In this post, I’ll share my journey exploring n8n —a flexible, open-source workflow automation tool with built-in AI integrations. I’ll walk through how I set it up locally on my Windows machine and later deployed it to my homelab environment.
Prerequiste: Cloning and Running n8n Locally
The Self-hosted AI Starter Kit is an open-source Docker Compose template designed to quickly spin up a comprehensive local AI and low-code automation environment.
Clone the Repository
git clone https://github.com/n8n-io/self-hosted-ai-starter-kit.git
cd self-hosted-ai-starter-kit.gitConfigure Local Settings
Start by copying the sample environment file:
cp .env.example .envSince I’m working on a Windows setup, and the Docker images are primarily Linux-based, I ran everything through WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux). I also modified the following environment variables to suit my setup:
N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true
N8N_LISTEN_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0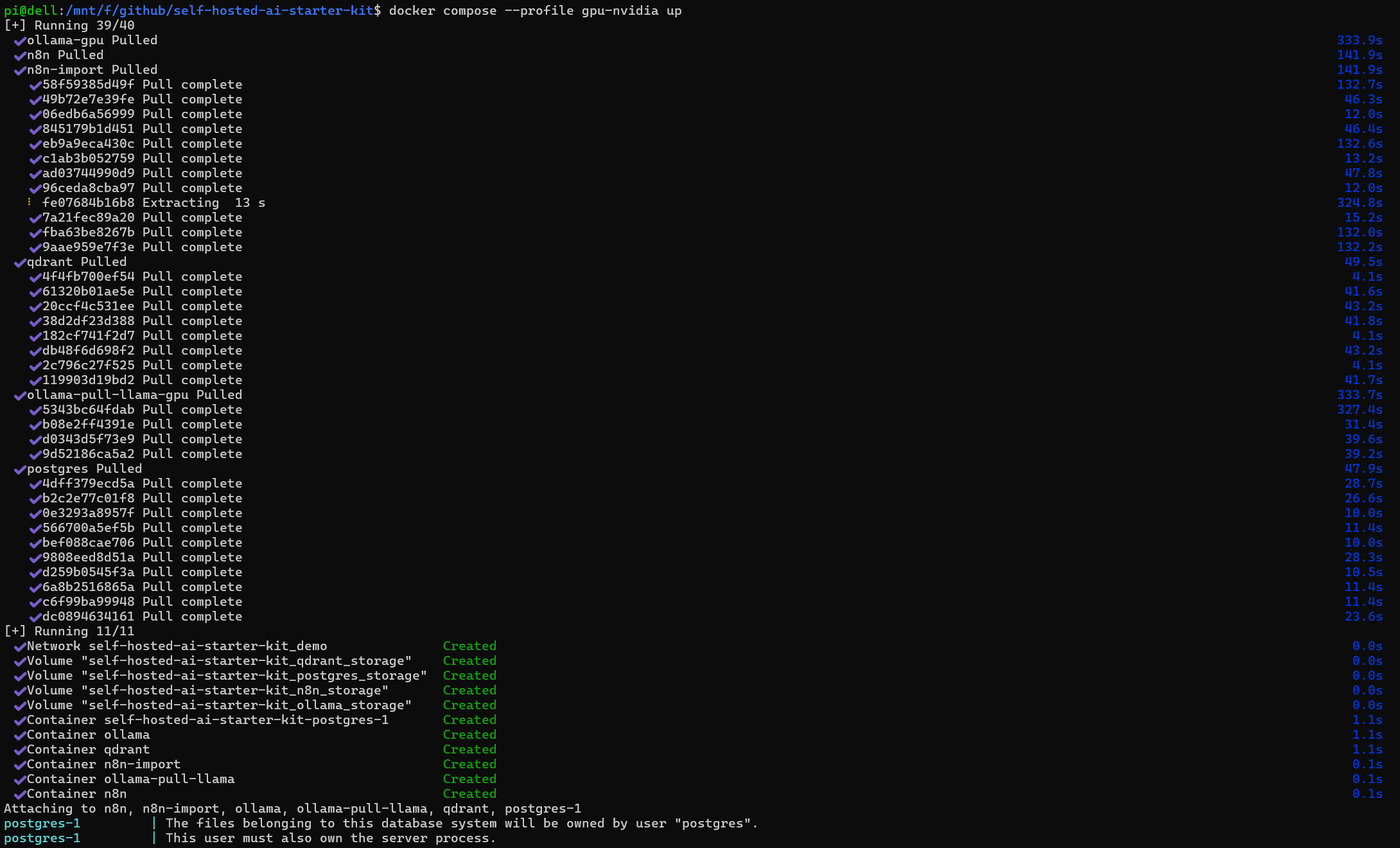
Start the Services
Spin up the necessary containers using:
docker compose --profile gpu-nvidia upOnce everything is up and running, visit http://localhost:5678 to access the n8n dashboard.
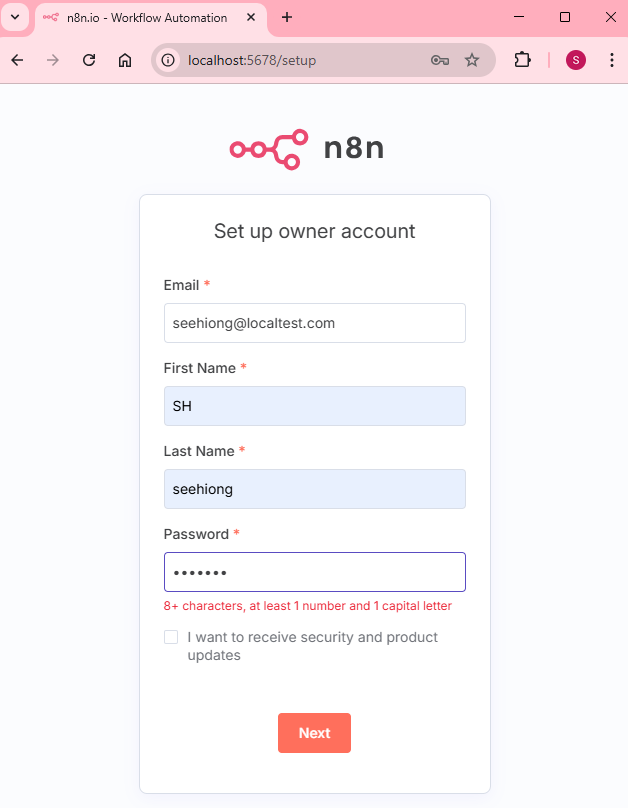
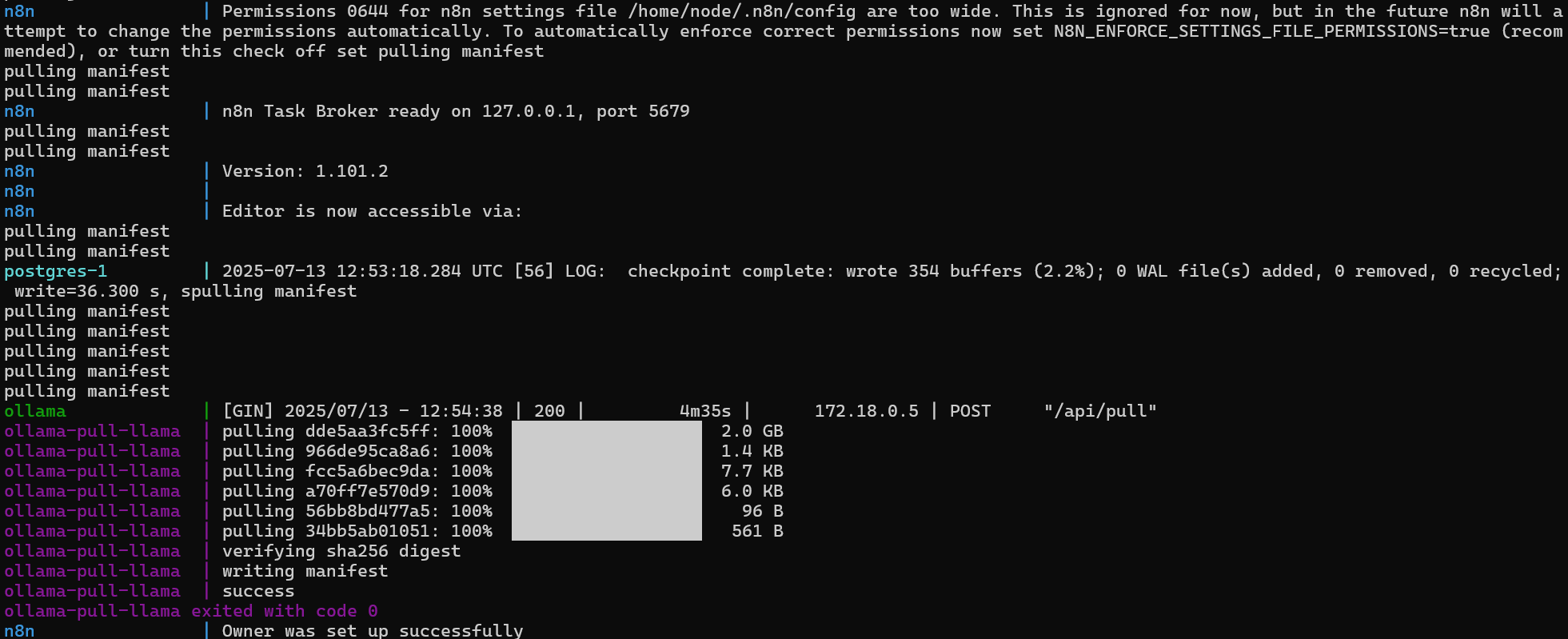
Demo Workflow
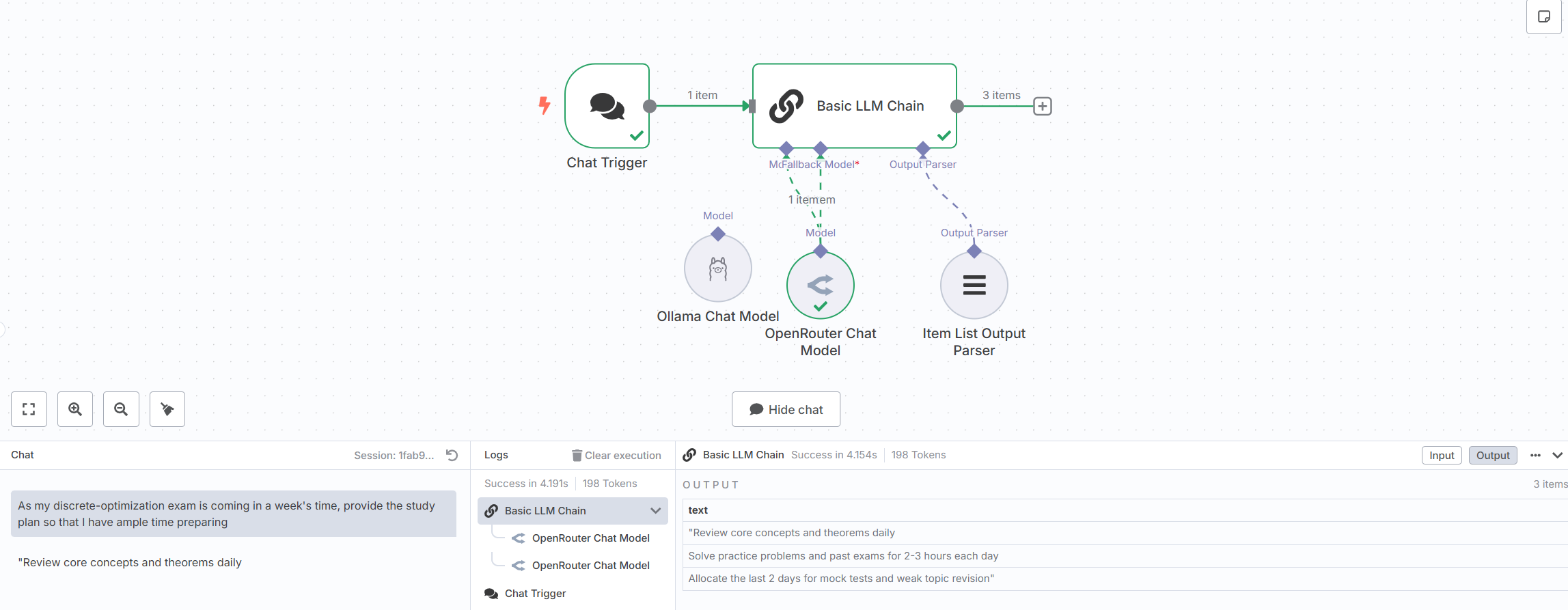
To get a quick feel of how things work, click on the Demo workflow from the Overview tab, or directly navigate to:
http://localhost:5678/workflow/srOnR8PAY3u4RSwbMake sure to configure the required fallback model. In my case, I used the OpenRouter Chat Model.
Learn by Examples
One of the best ways to explore n8n is by diving into real workflows. The official Workflow Automation Templates are a great starting point.
First Example: API Fundamentals
Let’s start with the tutorial: Learn API Fundamentals with an Interactive Hands-On Tutorial
- Open a Node
Select a node, press Enter or double-click to open its configuration panel.
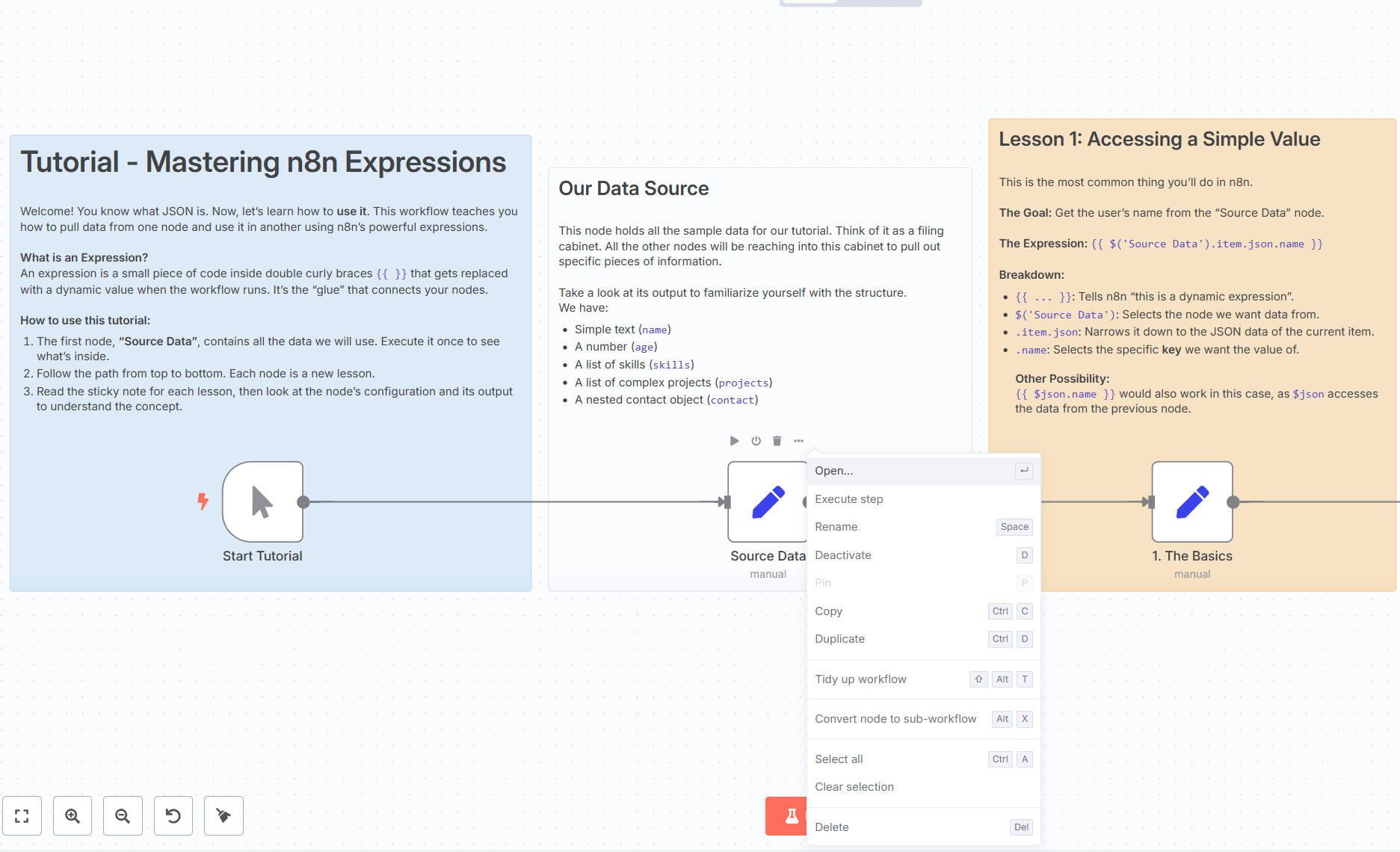
- Access a Simple Value
Use the expression:
{{ $('Source Data').item.json.name }}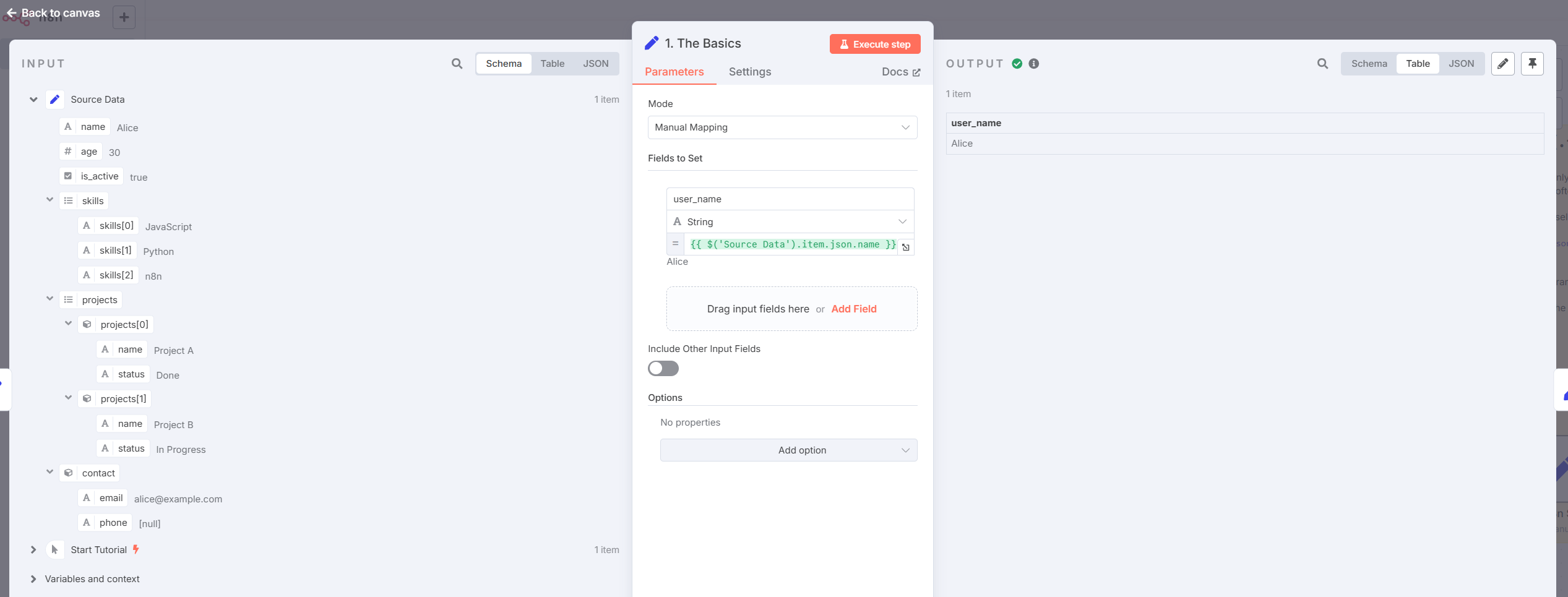
- Using n8n Selectors
Handy helpers like .first(), .last(), .all():
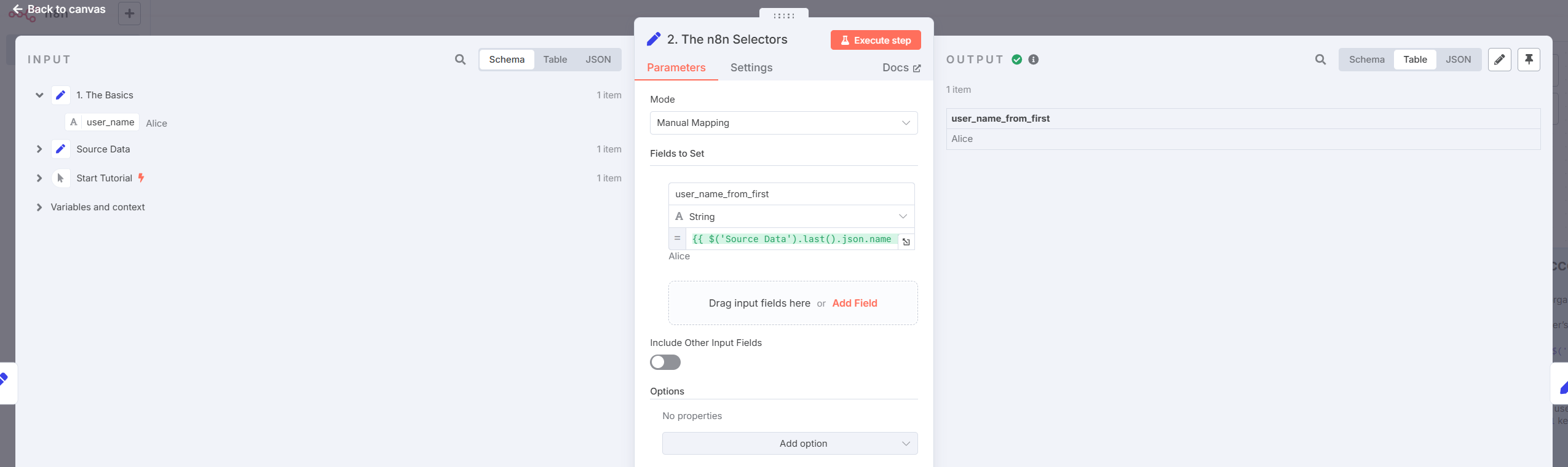
- Accessing Array Elements
Example:
{{ $('Source Data').last().json.skills[1] }}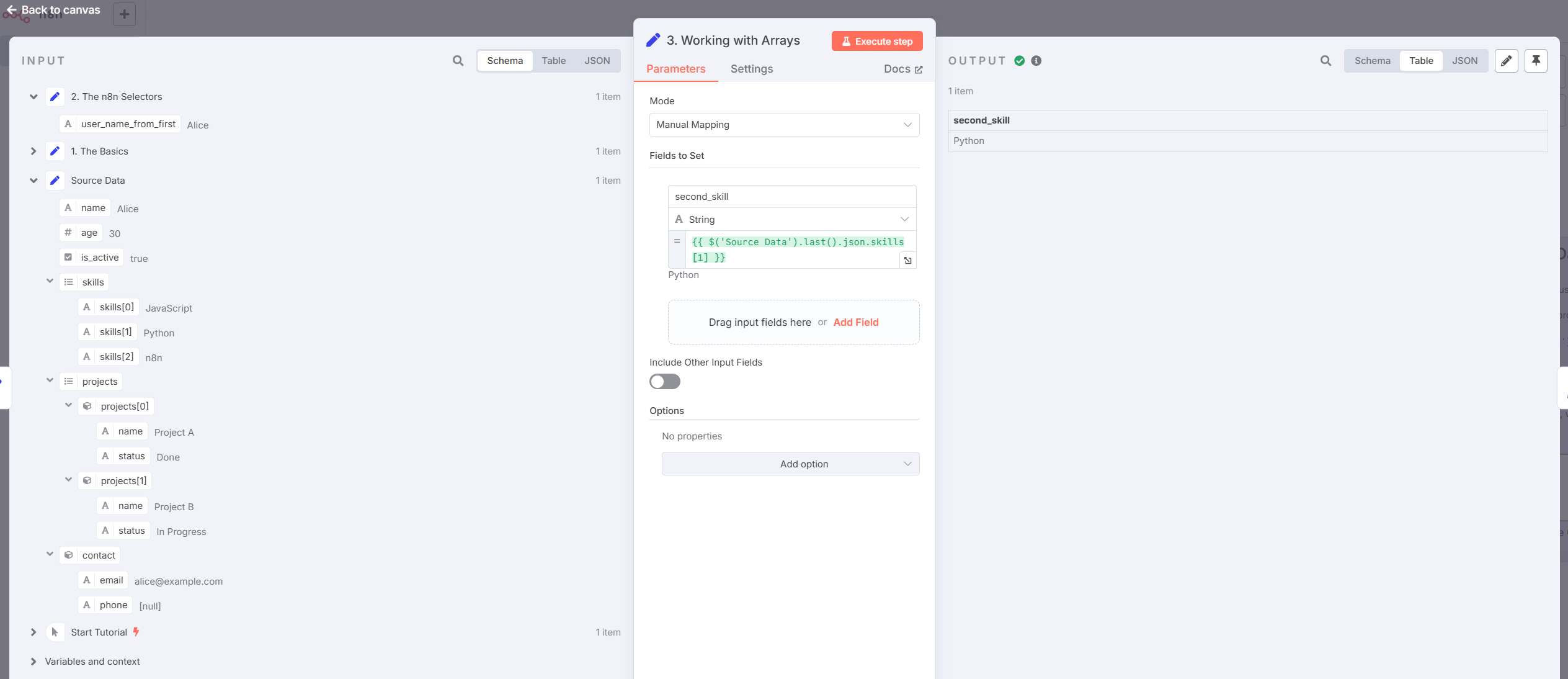
- Working with Nested Data
Example:
{{ $('Source Data').last().json.contact.email }}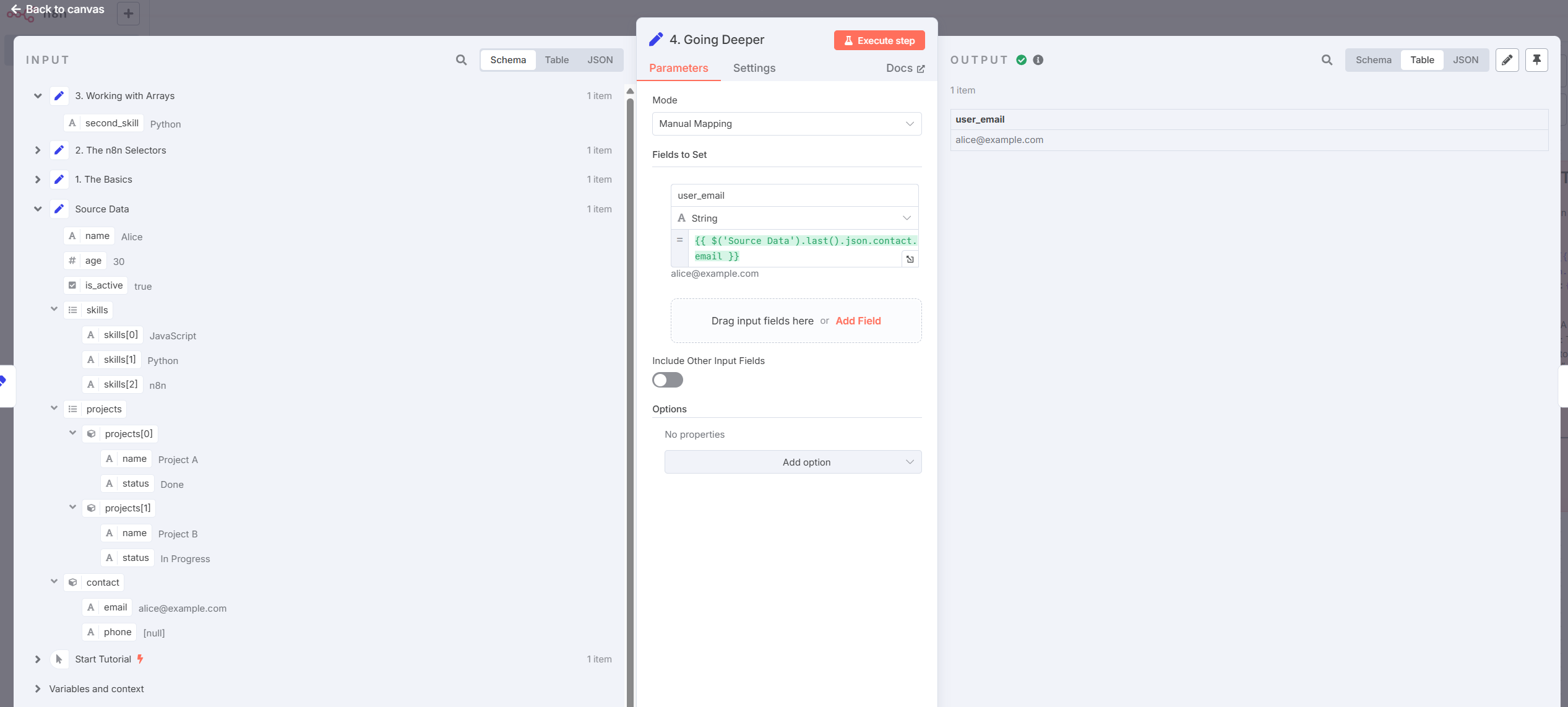
- Accessing Data in Object Arrays
Example:
{{ $('Source Data').last().json.projects[0].status }}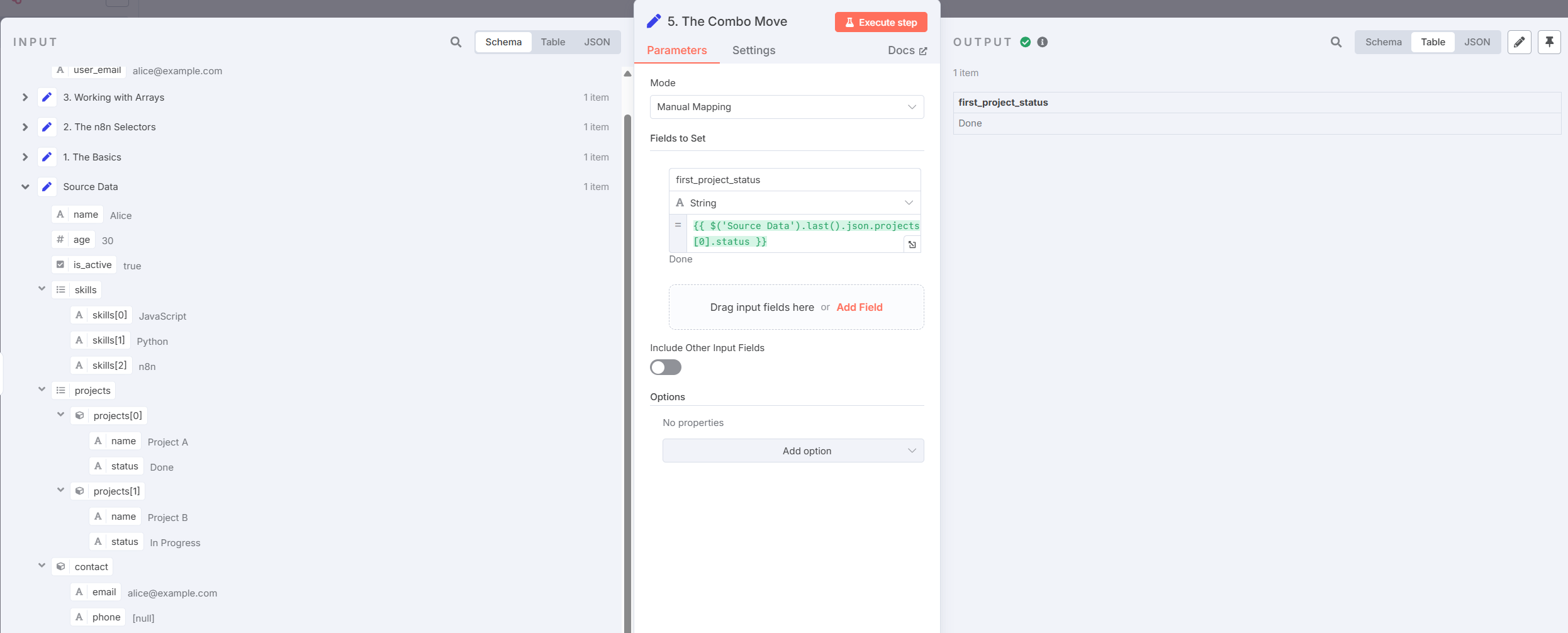
- Using JavaScript Functions
Example:
{{ $('Source Data').last().json.name.toUpperCase() }}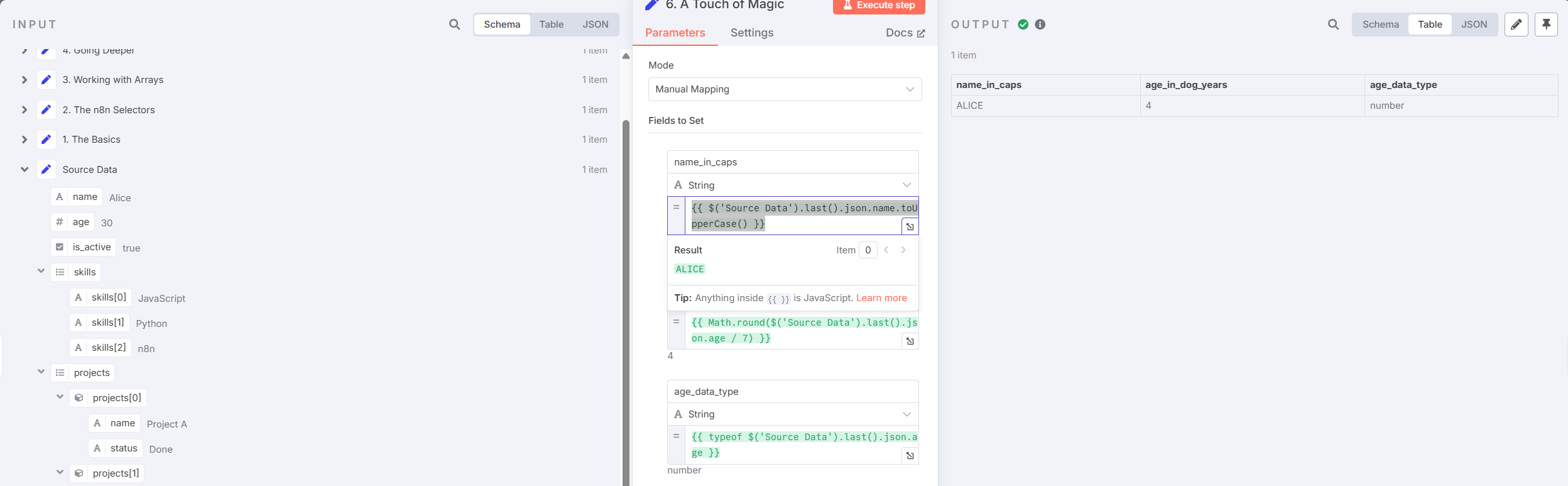
- Inspecting Objects
Useful when exploring dynamic JSON:
Object.keys($('Source Data').item.json)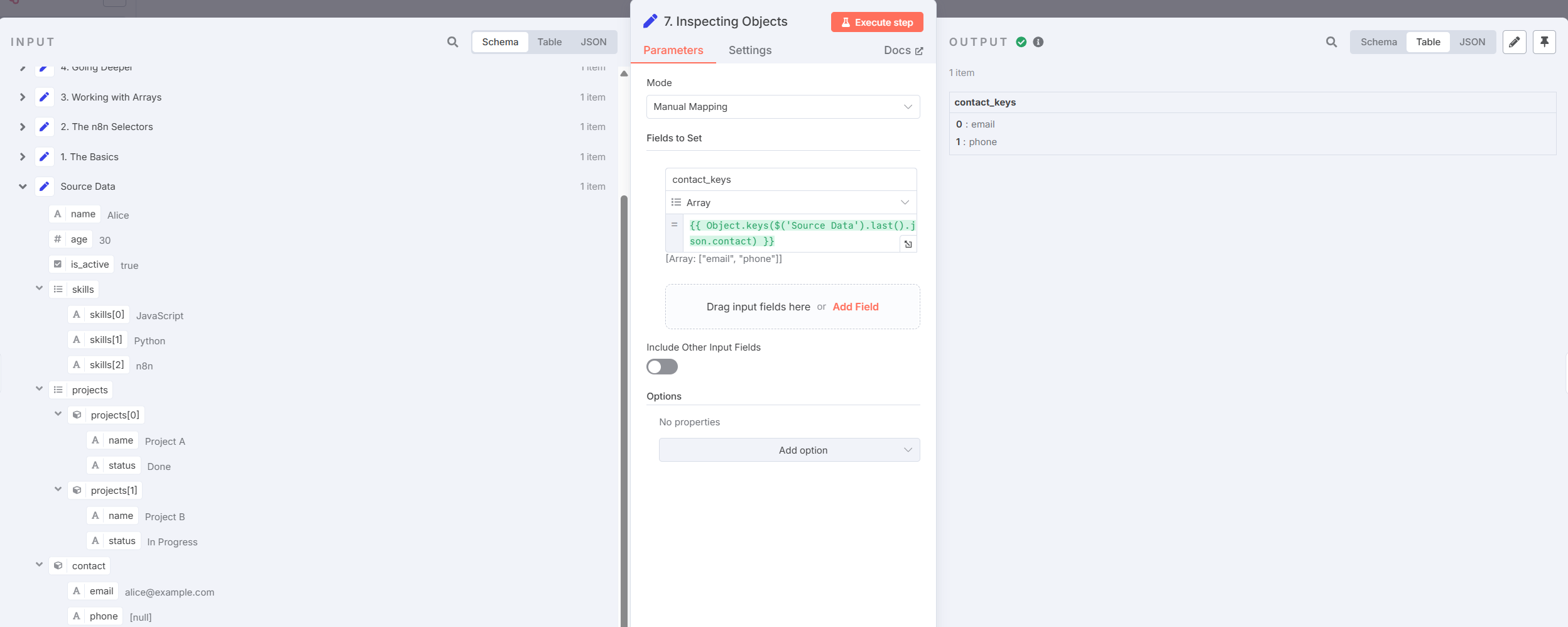
- Stringify Object Data
Example:
JSON.stringify($('Source Data').item.json)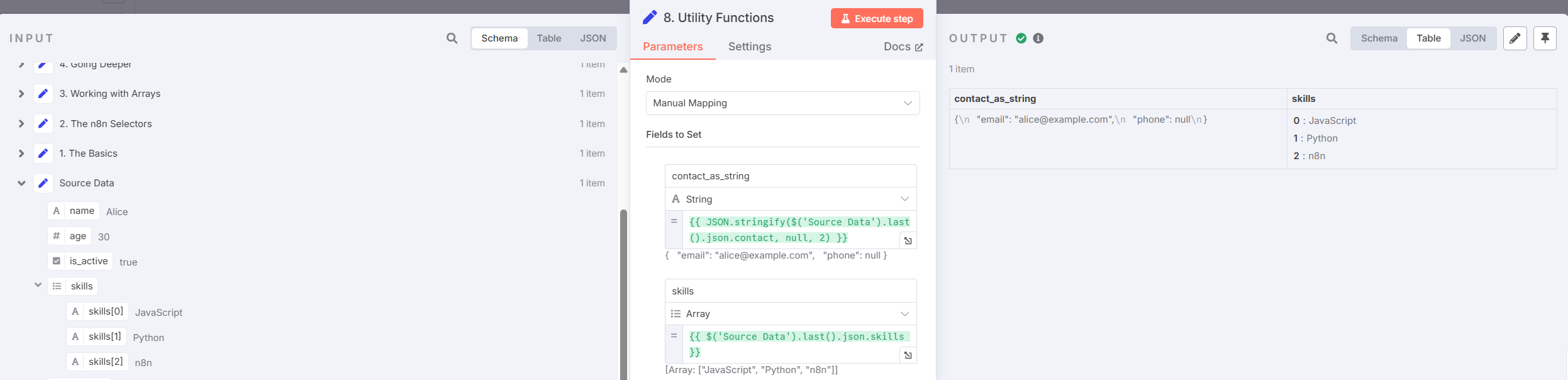
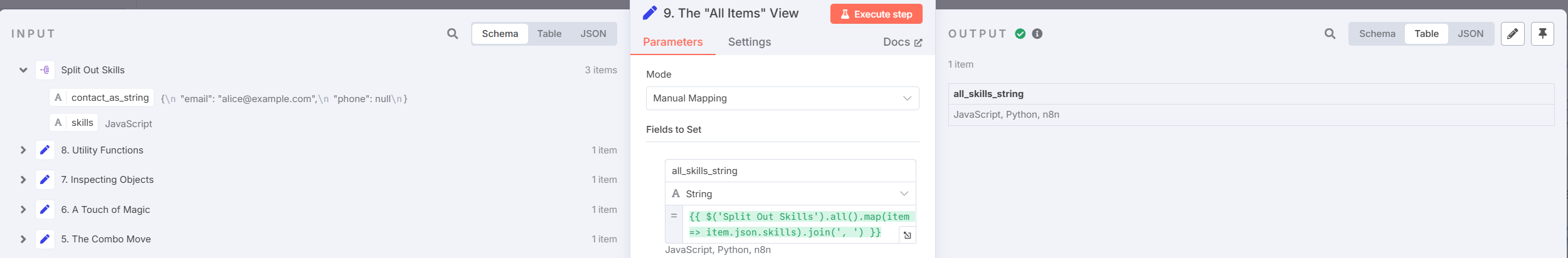
- Working with Multiple Items
Combine $items with arrow functions for batch processing:
Optional – Running n8n in My Homelab
For those who prefer deploying n8n on a Kubernetes cluster, I’ve included a streamlined setup using Kompose to convert the Docker Compose setup into Kubernetes manifests. Below is my working configuration deployed in my homelab.
PostgreSQL Deployment
Use the following commands to deploy the PostgreSQL database:
kubectl apply -f postgres-storage-persistentvolumeclaim.yaml
kubectl apply -f postgres-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f postgres-service.yamlPostgres K8s files
- Persistent Volume Claim
# postgres-storage-persistentvolumeclaim.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: postgres-storage
name: postgres-storage
namespace: n8n
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi- Deployment
# postgres-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: postgres
name: postgres
namespace: n8n
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
io.kompose.service: postgres
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: postgres
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: POSTGRES_DB
value: n8n
- name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD
value: postgres
- name: POSTGRES_USER
value: postgres
image: postgres:16-alpine
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pg_isready -h localhost -U postgres -d n8n
failureThreshold: 10
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 5
name: postgres
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
name: postgres-storage
hostname: postgres
restartPolicy: Always
volumes:
- name: postgres-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: postgres-storage- Service
# postgres-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: postgres
name: postgres
namespace: n8n
spec:
ports:
- name: "5432"
port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
selector:
io.kompose.service: postgres
type: ClusterIPn8n Deployment
Use the following commands to deploy n8n:
kubectl apply -f n8n-demo-persistentVolumeClaim.yaml
kubectl apply -f n8n-storage-persistentVolumeClaim.yaml
kubectl apply -f n8n-claim2-persistentVolumeClaim.yaml
kubectl apply -f n8n-job.yaml
kubectl apply -f n8n-configmap.yaml
kubectl apply -f n8n-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f n8n-service.yamln8n K8s files
- Persistent Volume Claims
Multiple PVCs are used to separate storage for runtime data, demo workflows, and shared content.
# n8n-demo-persistentVolumeClaim.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: demo-data-pvc
name: demo-data-pvc
namespace: n8n
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi # n8n-storage-persistentvolumeclaim.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n-storage
name: n8n-storage
namespace: n8n
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi# n8n-claim2-persistentVolumeClaim.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n-claim2
name: n8n-claim2
namespace: n8n
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi- Import Job
This job initializes the demo credentials and workflows:
# n8n-job.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n-import
name: n8n-import
namespace: n8n
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n-import
spec:
containers:
- args:
- -c
- n8n import:credentials --separate --input=/demo-data/credentials && n8n import:workflow --separate --input=/demo-data/workflows
command:
- /bin/sh
env:
- name: DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST
value: postgres
- name: DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD
value: postgres
- name: DB_POSTGRESDB_USER
value: postgres
- name: DB_TYPE
value: postgresdb
- name: N8N_DIAGNOSTICS_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: N8N_PERSONALIZATION_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: OLLAMA_HOST
value: ollama:11434
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: env
image: n8nio/n8n:latest
name: n8n-import
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /demo-data
name: demo-data
hostname: n8n-import
restartPolicy: Never
volumes:
- name: demo-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: demo-data-pvc- ConfigMap
Centralized environment variables:
# n8n-configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
N8N_DEFAULT_BINARY_DATA_MODE: filesystem
N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY: super-secret-key
N8N_LISTEN_ADDRESS: 0.0.0.0
N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED: "true"
N8N_USER_MANAGEMENT_JWT_SECRET: even-more-secret
N8N_SECURE_COOKIE: "false"
N8N_URL: "http://n8n.local"
WEBHOOK_URL: "http://n8n.local/"
POSTGRES_DB: n8n
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n-env
name: env
namespace: n8n- Deployment
# n8n-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n
name: n8n
namespace: n8n
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
io.kompose.service: n8n
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST
value: postgres
- name: DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD
value: postgres
- name: DB_POSTGRESDB_USER
value: postgres
- name: DB_TYPE
value: postgresdb
- name: N8N_DIAGNOSTICS_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: N8N_PERSONALIZATION_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: OLLAMA_HOST
value: ollama:11434
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: env
image: n8nio/n8n:latest
name: n8n
ports:
- containerPort: 5678
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/node/.n8n
name: n8n-storage
- mountPath: /data/shared
name: n8n-claim2
- mountPath: /demo-data
name: demo-data
hostname: n8n
restartPolicy: Always
volumes:
- name: n8n-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: n8n-storage
- name: n8n-claim2
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: n8n-claim2
- name: demo-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: demo-data-pvc- Service
# n8n-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
io.kompose.service: n8n
name: n8n
spec:
ports:
- name: "5678"
port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
io.kompose.service: n8n
type: LoadBalancerHomelab n8n In Action
Once the Kubernetes services are up and running, check the external IP address or NodePort exposed by your homelab cluster. In my case, I accessed n8n via:
http://192.168.68.222:5678/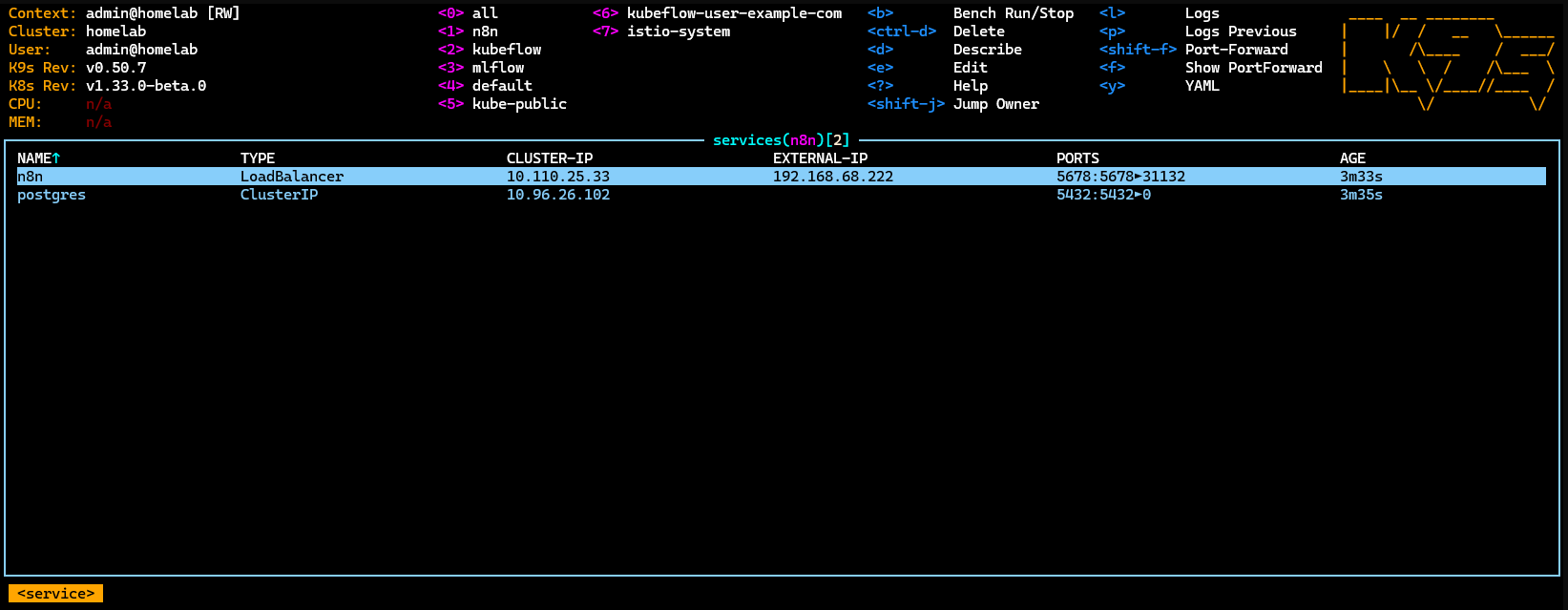
With n8n now running in my homelab, I imported the same demo workflow used earlier. Everything worked seamlessly—just like the local setup, but now running in a self-hosted, scalable Kubernetes environment.
Conclusion
Exploring n8n has been a rewarding experience—from running it locally with Docker to deploying it on a Kubernetes homelab. With its low-code interface, flexible integrations, and powerful scripting capabilities, n8n makes workflow automation approachable and scalable. Whether you’re just starting out or integrating AI into your pipelines, there’s a lot to build and automate.
Happy nodemating!
