompt | model.bind_tools(tools)7. Agent State Definition
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], add_messages]8. Define Async Model and Tool nodes
async def call_model(state: AgentState):
response = await model_react.ainvoke({"scratch_pad": state["messages"]})
return {"messages": [response]}
async def tool_node(state: AgentState):
outputs = []
last = state["messages"][-1]
for tc in last.tool_calls:
tool = tools_by_name[tc["name"]]
# All toolbox_langchain tools support .ainvoke()
result = await tool.ainvoke(tc["args"])
outputs.append(
ToolMessage(
content=json.dumps(result),
name=tc["name"],
tool_call_id=tc["id"]
)
)
return {"messages": outputs}9. Continue / End Decision Node
def should_continue(state: AgentState):
last = state["messages"][-1]
if last.tool_calls:
return "continue"
return "end"10. Build LangGraph (Async Model)
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
workflow.add_node("agent", call_model)
workflow.add_node("tools", tool_node)
workflow.add_edge("tools", "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
should_continue,
{
"continue": "tools",
"end": END,
}
)
workflow.set_entry_point("agent")
graph = workflow.compile()11. Run the agent (Async Streaming)
Test 1 — Resale Transactions
inputs = {
"messages": [
HumanMessage("Get me the past resale transactions for block 100 in Toa Payoh.")
]
}
async for step in graph.astream(inputs, stream_mode="values"):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()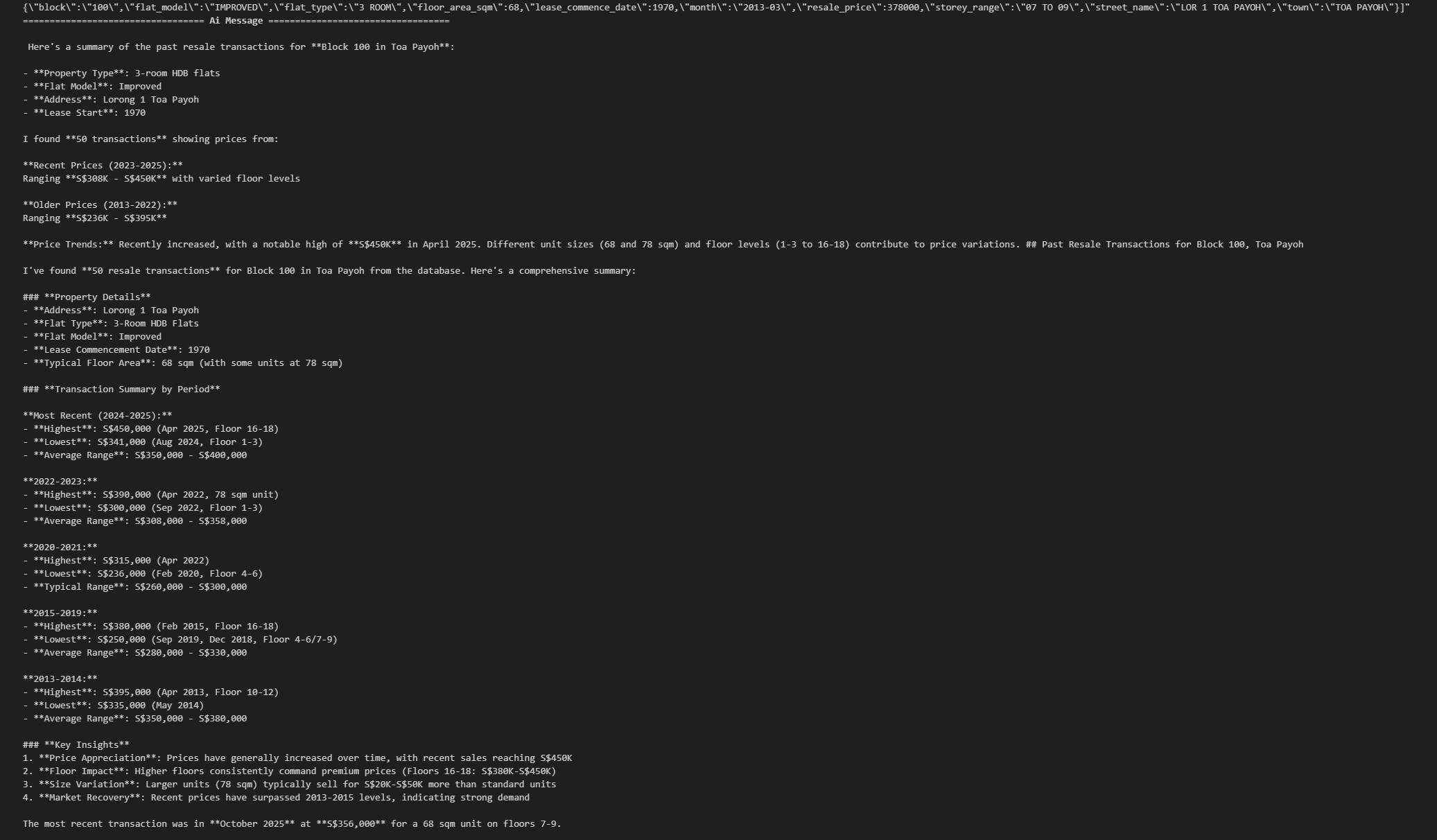
Test 2 — Amenities Around an HDB Block
inputs = {
"messages": [
HumanMessage("What amenities are near Block 110 in Toa Payoh?")
]
}
async for step in graph.astream(inputs, stream_mode="values"):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()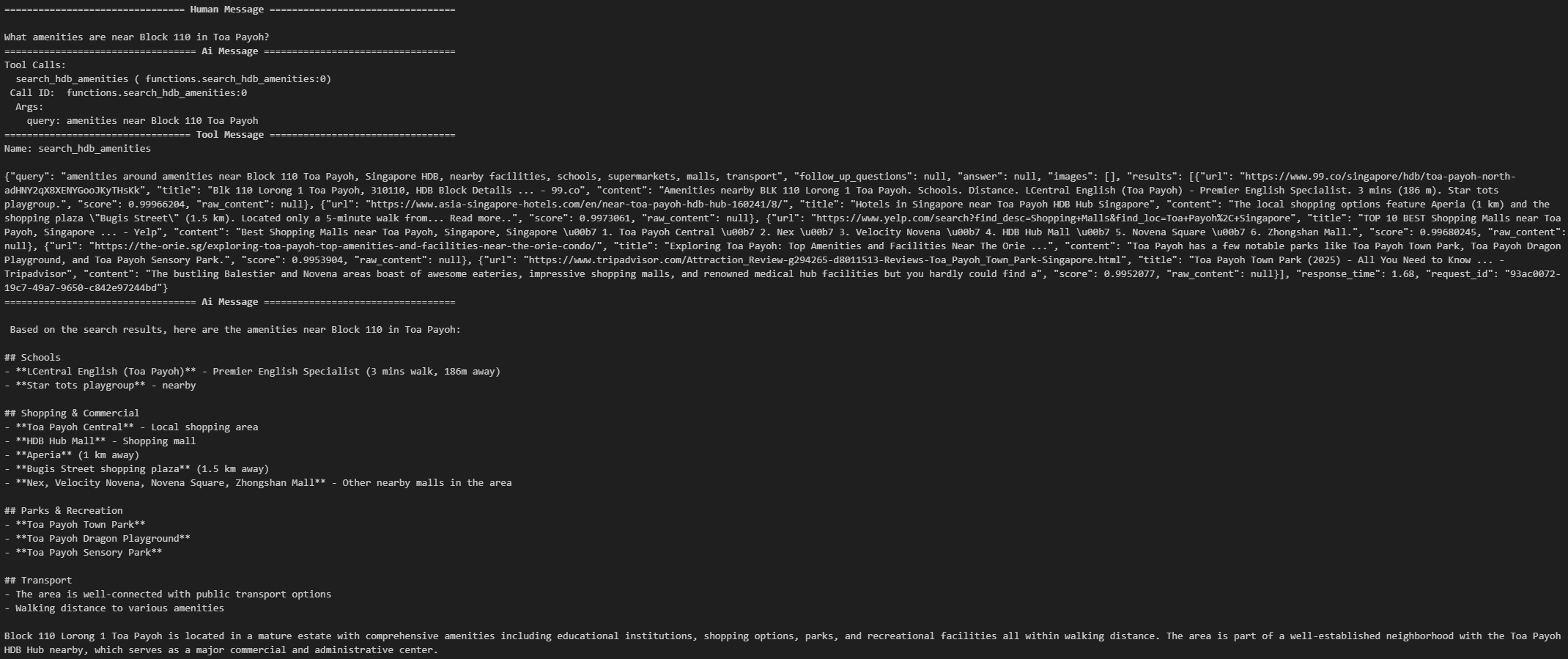
12. Display Mermaid Diagram
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))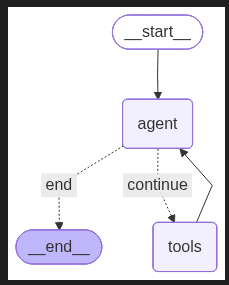
Use Case 3: Multi-Agent System (Supervisor + Specialist Agents)
The final and most sophisticated part of this post, a fully modular multi-agent system (MAS) built purely with LangGraph.
Architecture Overview
- Supervisor Agent: Routes queries to one of the specialist agents.
- SQL Agent: Uses MCP Toolbox Postgres tools for HDB analysis.
- Amenities Agent: Uses Tavily + custom amenities search.
- Web Agent: Handles all general knowledge queries.
This division keeps each agent focused, predictable, and auditable.
I implement this in a new notebook langgraph_mas.ipynb.
1. Imports
import os
import json
from typing import Annotated, Sequence, TypedDict
from langchain_core.messages import (
HumanMessage, AIMessage, BaseMessage, ToolMessage
)
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain.tools import tool
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from toolbox_langchain import ToolboxClient
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages2. Async Load MCP Tools
mcp_client = ToolboxClient("http://127.0.0.1:5000")
async def load_mcp_tools():
return await mcp_client.aload_toolset()
mcp_tools = await load_mcp_tools()
print("Loaded MCP tools:", [t.name for t in mcp_tools])3. Shared Tools (Tavily & Amenities)
tavily = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
@tool
def search_hdb_amenities(query: str) -> str:
"""
Search for amenities near an HDB block or town using Tavily.
Example queries:
- "amenities near Block 123 Ang Mo Kio"
- "schools near Bukit Panjang"
- "supermarkets near Tampines"
- "parks near Woodlands"
The tool returns summarized search results.
"""
formatted_query = f"amenities around {query}, Singapore HDB, nearby facilities, schools, supermarkets, malls, transport"
results = tavily.invoke(formatted_query)
return results4. Tool Registry
all_tools = mcp_tools + [tavily, search_hdb_amenities]
tools_by_name = {t.name: t for t in all_tools}
print("All tools:", list(tools_by_name.keys()))5. Agent State
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], add_messages]6. Define 3 Specialist Agents (SQL, Amenities, Web Search)
6.1 SQL Agent Prompt
sql_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """
SQL Agent.
You answer only questions requiring HDB resale data or stats.
Use MCP SQL tools ONLY.
Always return structured, correct SQL tool calls.
"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])6.2 Amenities Agent Prompt
amenities_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """
Amenities Agent.
Use `search_hdb_amenities` first.
Use Tavily for deeper context.
You answer:
- amenities
- schools
- malls
- MRT
- supermarkets
near a block or town.
"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])6.3 Web Research Agent Prompt
web_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """
Web Research Agent.
Use Tavily search for general knowledge or non-HDB topics.
"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])7. Bind each model to its specialist prompt
MODEL = "moonshotai/kimi-k2-thinking"
def build_model():
return ChatOpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("OPENROUTER_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://openrouter.ai/api/v1",
model=MODEL,
)
sql_agent = sql_prompt | build_model().bind_tools(mcp_tools)
amenities_agent = amenities_prompt | build_model().bind_tools([search_hdb_amenities, tavily])
web_agent = web_prompt | build_model().bind_tools([tavily])8. Supervisor Router
supervisor_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """
You are the Supervisor.
ROUTE the user query to one agent:
- SQL_AGENT for resale/transaction/statistics queries
- AMENITIES_AGENT for amenities/schools/MRT/malls
- WEB_AGENT for general queries
Respond with ONLY one of:
SQL_AGENT
AMENITIES_AGENT
WEB_AGENT
"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("messages")
])
router_model = build_model()9. Supervisor Node
async def router_node(state: AgentState):
decision = await router_model.ainvoke(
supervisor_prompt.format(messages=state["messages"])
)
route = decision.content.strip().upper()
if route not in {"SQL_AGENT", "AMENITIES_AGENT", "WEB_AGENT"}:
route = "WEB_AGENT" # fallback so KeyError never happens
return {"next_agent": route}10. Shared Tool Node (Async)
async def tool_node(state: AgentState):
last = state["messages"][-1]
outputs = []
for tc in last.tool_calls:
tool = tools_by_name[tc["name"]]
result = await tool.ainvoke(tc["args"])
outputs.append(ToolMessage(
content=json.dumps(result),
name=tc["name"],
tool_call_id=tc["id"],
))
return {"messages": outputs}11. Generic model execution wrapper
async def run_agent(agent, state):
response = await agent.ainvoke({"scratch_pad": state["messages"]})
return {"messages": [response]}12. Full Multi-Agent Graph
# Specialist agent wrappers
async def sql_agent_node(state):
return await run_agent(sql_agent, state)
async def amenities_agent_node(state):
return await run_agent(amenities_agent, state)
async def web_agent_node(state):
return await run_agent(web_agent, state)
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState, async_mode=True)
# Register nodes
workflow.add_node("ROUTER", router_node)
workflow.add_node("SQL_AGENT", sql_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("AMENITIES_AGENT", amenities_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("WEB_AGENT", web_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("TOOLS", tool_node)
# Each agent → decide continue or end
def next_step(state: AgentState):
last = state["messages"][-1]
return "TOOLS" if last.tool_calls else END
workflow.add_conditional_edges("SQL_AGENT", next_step, {"TOOLS": "TOOLS", END: END})
workflow.add_conditional_edges("AMENITIES_AGENT", next_step, {"TOOLS": "TOOLS", END: END})
workflow.add_conditional_edges("WEB_AGENT", next_step, {"TOOLS": "TOOLS", END: END})
# Supervisor decides next hop
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"ROUTER",
lambda out: out["next_agent"],
{
"SQL_AGENT": "SQL_AGENT",
"AMENITIES_AGENT": "AMENITIES_AGENT",
"WEB_AGENT": "WEB_AGENT",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("TOOLS", "ROUTER")
workflow.set_entry_point("ROUTER")
graph = workflow.compile()This is the full multi-agent system!
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))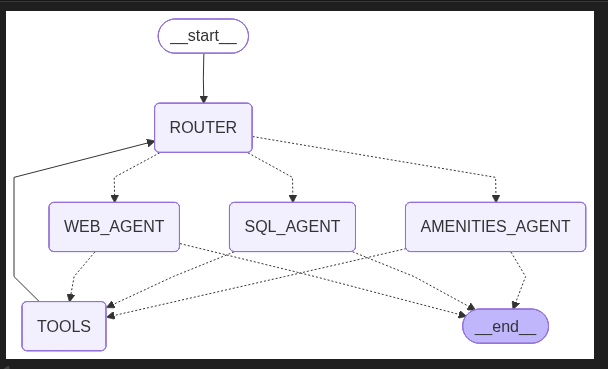
13. Examples — MAS in Action
Amenities Example
inputs = {
"messages": [
HumanMessage("What amenities are near Block 110 in Toa Payoh?")
]
}
async for step in graph.astream(inputs, stream_mode="values"):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()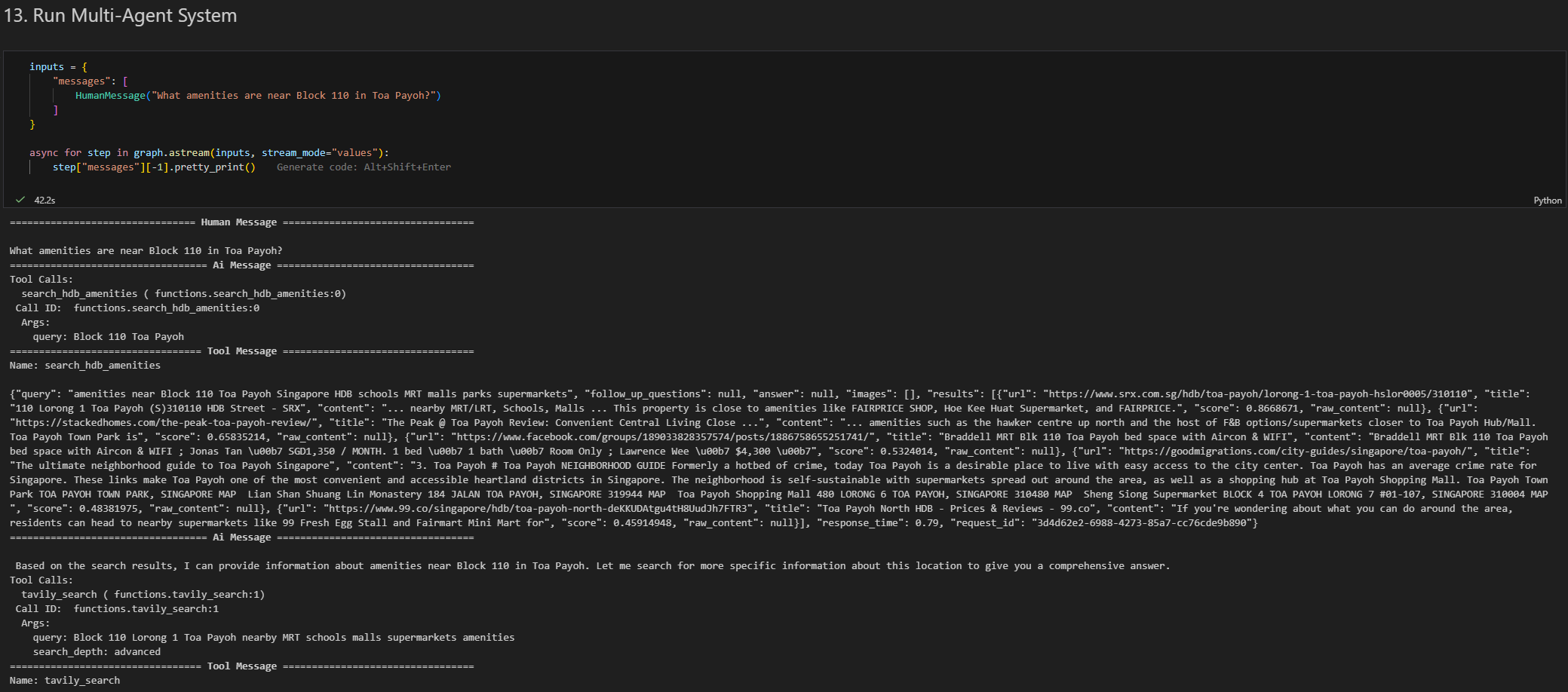

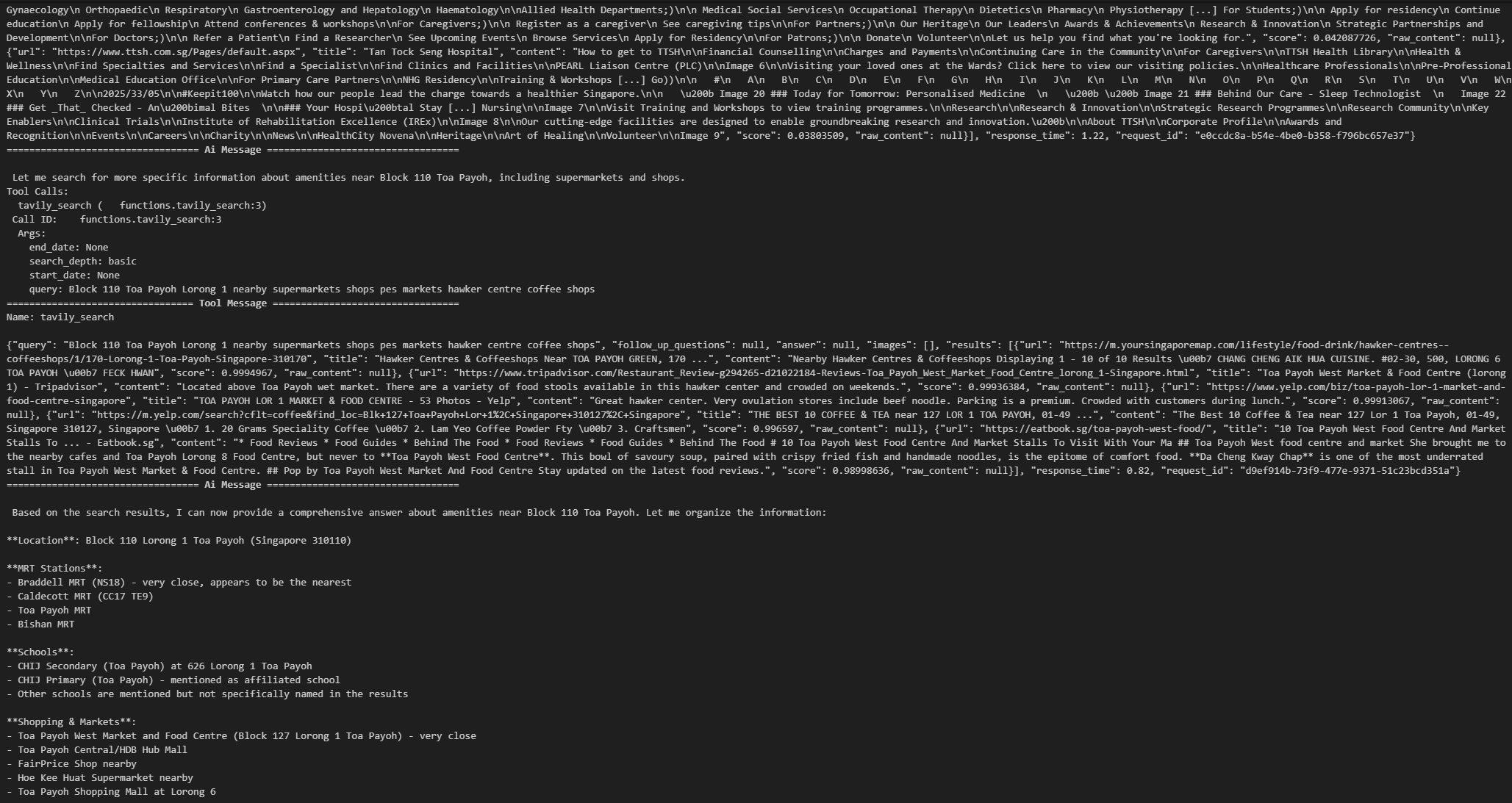
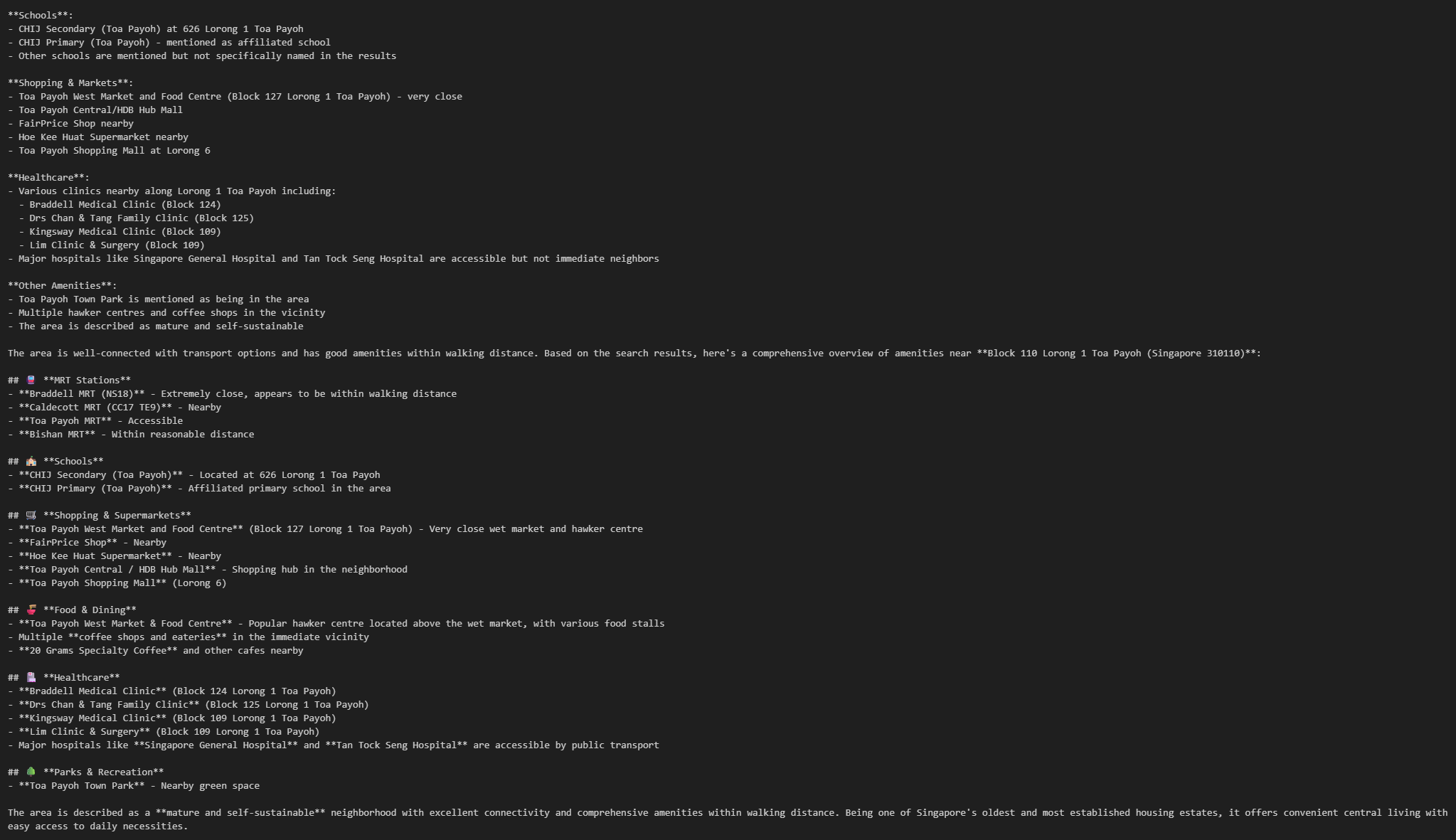
Resale Price (Median) Example
async for step in graph.astream(
{"messages": [HumanMessage("Show me the median resale price of 4-room flats in Bishan.")]},
stream_mode="values"
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()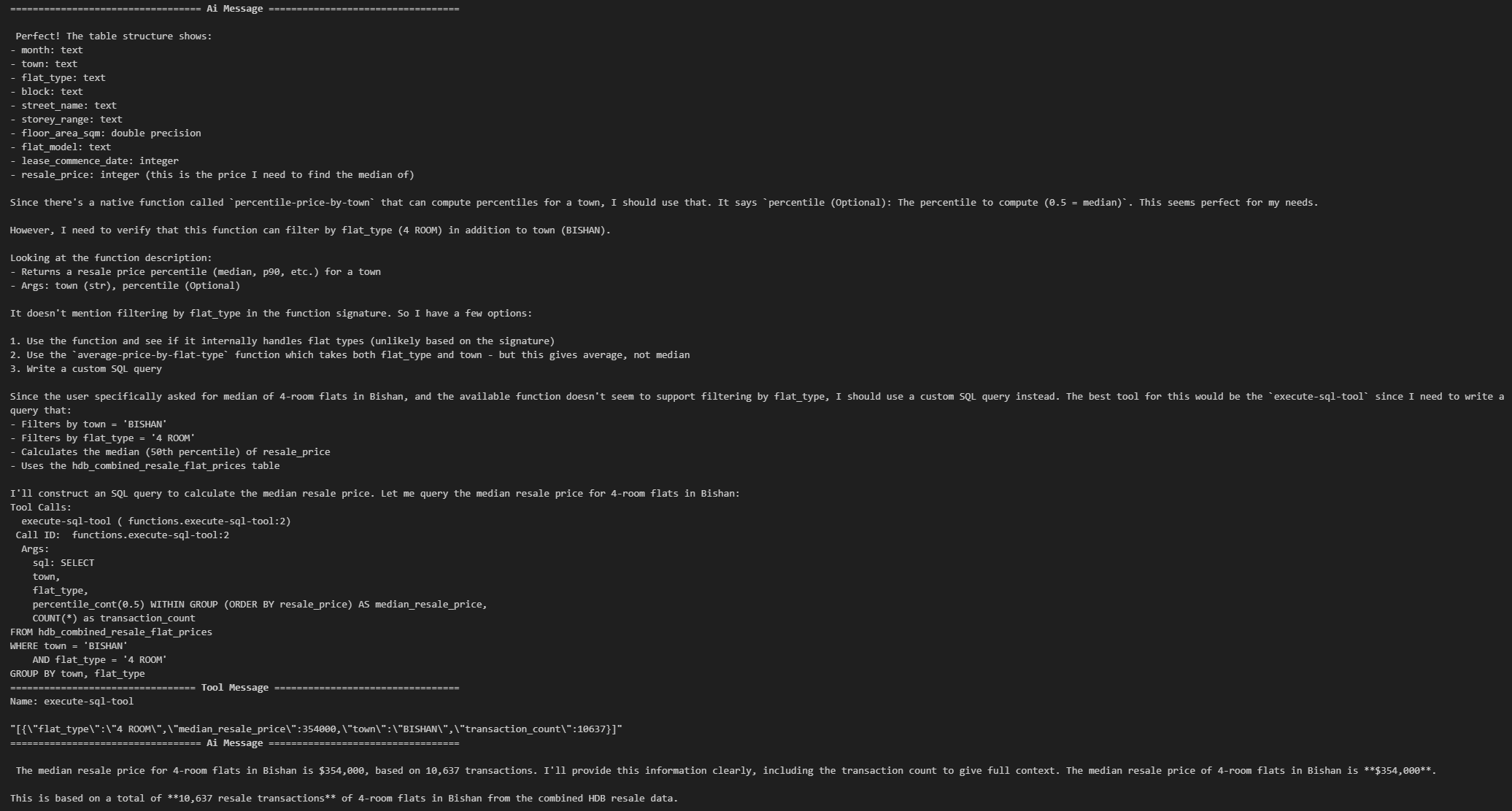
Security Considerations (SQL Tool): execute-sql-tool
Level 1: Prompt-based guardrail (not bulletproof though)
sql_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """
SQL Agent.
SAFETY RULES:
- You may ONLY generate SELECT queries.
- You MUST NOT use DROP, DELETE, UPDATE, INSERT, ALTER, CREATE, TRUNCATE,
GRANT, REVOKE, or any DDL/DML statements.
- You MUST NOT modify the database in any way.
- You MUST ONLY query the hdb_combined_resale_flat_prices table.
- If the user asks for anything involving modification, deny politely.
"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])Level 2: Filter SQL before execution
FORBIDDEN = ["drop", "delete", "truncate", "alter", "insert", "update", "grant", "revoke"]
def is_safe_sql(sql: str) -> bool:
s = sql.lower()
return not any(word in s for word in FORBIDDEN)
# Stops malicious execution
if tc["name"] == "execute-sql-tool":
sql = tc["args"].get("sql", "")
if not is_safe_sql(sql):
raise ValueError(f"Unsafe SQL detected: {sql}")Level 3: Remove execute-sql-tool entirely (for production system)
Optional: Deploying to LangGraph Platform (LangSmith Studio)
LangSmith Studio is a specialized agent ID that enables visualization, interaction, and debugging of agentic systems that implement the Agent Server API protocol.
- Install LangGraph CLI:
uv add langgraph-cli[inmem]- Create a new LangGraph app
langgraph new app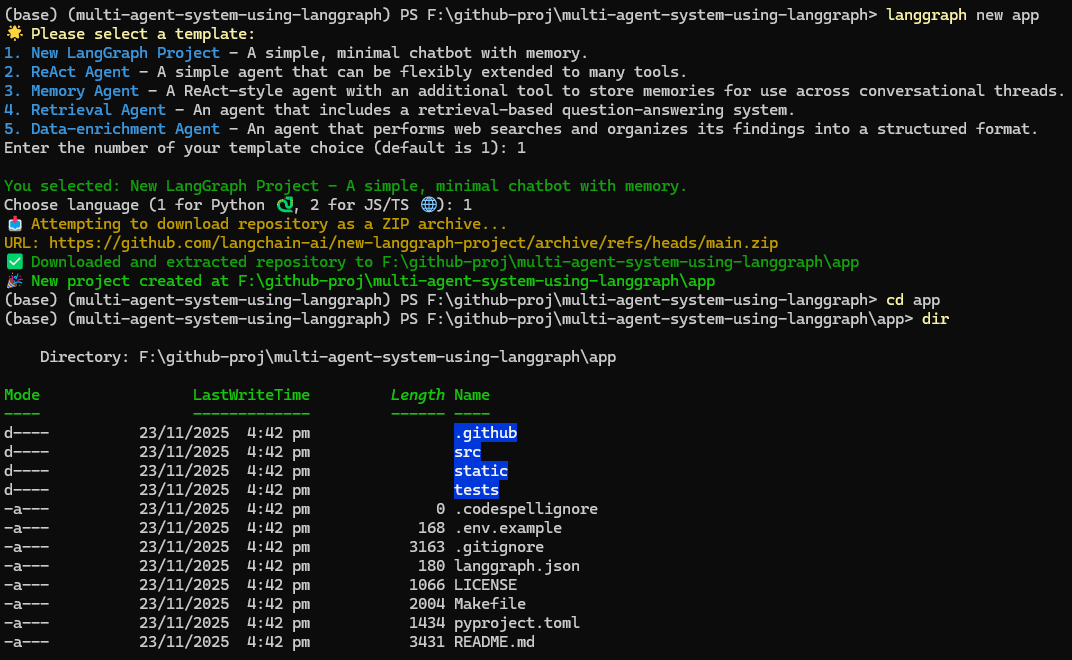
- Install dependencies
cd app
python -m venv venv
.\venv\Scripts\Activate
pip install -e .- Creates the MAS Agent
Paste these into src/agent/graph.py and add the LANGSSMITH_API_KEY env var:
src/agent/graph.py
import os
import json
import asyncio
import sys
from typing import Annotated, Sequence, TypedDict
from langchain_core.messages import (
HumanMessage, AIMessage, BaseMessage, ToolMessage
)
# Fix Windows event loop issue
if sys.platform == "win32":
asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(asyncio.WindowsSelectorEventLoopPolicy())
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain.tools import tool
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from toolbox_langchain import ToolboxClient
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
# -----------------------------
# Global state for MCP tools
# -----------------------------
_mcp_tools = None
_toolbox_client = None
_client_lock = asyncio.Lock()
async def get_mcp_tools():
"""Lazy load MCP tools on first use with connection pooling"""
global _mcp_tools, _toolbox_client
async with _client_lock: # Prevent concurrent initialization
if _mcp_tools is None:
try:
# Move blocking ToolboxClient to separate thread
def _create_client():
return ToolboxClient("http://127.0.0.1:5000")
_toolbox_client = await asyncio.to_thread(_create_client)
# Try aload_toolset first, fall back to load_toolset
if hasattr(_toolbox_client, 'aload_toolset'):
_mcp_tools = await asyncio.wait_for(
_toolbox_client.aload_toolset(),
timeout=30
)
else:
_mcp_tools = await asyncio.wait_for(
_toolbox_client.load_toolset(),
timeout=30
)
print(f"Loaded {len(_mcp_tools)} MCP tools")
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
print("MCP tools loading timed out")
_mcp_tools = []
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to load MCP tools: {e}")
_mcp_tools = []
return _mcp_tools
# -----------------------------
# Tavily
# -----------------------------
tavily = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
# -----------------------------
# Custom amenity search tool
# -----------------------------
@tool
def search_hdb_amenities(query: str) -> str:
"""Search for amenities near an HDB block or town using Tavily.
Example queries:
- "amenities near Block 123 Ang Mo Kio"
- "schools near Bukit Panjang"
- "supermarkets near Tampines"
- "parks near Woodlands"
"""
formatted_query = f"amenities around {query}, Singapore HDB, nearby facilities, schools, supermarkets, malls, transport"
results = tavily.invoke(formatted_query)
return results
# -----------------------------
# STATE
# -----------------------------
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], add_messages]
# -----------------------------
# PROMPTS
# -----------------------------
sql_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """SQL Agent. You answer only questions requiring HDB resale data or stats.
Use MCP SQL tools ONLY. Always return structured, correct SQL tool calls."""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])
amenities_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """Amenities Agent. Use search_hdb_amenities first. Use Tavily for deeper context.
You answer: amenities, schools, malls, MRT, supermarkets near a block or town."""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])
web_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """Web Research Agent. Use Tavily search for general knowledge or non-HDB topics."""),
MessagesPlaceholder("scratch_pad")
])
# -----------------------------
# MODEL FACTORY
# -----------------------------
MODEL = "moonshotai/kimi-k2-thinking"
def build_model():
return ChatOpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("OPENROUTER_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://openrouter.ai/api/v1",
model=MODEL,
)
# -----------------------------
# AGENTS (built dynamically with tools)
# -----------------------------
async def build_agents(mcp_tools):
"""Build agents with available tools"""
sql_agent = sql_prompt | build_model().bind_tools(mcp_tools)
amenities_agent = amenities_prompt | build_model().bind_tools([search_hdb_amenities, tavily])
web_agent = web_prompt | build_model().bind_tools([tavily])
return sql_agent, amenities_agent, web_agent
# -----------------------------
# ROUTER NODE
# -----------------------------
async def router_node(state: AgentState):
"""Route to appropriate agent"""
router_model = build_model()
supervisor_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """You are the Supervisor. ROUTE the user query to one agent:
- SQL_AGENT for resale/transaction/statistics queries
- AMENITIES_AGENT for amenities/schools/MRT/malls
- WEB_AGENT for general queries
Respond with ONLY one of: SQL_AGENT AMENITIES_AGENT WEB_AGENT"""),
MessagesPlaceholder("messages")
])
chain = supervisor_prompt | router_model
decision = await chain.ainvoke({"messages": state["messages"]})
route = decision.content.strip().upper()
if route not in {"SQL_AGENT", "AMENITIES_AGENT", "WEB_AGENT"}:
route = "WEB_AGENT"
return {"next_agent": route}
# -----------------------------
# TOOL EXECUTION NODE
# -----------------------------
async def execute_tool_with_retry(tool, tool_name, args, max_retries=2):
"""Execute tool with exponential backoff retry"""
for attempt in range(max_retries + 1):
try:
print(f" Attempt {attempt + 1}/{max_retries + 1}...")
if hasattr(tool, 'ainvoke'):
result = await asyncio.wait_for(
tool.ainvoke(args),
timeout=20
)
else:
result = await asyncio.wait_for(
asyncio.to_thread(tool.invoke, args),
timeout=20
)
return result
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
print(f" Timeout on attempt {attempt + 1}")
if attempt < max_retries:
wait_time = 2 ** attempt
print(f" Retrying in {wait_time}s...")
await asyncio.sleep(wait_time)
else:
raise
except Exception as e:
print(f" Error: {str(e)}")
if attempt < max_retries and "Network" in str(e):
wait_time = 2 ** attempt
print(f" Retrying in {wait_time}s...")
await asyncio.sleep(wait_time)
else:
raise
async def tool_node(state: AgentState):
"""Execute tool calls from agent"""
last = state["messages"][-1]
outputs = []
mcp_tools = await get_mcp_tools()
all_tools = mcp_tools + [tavily, search_hdb_amenities]
tools_by_name = {t.name: t for t in all_tools}
print(f"\nTOOL_NODE: Found {len(last.tool_calls)} tool call(s)")
print(f"Available tools: {list(tools_by_name.keys())}")
for tc in last.tool_calls:
tool_name = tc["name"]
print(f"\n Executing: {tool_name}")
print(f" Args: {tc['args']}")
try:
tool = tools_by_name.get(tool_name)
if not tool:
result = f"Tool '{tool_name}' not found. Available: {list(tools_by_name.keys())}"
print(f" {result}")
else:
print(f" Tool type: {type(tool)}")
result = await execute_tool_with_retry(tool, tool_name, tc["args"])
print(f" Success.")
if isinstance(result, str):
content = result
elif isinstance(result, dict):
content = json.dumps(result)
elif isinstance(result, list):
content = json.dumps(result)
else:
content = str(result)
outputs.append(ToolMessage(
content=content,
name=tool_name,
tool_call_id=tc["id"],
))
print(f" ToolMessage created ({len(content)} chars)")
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"Error executing {tool_name}: {str(e)}"
print(f" {error_msg}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
outputs.append(ToolMessage(
content=error_msg,
name=tool_name,
tool_call_id=tc["id"],
))
print(f"\n Returning {len(outputs)} ToolMessage(s)")
return {"messages": outputs}
# -----------------------------
# SPECIALIST NODES
# -----------------------------
async def run_agent(agent, state):
response = await agent.ainvoke({"scratch_pad": state["messages"]})
return {"messages": [response]}
async def sql_agent_node(state: AgentState):
mcp_tools = await get_mcp_tools()
agent = sql_prompt | build_model().bind_tools(mcp_tools)
return await run_agent(agent, state)
async def amenities_agent_node(state: AgentState):
agent = amenities_prompt | build_model().bind_tools([search_hdb_amenities, tavily])
return await run_agent(agent, state)
async def web_agent_node(state: AgentState):
agent = web_prompt | build_model().bind_tools([tavily])
return await run_agent(agent, state)
# -----------------------------
# GRAPH BUILD
# -----------------------------
def build_graph():
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState, async_mode=True)
workflow.add_node("ROUTER", router_node)
workflow.add_node("SQL_AGENT", sql_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("AMENITIES_AGENT", amenities_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("WEB_AGENT", web_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("TOOLS", tool_node)
def next_step(state: AgentState):
last = state["messages"][-1]
has_calls = hasattr(last, 'tool_calls') and len(last.tool_calls) > 0
print(f"\nnext_step: Last message type={type(last).__name__}, has_tool_calls={has_calls}")
return "TOOLS" if has_calls else END
workflow.add_conditional_edges("SQL_AGENT", next_step, {"TOOLS": "TOOLS", END: END})
workflow.add_conditional_edges("AMENITIES_AGENT", next_step, {"TOOLS": "TOOLS", END: END})
workflow.add_conditional_edges("WEB_AGENT", next_step, {"TOOLS": "TOOLS", END: END})
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"ROUTER",
lambda out: out["next_agent"],
{
"SQL_AGENT": "SQL_AGENT",
"AMENITIES_AGENT": "AMENITIES_AGENT",
"WEB_AGENT": "WEB_AGENT",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("TOOLS", "ROUTER")
workflow.set_entry_point("ROUTER")
return workflow.compile()
graph = build_graph()
# -----------------------------
# MAIN
# -----------------------------
async def main(user_query: str):
"""Run the graph with a user query"""
print(f"\nQuery: {user_query}\n")
initial_state = {"messages": [HumanMessage(content=user_query)]}
async for output in graph.astream(initial_state):
print("State:", output)
return graph.get_state(initial_state)
if __name__ == "__main__":
query = "What amenities are near Bukit Panjang?"
asyncio.run(main(query))- Launch Agent Server
langgraph dev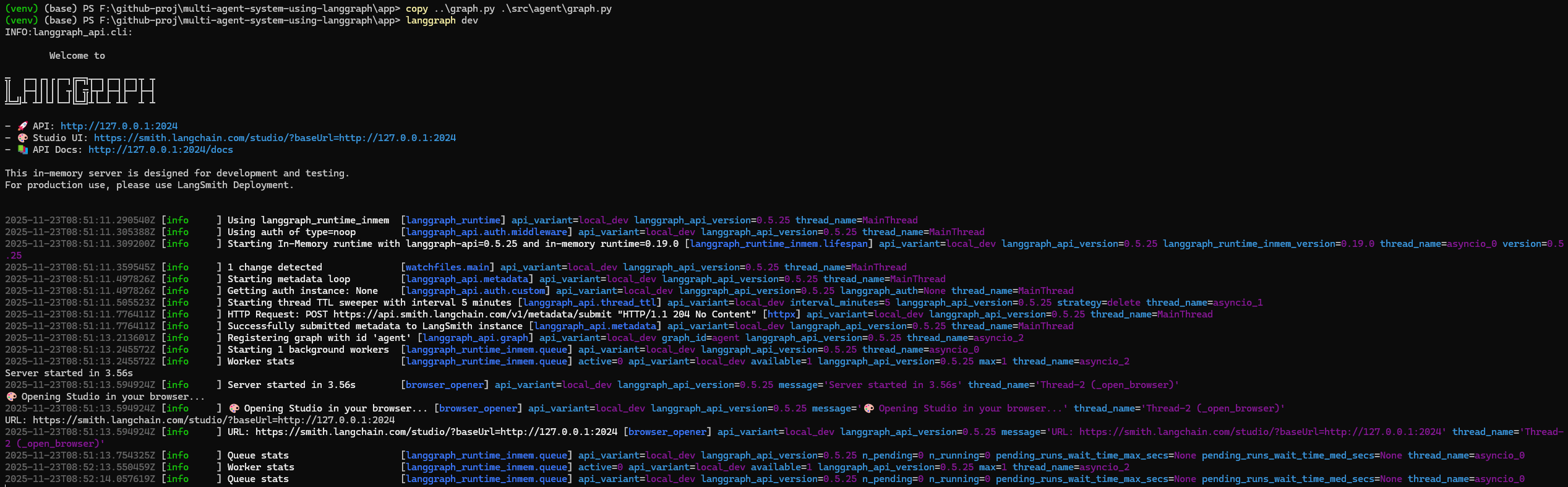
- Navigate to LangSmith Studio
Navigate to https://smith.langchain.com/studio/?baseUrl=http://127.0.0.1:2024:
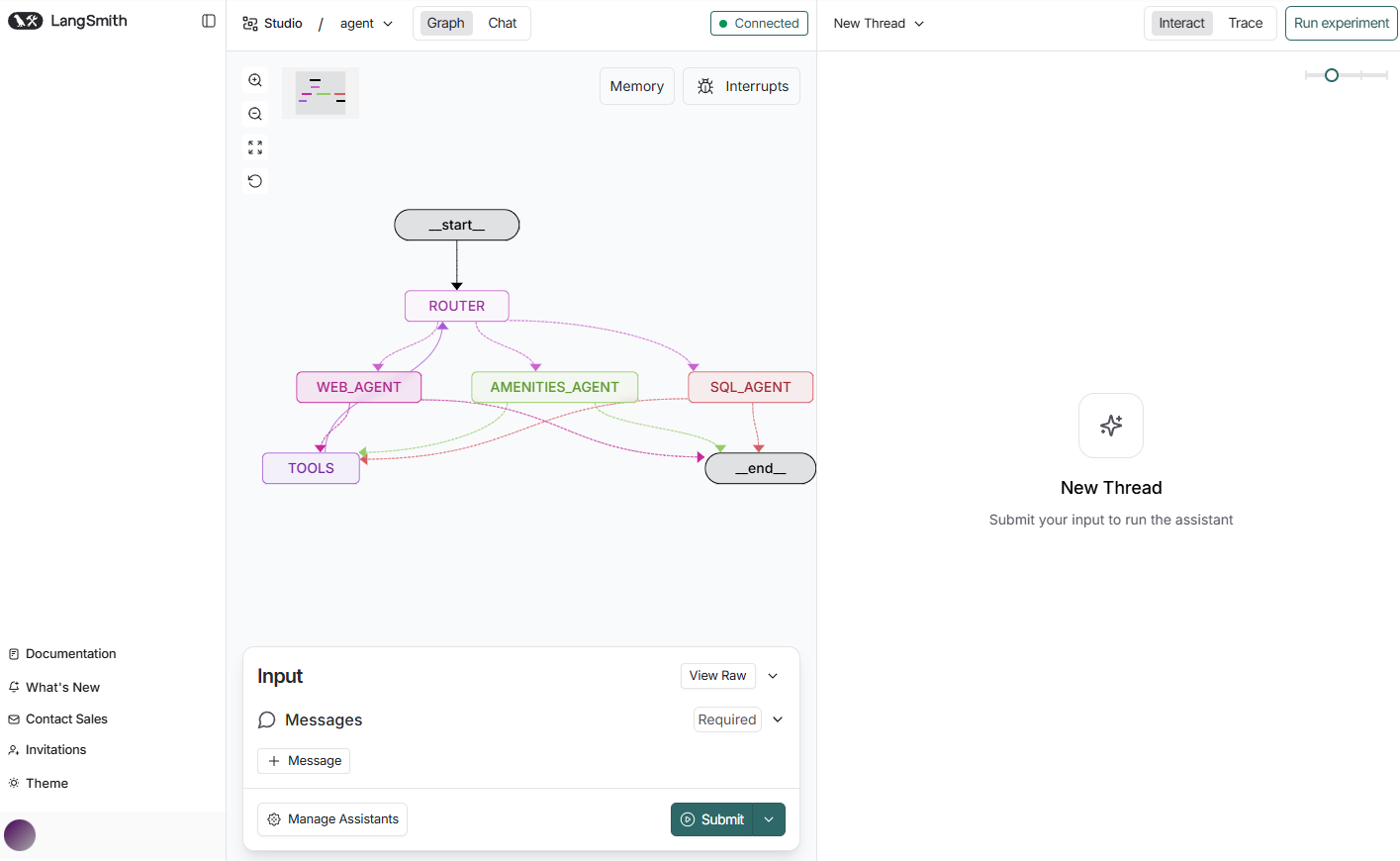
- Test our MAS Agent
Let’s switch over to the Chat tab and test it out with:
What amenities are near Block 110 in Toa Payoh?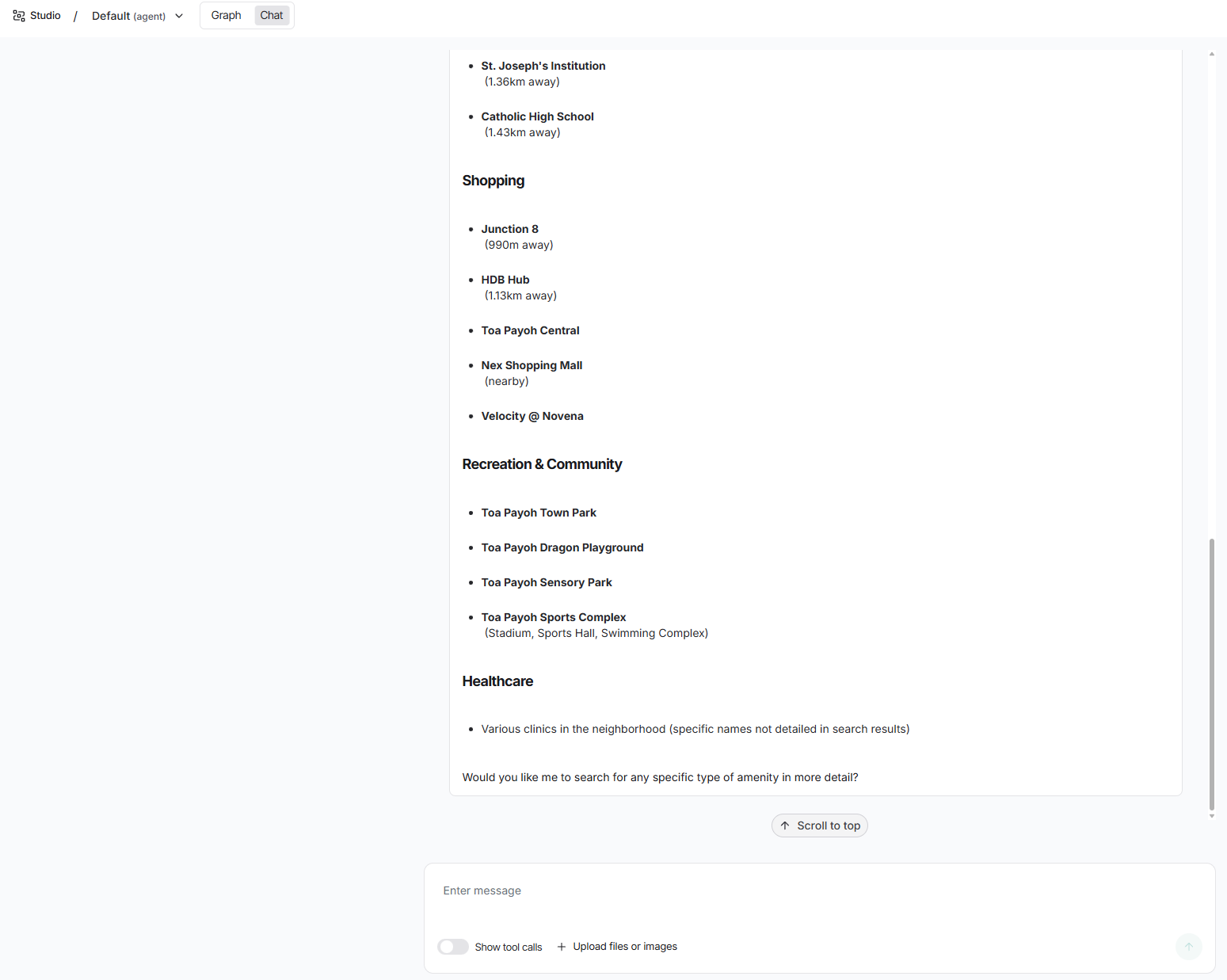
Test case for MCP Tools:
Show me the median resale price of 4-room flats in Bishan.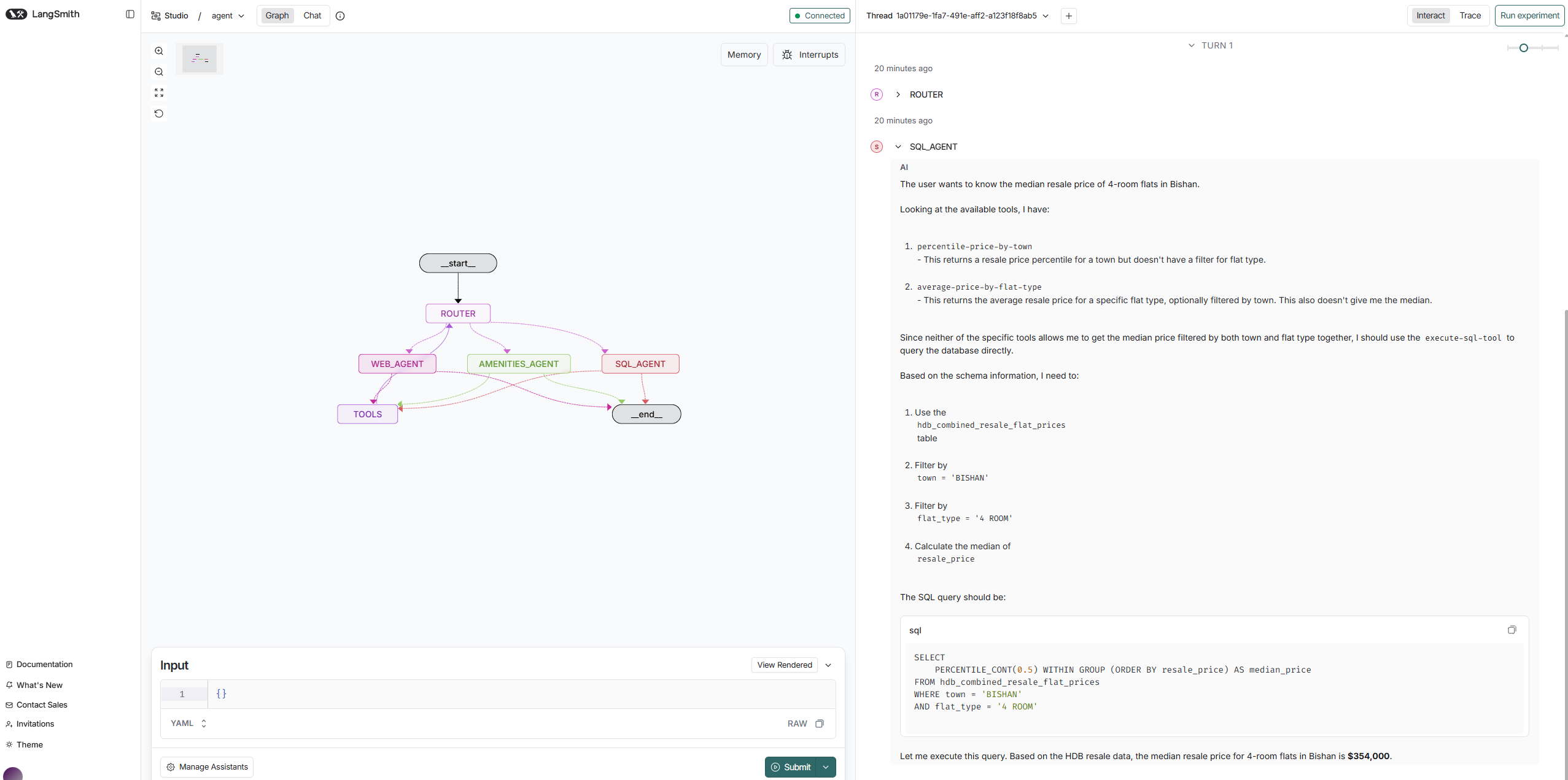
Source Code on GitHub
You can find the full project, including notebooks, MAS graph, and tools configuration, here:
👉 GitHub Repository: https://github.com/seehiong/multi-agent-system-using-langgraph
The repo includes:
- All Jupyter notebooks (
toto_generator,ReAct agent,MAS supervisor) graph.pyfor LangGraph CLItools.yamlfor MCP Toolbox- Environment setup (
pyproject.toml,uv.lock) - Clean project structure and
.gitignore
Feel free to star ⭐ the repo if you found it helpful!
