While working on one of the hackathon projects, I encountered a tricky issue when uploading a PDF document to a web-based application. As it was a race against time, I quickly decided to use pdf.js to get things going. As a reminder, PDF is a file format developed by Adobe.
Setup
Since I already use Notepad++ , I installed the HEX-Editor plugin via Plugins > Plugins Admin…. Simply search and install it from there.
For the purpose of this post, I will use the reserach paper Attention Is All You Need as the example PDF.
To manipulate and inspect the PDF structure, I installed qpdf , a C++ library that enables structural, content-preserving transformations on PDF files. The latest version e.g. qpdf 12.2.0 can be downloaded from GitHub.
HEX Editing with NotePad++
Dragging the Attention Is All You Need PDF into Notepad++ gives us a hex representation of the file. However, since it’s in raw hex, it’s not easy to interpret.
Using qpdf for Extraction
Let’s now try some
cli commands
. Using the --qdf option, we can create a human-readable version of the PDF:
qpdf 1706.03762v7.pdf --qdf file.pdfHere’s a snippet of the output:
%PDF-1.5
%¿÷¢þ
%QDF-1.0
%% Original object ID: 5953 0
1 0 obj
<<
/Names 3 0 R
/OpenAction 4 0 R
/Outlines 5 0 R
/PageMode /UseOutlines
/Pages 6 0 R
/Type /Catalog
>>
endobj
%% Original object ID: 5954 0
2 0 obj
<<
/Author ()
/CreationDate (D:20240410211143Z)
/Creator (LaTeX with hyperref)
/Keywords ()
/ModDate (D:20240410211143Z)
/PTEX.Fullbanner (This is pdfTeX, Version 3.141592653-2.6-1.40.25 \(TeX Live 2023\) kpathsea version 6.3.5)
/Producer (pdfTeX-1.40.25)
/Subject ()
/Title ()
/Trapped /False
>>
endobj
%% Original object ID: 5952 0
3 0 obj
<<
/Dests 7 0 R
>>
endobjWe can also output the PDF in JSON format:
qpdf 1706.03762v7.pdf --json-output inline.jsonHere’s a sample:
{
"qpdf": [
{
"jsonversion": 2,
"pdfversion": "1.5",
"pushedinheritedpageresources": false,
"calledgetallpages": false,
"maxobjectid": 5957
},
{
"obj:1 0 R": {
"value": {
"/D": "u:section.1",
"/S": "/GoTo"
}
},
"obj:2 0 R": {
"stream": {
"data": "eNrFWltv20YWftevmMf2odTcL0BQIE7qJLubNIiD3e4mwYKWxrIaRTQo0o7z6/sdiqZEiRKVhEEBmyOSwzPfucy5kYJxZpjizDLBBQtMKIFfTASJn0xKDJopiduOKYt7nhkhmBTMaDvCbcslk4ZZjcEyFwKTgXkViGgwiinFQsCgmZAcVx1GDZIehJVlGiS1EyM8LkzwTBsmLJ7RtCIuakByTjIDTN5ZBooicIygF4xj+BMBYI0HJsy3hM25kQUcCTDWMKmwuLUYA/gEPg28jgM16DgwaYDDaYxeMufABnh1oOfAkAc9Z8UIt6Q3hnnQ86DjLRjUjnliFA/hkhJgKgiMIC4gFogN3HCSAacfmKKIXyyntPYjwFbO41nMCEqyoJnmjsTGtISQA8SjTGDBQSxcMxKPhWDAlnaYJKAoHUhCmGwENyMhIAnwgSsKIgJ/AuozxkJqwkBYOBMC0vOGbjloD1oXUKoVmp6CwBRdkZCUJqxQtMXskSBVOyAXUjHrPd3SkCKULUicAoIUZACKlpAQoDZkTZw5SzBgVs4ZMirIOEAUAkr2XMsRSc0Lkhvzku5isMQTrIgsUUHoitSPi14Hsh/8sBrrQa/e0hVo13uyXEsagTkJB/ER7wK2EwQUB/aDpHUBNEhiDSoPEnoF05A+yFmoT1k8A+VCrPQwrlgSjCMteDl69IiNL9j4WfY2Y+On7KdVnBTzbJmIn9mvv45+eq+cxb97zzl/QYclHQo65HTI6DClQ0mHSXN33txd/nxwEbm/yBkd0obWRzrM2suVDY7pYdJqn/TLNuBIhwUd3nPNaXzcrFOtfd3wUTTzNwyWzeTYgaK8bIB0ifK3hoVJB6h8G1S64Xb78tM2pGMULhrMO3Jd9QDvUM/jhtZGJssTlQ7SLepdgrloEKaNemI381mz7C90eN1vky09D8WEPGBoZYN/Q7UC+rxZM91jbFBk6oD6bprDoqG6EfnuSpWhbGOsLl99E+rth+Z7V7L2tnq43Llteyy3g/XXDZlVe1/v4Kt0dNfcWDVrPuA5b65sDPOX5kbW4L9rRJrv6flV83jRTN08edLm1Ae8yic6XLbhTdsCn+3p9ICTuWjru2joV/M/9yA0366EdM83H/SYW2wdjgYdwvpP4+Lv91jehIarRrvfszVrFB0CedsoPW0zc5ytjZhNlxc9heqeP03bYaLHNM7aj+wEzJOAd3jO5x17ZmcfxVPtdgMptgPCoj9omy4P8nvjNzcq/9T8+rIJvj2kO4zxTfPwrA1zw/dmkfTrrM4eW27VEaqOex7bZXAv29nFjiG0VLZjm5v4svga3rbxyG9I9f7dIdzD4a8HgDqW4M3agXbVyOcBypOOWFu0vWPZ9jiTPa/1us3O6mTH6Pah7+CZNPjLNukDunmHwoezN2x8Pi8+EPFHj0bjt/c3kY1fp7M4Gj/JlkVcFquqPsfM0fhNXGVlPomrqqSsLr2M03l6ln1m7+iCFVRjyQ8jkMjxLOaFal5NfmvVP/77P9xFtWZc4lEzL8vF4sPBeZ45FIatOeeAx4inc496CUXqmhlUtahH6xOqEVEDrk+o8MSC65OqPvbVCeiNX+fZ5CIW7B2Yf3rOxm/j54I1S3VLRbk9qSjzVVIZP14uM5B6h3KwgoJ6vBrWzIQ1G2HNQFhDD2vQoaJQFeLrUdSjrEdVj7oeTT3aenT16OuxpidrerKmJ2t6sqYna3qypidrerKmp+rnVf28qp9X6+d3RFrxPxpflJdFdf6v+fLjaHyW5dOYV6ITH8bPxy/GT3ACgh9I2BNoSUmTUA/Gep1Q00EplwSwbAOqOG4w7zHb3UmTeRGT62xynUf8ykUI6z01CCAtbUJNmwdAWqkE8IJMvLKH4czy8rfbdCH0gEhESKiRYq1MtAYQAUAA5jB6dxjKqixWH+MtBDMkGKUTZ30FxgCMFgm11nrBXKbX03SZlpILvYxlni4GxKSR0RjdCMigNJS+H9PkOiM4i5jmy/lyNhwgYWErUJjmiaWupzOJtdTXDIm24TCgOxKPnWXZbBEHRON8Ykk8gOPgBUQALPirXjiLMlvOgMjEqysKWrdDgsK+ph7tg4wkN4kxqh/Un9mXeJXdzSdfSFbx880iywdVnpYuoVaesSFxnjZ+SKSi7rBPjDriif5ZTq7TebwFLneeTgrg+pJSqB/WsOCLjPGJc6EyLEACVAchHvFKq+v0S4w5IcvKIkfYy8rV4n44YBLe0hvBDIfQrKI+eeIRUYyA0MTf4xaksrB7X2EyGpg09gH1snswrYq8nBRlHqePC0oMoMFXsbjL8o+r4cApDV8l1wKzEJgyOlH0TqIH3DROsk832Sq9XETAW77MpnFAmSH7gCs1THmV8KpDD18qmAoi8V4ehoXkKi6ncbqc3ZRDmjsyfORFDRpsQQiqH86rdHF2D0SxIJMf0KTgrTRlJ14iO7EwKZdoJES9gP6RLdMVnEJ8NTQklA4JvYdQcFO6klVIBKKfgrVLbU9JnCTnYpan0zmM/XuAUYK4pTyP7YYkUnFsQ0ceHkrEqAScluj28B098GF8OjDQ6x6J0sQaelOoEo0ILWFgmqtjKUKsQqBdZIPGGIF1bQXHEBzpE418vhfOD979lFpqrje4tEropWEvrpu0XJQrMuxpjDdDZnZwANpv9IbAp7jqB7SYLwnNxpUP6AOESJSkV8NIy6EzCUulN73QoQjHYnD58foyTYuUwrAZ0AEgclh6G+rguhWcI2RjURULFxLuj4SSdbz9/6AeWyFpMsFuwHgBSxL9YH6Ux9aUV9K3BgBEpbMWskqZegH9OI+N9BZL01tpjbxEMO1swumtOixJ/S31iiZhaFchspCRByAqFPoA/dCiDnGM06cOtZQM50mwJ4D6IWUv5UW06WFFget1WuToE5XEHcvWEFVvI/lFNYNp56gG2mp7CsrKntY+25nY0T/rmqSRBIeg+ycK8vnhYENuuwfX6s4hwgsVHk6w8zXvatXRNxH6oT0pQUDL+kRUZ+q7GneO7zXurP+6xt2zPCtvqu9B2n08+jCk6nfZui9m3XbfqwJUPzy+GL/N0+XqhkhP7tn4ycX4abydT+KbZ2ds/IIhGsVBcisd4OMpyVNUD6LMQm7luKBPgRLtfadBXs1nCIT1K4TBKmUeKDqjZnFVocwNBWeXKHFkh15HyqiGzRQUYaEPrZCRQ1NKaWChr8koUfBHEoX0PubLLP9EkHa3pg0nbs3tiVJTXkCfYVGbxR+fTDuvSoi7tujuRBngdYI6YSKZg3D9E4VA8SDCN7ThW7t+s51pA//x++WfpBMi8eITeeyerjxmYT8/6dvkfr87781Am9zVTXNXN8193fT24vua3DvblksEVkpCkBVRMoLinzaQRjjR4ui2HbAYUgFFKyQiUVXDmpDwI6Cqyrqs+6Zo/xdsv40P",
"dict": {
"/Filter": "/FlateDecode",
"/First": 816,
"/N": 100,
"/Type": "/ObjStm"
}
}
},
"obj:3 0 R": {
"value": {
"/D": [
"136 0 R",
"/XYZ",
108,
720,
null
]
}
},
"obj:128 0 R": {
"stream": {
"data": "eNrs3W+vHNd92PF9JxT14PJ1XMpSboWgQHRFK05rizTNJEpIM6plhTQjwwEZM1JsgjEhxyJo0RZMy6KsNiJhwpHiv7Jk2JRFtVBtklJQwAVvAudBgSZAH7IHWXRwOrs7e2Z2ZnbO7ueDHwr56t79M0teZb49c+buXQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACApRmlcaAAAAAAlm7UiOMGAAAA0L/RwhxDAAAAgH6MWjXwN+hTVt4AAABglU7zE/tMdklHynAQAAAAYCXP8Rs0mVySjpThIAAAAMDqneAvcrI//KQjZTgIAAAAsGJn962c5g856UgZDgIAAACs2Nl9W+f4ek4un7g//wAAAJD1qX27J/jDTDpShoMAAAAAK3Ne3/rZ/TCvupIyHAQAAABYmfP6Ls7u9Zzhf+7+FgAAAEC+5/Udndqvds8ZVcric/e3AAAAADLST39IeZbFX8asRxjVl/jCmj1gg7ew9IMAAAAADEdvp/Ar1nNGjfTwceg5AAAAsPL0nAY9p8FPJb4vPQcAAACode7fZ8+ZfK7uUkb1dzZ45c2eqMH3D+cgAAAAAAPR83qM1es5zV5YxQ/qOQAAAEBb5/49PF12PaeL16bnAAAAAG2d+/fwdHn1nAVf26xH0HMAAACAts79e3i61e45iS9PzwEAAADaOvfv4eky6jmtvP2eb/K14EEAAAAABkLP6bPn3F3qTdsXPAgAAADAQOg5eo6eAwAAAHnRcxr0nE4PuJ4DAAAAtHXu38PTrUPPmfvUeg4AAADQ1rl/D0+3hj0no4MAAAAADISeo+foOQAAAJCXPnvO3F2F9Zy7eg4AAABQ89y/0/N6PSfl0fQcAAAAoMXT/66fSM+5q+cAAAAArZ7+d/1Ees5dPQcAAACof/rf0al9yrO4X/l
...
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABgz/4/6jXPIg==",
"dict": {
"/BitsPerComponent": 8,
"/ColorSpace": "/DeviceRGB",
"/Filter": "/FlateDecode",
"/Height": 2239,
"/SMask": "175 0 R",
"/Subtype": "/Image",
"/Type": "/XObject",
"/Width": 1520
}
}
},
}
]
}To decode stream data more effectively, use:
mkdir json
qpdf 1706.03762v7.pdf --json-output --decode-level=generalized --json-stream-data=file json\file.jsonHere’s a sample:
{
"qpdf": [
{
"jsonversion": 2,
"pdfversion": "1.5",
"pushedinheritedpageresources": false,
"calledgetallpages": false,
"maxobjectid": 5957
},
{
"obj:1 0 R": {
"value": {
"/D": "u:section.1",
"/S": "/GoTo"
}
},
"obj:2 0 R": {
"stream": {
"datafile": "json\\file.json-2",
"dict": {
"/First": 816,
"/N": 100,
"/Type": "/ObjStm"
}
}
},
"obj:3 0 R": {
"value": {
"/D": [
"136 0 R",
"/XYZ",
108,
720,
null
]
}
},
"obj:128 0 R": {
"stream": {
"datafile": "json\\file.json-128",
"dict": {
"/BitsPerComponent": 8,
"/ColorSpace": "/DeviceRGB",
"/Height": 2239,
"/SMask": "175 0 R",
"/Subtype": "/Image",
"/Type": "/XObject",
"/Width": 1520
}
}
},
}
]
}Reconstructing Images from PDFs
From the earlier step, we can reconstruct an image from one of the streams (e.g., file.json-128). This is done using Python and the Pillow library inside a Jupyter plugin using a local .venv environment.
First, install the required packages:
pip install pillow numpyThen use the script to reconstruct the image.
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import struct
def reconstruct_image_from_pdf_stream(stream_file_path, width, height, bits_per_component=8, colorspace="RGB"):
"""
Reconstruct an image from PDF stream data extracted by qpdf.
Args:
stream_file_path: Path to the stream data file (e.g., 'json\\file.json-128')
width: Image width from PDF dictionary
height: Image height from PDF dictionary
bits_per_component: Bits per color component (usually 8)
colorspace: Color space (RGB, CMYK, etc.)
"""
# Read the raw stream data
with open(stream_file_path, 'rb') as f:
raw_data = f.read()
print(f"Raw data size: {len(raw_data)} bytes")
# Calculate expected size
if colorspace == "RGB":
channels = 3
elif colorspace == "CMYK":
channels = 4
elif colorspace == "Gray":
channels = 1
else:
channels = 3 # Default to RGB
bytes_per_pixel = (bits_per_component * channels) // 8
expected_size = width * height * bytes_per_pixel
print(f"Expected size: {expected_size} bytes")
print(f"Image dimensions: {width} x {height}")
print(f"Channels: {channels}, Bits per component: {bits_per_component}")
try:
# Method 1: Direct reconstruction (most common case)
if len(raw_data) == expected_size:
# Create numpy array from raw data
if bits_per_component == 8:
img_array = np.frombuffer(raw_data, dtype=np.uint8)
elif bits_per_component == 16:
img_array = np.frombuffer(raw_data, dtype=np.uint16)
# Convert to 8-bit for PIL
img_array = (img_array // 256).astype(np.uint8)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported bits per component: {bits_per_component}")
# Reshape to image dimensions
if channels == 1:
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width))
mode = 'L' # Grayscale
elif channels == 3:
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width, 3))
mode = 'RGB'
elif channels == 4:
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width, 4))
mode = 'CMYK'
# Create PIL Image
image = Image.fromarray(img_array, mode=mode)
# Convert CMYK to RGB if necessary
if mode == 'CMYK':
image = image.convert('RGB')
return image
# Method 2: Try to handle compressed data
else:
print("Data size doesn't match expected size. Trying decompression...")
# Try zlib decompression (FlateDecode)
try:
import zlib
decompressed = zlib.decompress(raw_data)
print(f"Decompressed size: {len(decompressed)} bytes")
if len(decompressed) == expected_size:
img_array = np.frombuffer(decompressed, dtype=np.uint8)
if channels == 1:
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width))
mode = 'L'
elif channels == 3:
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width, 3))
mode = 'RGB'
elif channels == 4:
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width, 4))
mode = 'CMYK'
image = Image.fromarray(img_array, mode=mode)
if mode == 'CMYK':
image = image.convert('RGB')
return image
except Exception as e:
print(f"Zlib decompression failed: {e}")
# Try other decompression methods if needed
# You might need to handle DCTDecode (JPEG), etc.
raise ValueError("Could not reconstruct image from stream data")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reconstructing image: {e}")
raise
# Usage example based on your PDF data
def main():
# Your image parameters from the PDF dictionary
width = 1520
height = 2239
bits_per_component = 8
colorspace = "RGB" # DeviceRGB
# Path to your stream data file
stream_file = r"json\file.json-128"
try:
# Reconstruct the image
image = reconstruct_image_from_pdf_stream(
stream_file,
width,
height,
bits_per_component,
colorspace
)
# Save the reconstructed image
output_path = "reconstructed_image.png"
image.save(output_path)
print(f"Image saved as: {output_path}")
# Optionally display the image
# image.show()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to reconstruct image: {e}")
print("You may need to handle specific PDF filters or compression methods.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()This is the sample output:
Raw data size: 10209840 bytes
Expected size: 10209840 bytes
Image dimensions: 1520 x 2239
Channels: 3, Bits per component: 8
Image saved as: reconstructed_image.png
C:\ProgramData\Temp\ipykernel_34232\1422296325.py:65: DeprecationWarning: 'mode' parameter is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 13 (2026-10-15)
image = Image.fromarray(img_array, mode=mode)
Detecting Tables in PDF Content
To detect and extract tables from the PDF, I used
PyMuPDF
.
Install the packages:
pip install PyMuPDF pandasThen run the script to scan pages and extract table content. It supports exporting to CSV, Markdown, and more.
import fitz
import pandas as pd
def extract_tables_from_page(pdf_path, page_number):
"""
Extract tables from a specific page with enhanced error handling
"""
doc = fitz.open(pdf_path)
try:
# Check if page number is valid
if page_number >= doc.page_count:
print(f"Error: Page {page_number + 1} doesn't exist. PDF has {doc.page_count} pages.")
return
page = doc[page_number]
print(f"Analyzing page {page_number + 1} of {doc.page_count}")
# Find tables
table_finder = page.find_tables()
tables = list(table_finder)
if not tables:
print("No tables found on this page.")
return
print(f"Found {len(tables)} table(s)")
for i, table in enumerate(tables):
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print(f"TABLE {i + 1}")
print(f"{'='*50}")
print(f"Position (bbox): {table.bbox}")
print(f"Dimensions: {table.row_count} rows × {table.col_count} columns")
try:
# Extract as list of lists
print(f"\n--- Raw Data (first 5 rows) ---")
data_list = table.extract()
if data_list:
for j, row in enumerate(data_list[:5]): # Show first 5 rows
print(f"Row {j}: {row}")
if len(data_list) > 5:
print(f"... and {len(data_list) - 5} more rows")
else:
print("No data extracted")
continue
# Convert to pandas DataFrame
print(f"\n--- DataFrame ---")
try:
df = table.to_pandas()
print(df.head())
print(f"Shape: {df.shape}")
# Save to CSV
csv_filename = f"table_page{page_number + 1}_table{i + 1}.csv"
df.to_csv(csv_filename, index=False)
print(f"Saved to: {csv_filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Could not convert to DataFrame: {e}")
# Fallback: create DataFrame manually
if data_list and len(data_list) > 1:
df = pd.DataFrame(data_list[1:], columns=data_list[0])
print("Manual DataFrame creation:")
print(df.head())
# Convert to Markdown
print(f"\n--- Markdown ---")
try:
md_text = table.to_markdown()
print(md_text[:500] + ("..." if len(md_text) > 500 else ""))
# Save markdown
md_filename = f"table_page{page_number + 1}_table{i + 1}.md"
with open(md_filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(md_text)
print(f"Markdown saved to: {md_filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Could not convert to Markdown: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing table {i + 1}: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing page: {e}")
finally:
doc.close()
def scan_all_pages_for_tables(pdf_path):
"""
Scan all pages to find which ones contain tables
"""
doc = fitz.open(pdf_path)
print(f"Scanning {doc.page_count} pages for tables...")
pages_with_tables = []
for page_num in range(doc.page_count):
page = doc[page_num]
table_finder = page.find_tables()
tables = list(table_finder)
if tables:
pages_with_tables.append((page_num, len(tables)))
print(f"Page {page_num + 1}: {len(tables)} table(s)")
doc.close()
if pages_with_tables:
print(f"\nSummary: Tables found on {len(pages_with_tables)} page(s)")
for page_num, table_count in pages_with_tables:
print(f" Page {page_num + 1}: {table_count} table(s)")
else:
print("No tables found in the entire document")
return pages_with_tables
def extract_table_with_options(pdf_path, page_number, table_index=0):
"""
Extract a specific table with different formatting options
"""
doc = fitz.open(pdf_path)
page = doc[page_number]
table_finder = page.find_tables()
tables = list(table_finder)
if table_index >= len(tables):
print(f"Table {table_index} not found. Only {len(tables)} table(s) on page {page_number + 1}")
doc.close()
return
table = tables[table_index]
print(f"Extracting Table {table_index + 1} from Page {page_number + 1}")
print(f"Table bounds: {table.bbox}")
# Different extraction options
formats = {
"Raw List": lambda: table.extract(),
"Pandas DataFrame": lambda: table.to_pandas(),
"Markdown": lambda: table.to_markdown(),
"CSV String": lambda: table.to_csv(),
}
for format_name, extract_func in formats.items():
try:
print(f"\n--- {format_name} ---")
result = extract_func()
if isinstance(result, str):
print(result[:300] + ("..." if len(result) > 300 else ""))
elif isinstance(result, pd.DataFrame):
print(result)
elif isinstance(result, list):
for i, row in enumerate(result[:3]):
print(f"Row {i}: {row}")
if len(result) > 3:
print(f"... {len(result) - 3} more rows")
else:
print(result)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error with {format_name}: {e}")
doc.close()
# Usage examples
if __name__ == "__main__":
pdf_file = "1706.03762v7.pdf"
print("=== EXTRACTING FROM PAGE 10 ===")
extract_tables_from_page(pdf_file, 9) # Page 10 (0-indexed)
print("\n=== SCANNING ALL PAGES ===")
pages_with_tables = scan_all_pages_for_tables(pdf_file)
# Extract from other pages if found
if pages_with_tables:
print("\n=== EXTRACTING FROM FIRST TABLE-CONTAINING PAGE ===")
first_page_with_tables = pages_with_tables[0][0]
extract_table_with_options(pdf_file, first_page_with_tables)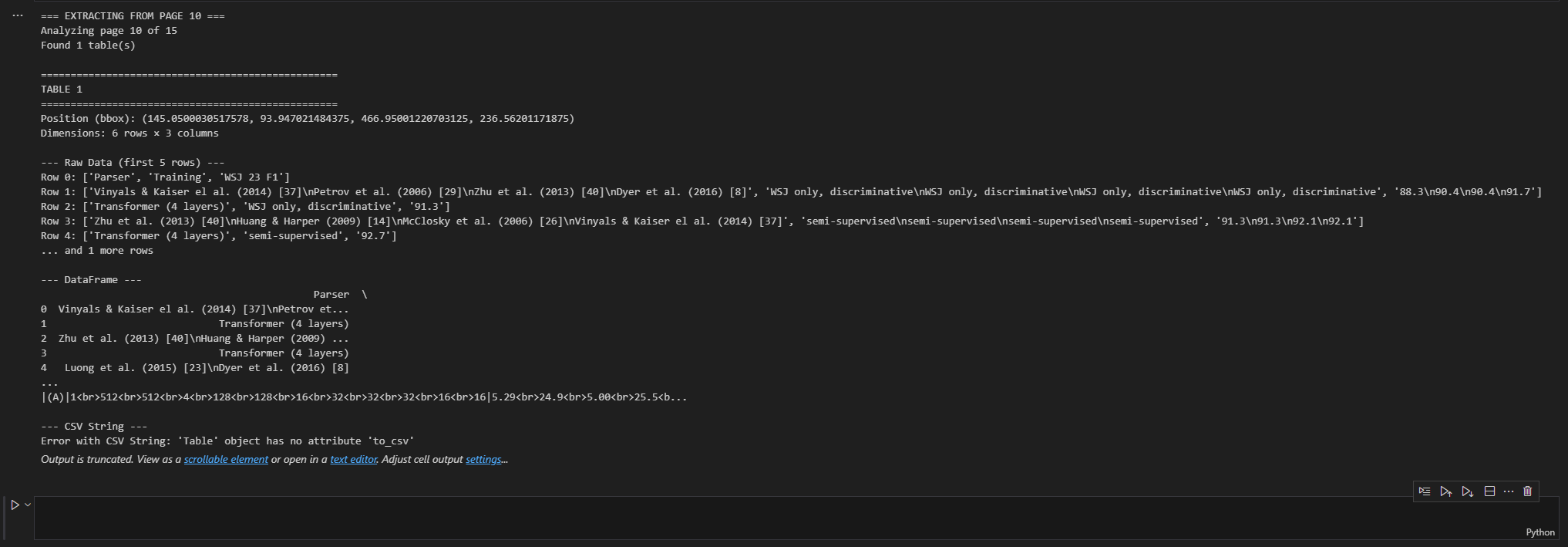
The Vibe Coding Challenge
xAI Grok Code Fast 1ad
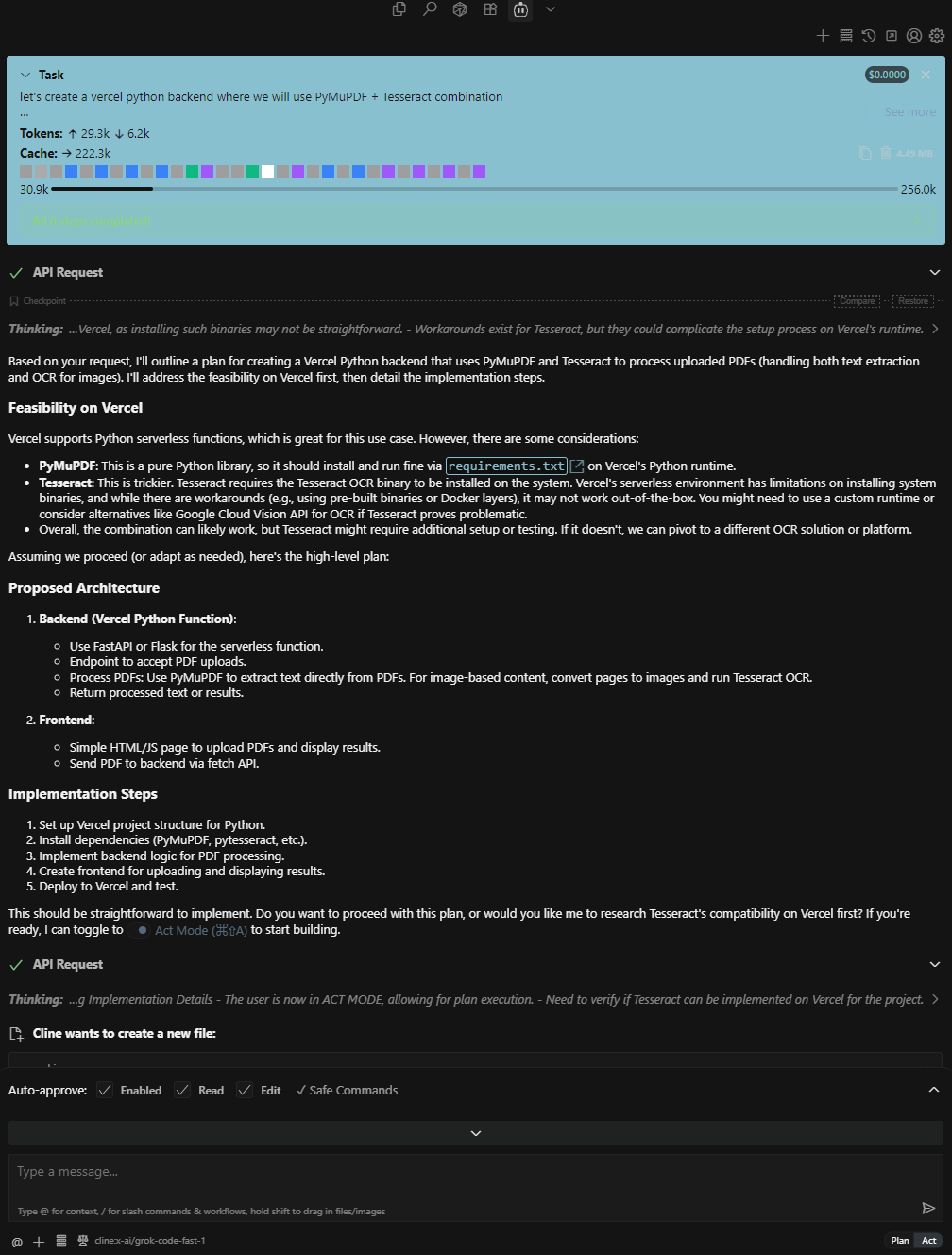
With the release of Grok Code Fast 1 , now available for free via exclusive launch partners, I gave it a try! For my setup, I installed Cline inside Cursor , an AI-powered code editor.
Unfortunately, after several attempts, the project didn’t run as expected. Below is the sample autonomous coding agent setup in Cursor using Cline:
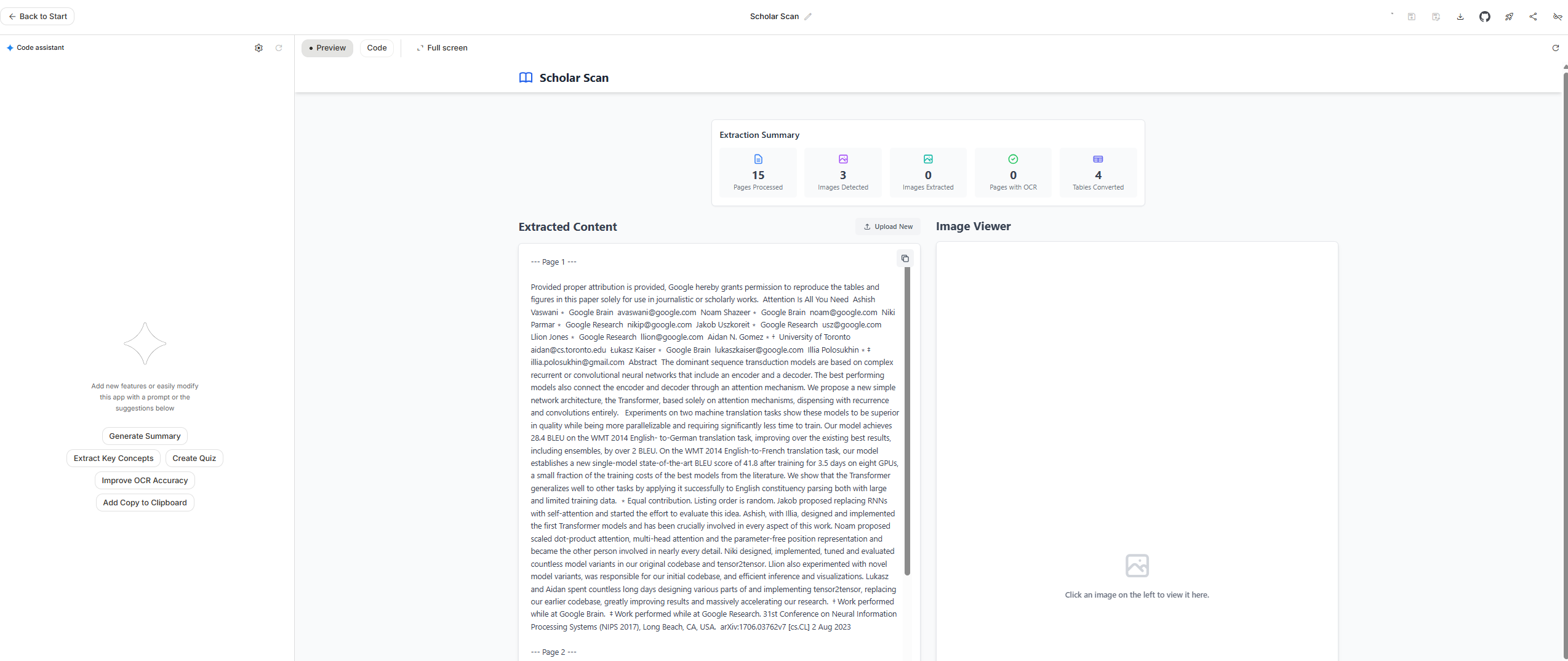
Google AI Studio
With Google AI Studio , an easy and free way to start building with Gemini, I tried the same prompts there…
Conclusion
This exploration began with a simple PDF upload challenge and expanded into a deep dive through PDF internals—from inspecting raw hex data, manipulating structure with qpdf, reconstructing embedded images, to extracting tables using PyMuPDF. Along the way, I experimented with new tools like Grok Code Fast 1 and AI Studio to assess their potential in handling real-world document analysis.
If you’re working on similar PDF-related tasks, want to experiment with document internals, or just enjoy tinkering with file formats—hopefully this walkthrough gives you a head start.
Have your own tricks for working with PDFs?
Or found a better way to extract structured data from academic papers?
👉 Drop me a message or share your approach—I’d love to learn more!
