Streamlining API Management with Kong
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk through the process of integrating Kong, a robust unified API platform, into our home lab environment.
Prerequistes
To begin, I will start with a fresh Ubuntu server instance. We’ll start by installing Docker and configuring it for non-root usage:
sudo apt install docker.io
sudo usermod -aG docker pi
# Run Docker without sudo by logging back in or executing this
su - pi
Building a Custom Kong Image
As we are utilizing the open-source version (OSS), let’s create a custom Kong image.
First, download the docker-entrypoint.sh script:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/docker-kong/master/docker-entrypoint.sh
chmod +x docker-entrypoint.sh
Next, obtain the Debian build from here and rename it to kong.deb:
wget https://packages.konghq.com/public/gateway-35/deb/debian/pool/bullseye/main/k/ko/kong_3.5.0/kong_3.5.0_amd64.deb
The Dockerfile, accompanied by the docker-entrypoint.sh and kong.deb files located in the same folder, is as follows:
FROM debian:bullseye-slim
COPY kong.deb /tmp/kong.deb
RUN set -ex; \
apt-get update \
&& apt-get install --yes /tmp/kong.deb \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* \
&& rm -rf /tmp/kong.deb \
&& chown kong:0 /usr/local/bin/kong \
&& chown -R kong:0 /usr/local/kong \
&& ln -s /usr/local/openresty/luajit/bin/luajit /usr/local/bin/luajit \
&& ln -s /usr/local/openresty/luajit/bin/luajit /usr/local/bin/lua \
&& ln -s /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/bin/nginx \
&& kong version
COPY docker-entrypoint.sh /docker-entrypoint.sh
USER kong
ENTRYPOINT ["/docker-entrypoint.sh"]
EXPOSE 8000 8443 8001 8444 8002 8445 8003 8446 8004 8447
STOPSIGNAL SIGQUIT
HEALTHCHECK --interval=10s --timeout=10s --retries=10 CMD kong health
CMD ["kong", "docker-start"]
Build the Kong custom image:
docker build --platform linux/amd64 --no-cache -t kong-image:3.5.0 .
# Check kong version, should return 3.5.0
docker run -it --rm kong-image:3.5.0 kong version
Since we plan to configure services and routes later, we cannot use the DB-less mode. Follow the install Kong Gateway on Docker installation guide to create the Docker network and start a PostgreSQL container:
docker network create kong-net
docker run -d --name kong-database \
--network=kong-net \
-p 5432:5432 \
-e "POSTGRES_USER=kong" \
-e "POSTGRES_DB=kong" \
-e "POSTGRES_PASSWORD=kongpass" \
postgres:13
Prepare the database with our custom image:
docker run --rm --network=kong-net \
-e "KONG_DATABASE=postgres" \
-e "KONG_PG_HOST=kong-database" \
-e "KONG_PG_PASSWORD=kongpass" \
-e "KONG_PASSWORD=test" \
kong-image:3.5.0 kong migrations bootstrap
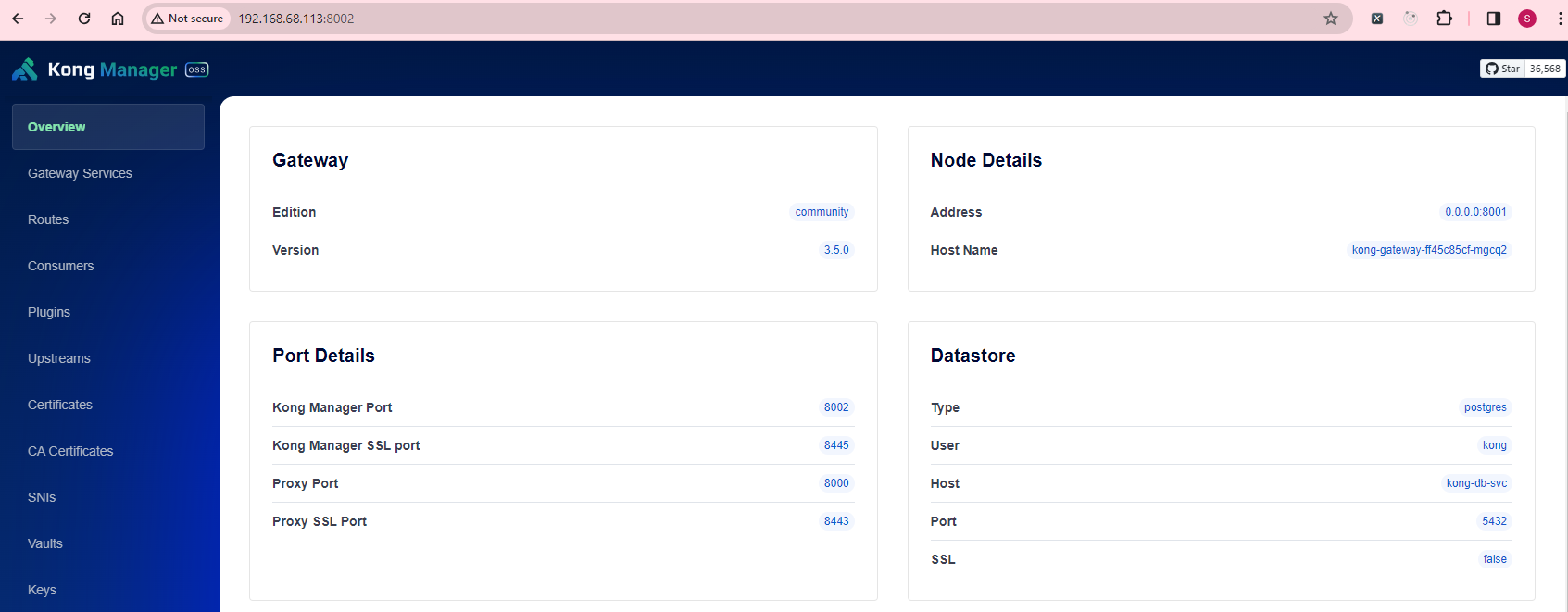
Lastly, replace the GUI URL with your IP address and run the Kong Gateway:
docker run -d --name kong-gateway \
--network=kong-net \
-e "KONG_DATABASE=postgres" \
-e "KONG_PG_HOST=kong-database" \
-e "KONG_PG_USER=kong" \
-e "KONG_PG_PASSWORD=kongpass" \
-e "KONG_PROXY_ACCESS_LOG=/dev/stdout" \
-e "KONG_ADMIN_ACCESS_LOG=/dev/stdout" \
-e "KONG_PROXY_ERROR_LOG=/dev/stderr" \
-e "KONG_ADMIN_ERROR_LOG=/dev/stderr" \
-e "KONG_ADMIN_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8001" \
-e "KONG_ADMIN_GUI_URL=http://192.168.68.113:8002" \
-e KONG_LICENSE_DATA \
-p 8000:8000 \
-p 8443:8443 \
-p 8001:8001 \
-p 8444:8444 \
-p 8002:8002 \
-p 8445:8445 \
-p 8003:8003 \
-p 8004:8004 \
kong-image:3.5.0
The following commands can be helpful during the initial setup:
# Kill and remove the docker container
docker kill kong-gateway
docker container rm kong-gateway
# Tail the Kong Gateway logs for debugging purposes
docker logs -f kong-gateway
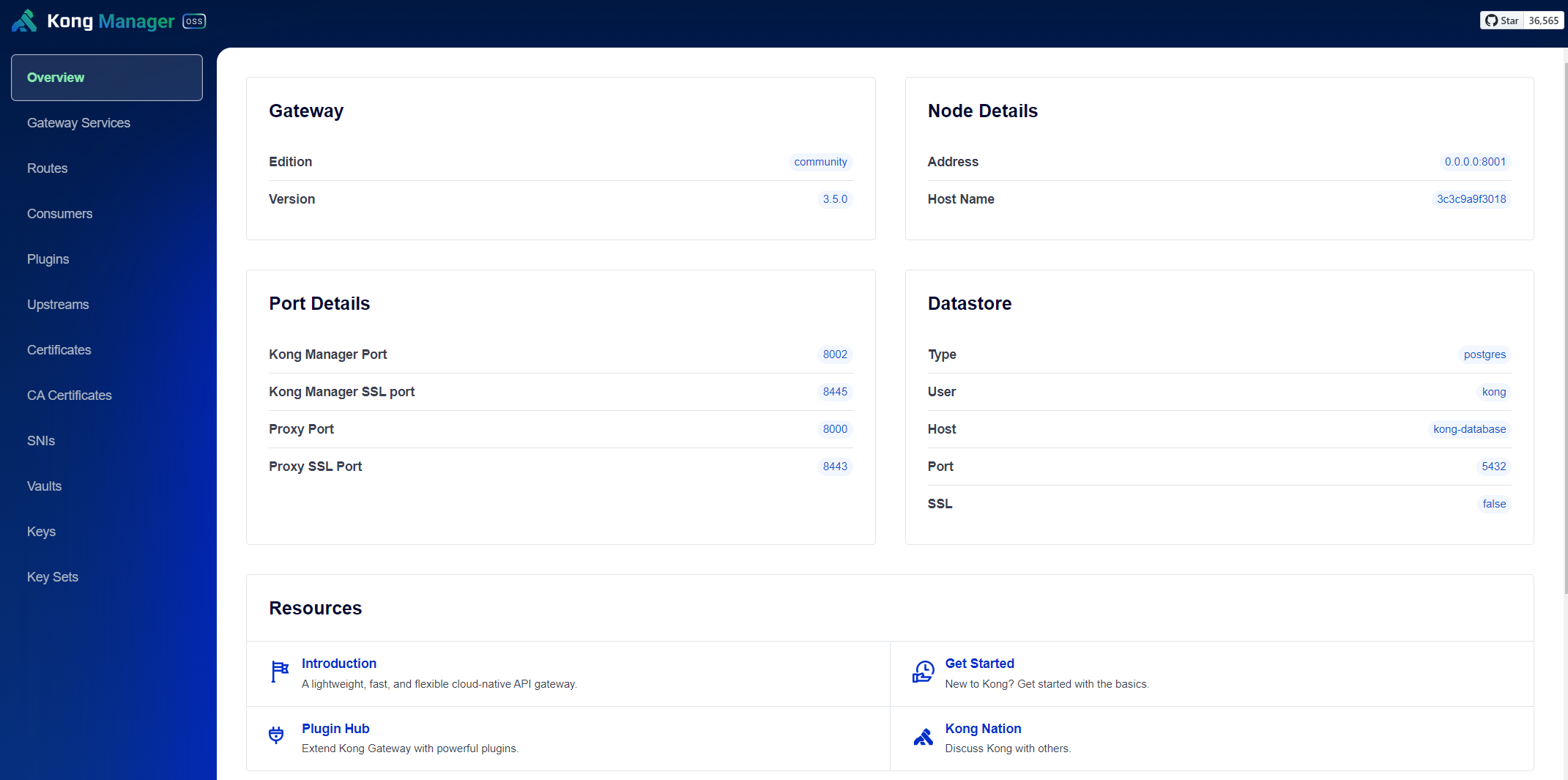
As the final step, after confirming the successful operation of the custom image, proceed to join as a K3s node, tag the image and push it to our home lab registry:
# Join as K3s node
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_URL=https://192.168.68.115:6443 K3S_TOKEN=K10e848701b18977c63d7abfce920cf66c0f19bdd18a40862b2e7a14b89c4eb2742::server:ac92f2b7ccebbb46bf241bdaea3c99bf sh -
echo -e ' --docker\n --insecure-registry=http://192.168.68.115:30500' | sudo tee -a /etc/systemd/system/k3s-agent.service
# Restart K3s agent
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart k3s-agent
# Setup local registry
sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF > /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"insecure-registries": [
"192.168.68.115:30500"
]
}
EOF'
sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF > /etc/default/docker
DOCKER_OPTS="--config-file=/etc/docker/daemon.json"
EOF'
sudo systemctl restart docker
docker tag kong-image:3.5.0 192.168.68.115:30500/kong-image:3.5.0
docker push 192.168.68.115:30500/kong-image:3.5.0
Deploying PostgreSQL to the Home Lab
For PostgreSQL deployment, use the kong-db-deploy-svc.yaml file, ensuring data storage on the host machine hp:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kong-db
namespace: llm
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kong-db
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kong-db
spec:
containers:
- name: postgres
image: postgres:13
ports:
- containerPort: 5432
env:
- name: POSTGRES_USER
value: "kong"
- name: POSTGRES_DB
value: "kong"
- name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD
value: "kongpass"
volumeMounts:
- name: kong-db-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: hp
volumes:
- name: kong-db-storage
hostPath:
path: /docker-data/kong-db
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kong-db-svc
namespace: llm
spec:
selector:
app: kong-db
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
Deploy to the home lab:
kca kong-db-deploy-svc.yaml
Deploying Kong Custom Image to the Home Lab
Create the kong-deploy-svc.yaml file using LoadBalancer to expose Kong Manager. Note: Avoid using this configuration in production without setting up proper credential logins. IP address of hp is 192.168.68.113:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kong-gateway
namespace: llm
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kong-gateway
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kong-gateway
spec:
initContainers:
- name: kong-init
image: 192.168.68.115:30500/kong-image:3.5.0
command: ["kong", "migrations", "bootstrap"]
env:
- name: KONG_DATABASE
value: "postgres"
- name: KONG_PG_HOST
value: "kong-db-svc"
- name: KONG_PG_PASSWORD
value: "kongpass"
- name: KONG_PASSWORD
value: "test"
containers:
- name: kong-gateway
image: 192.168.68.115:30500/kong-image:3.5.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
- containerPort: 8443
- containerPort: 8001
- containerPort: 8444
- containerPort: 8002
- containerPort: 8445
- containerPort: 8003
- containerPort: 8004
env:
- name: KONG_DATABASE
value: "postgres"
- name: KONG_PG_HOST
value: "kong-db-svc"
- name: KONG_PG_USER
value: "kong"
- name: KONG_PG_PASSWORD
value: "kongpass"
- name: KONG_PROXY_ACCESS_LOG
value: "/dev/stdout"
- name: KONG_ADMIN_ACCESS_LOG
value: "/dev/stdout"
- name: KONG_PROXY_ERROR_LOG
value: "/dev/stderr"
- name: KONG_ADMIN_ERROR_LOG
value: "/dev/stderr"
- name: KONG_ADMIN_LISTEN
value: "0.0.0.0:8001"
- name: KONG_ADMIN_GUI_URL
value: "http://192.168.68.113:8002"
- name: KONG_LICENSE_DATA
value: ""
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: hp
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kong-gateway-svc
namespace: llm
spec:
selector:
app: kong-gateway
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
- name: admin
protocol: TCP
port: 8001
targetPort: 8001
- name: manager
protocol: TCP
port: 8002
targetPort: 8002
Deploy to the home lab:
kca kong-deploy-svc.yaml
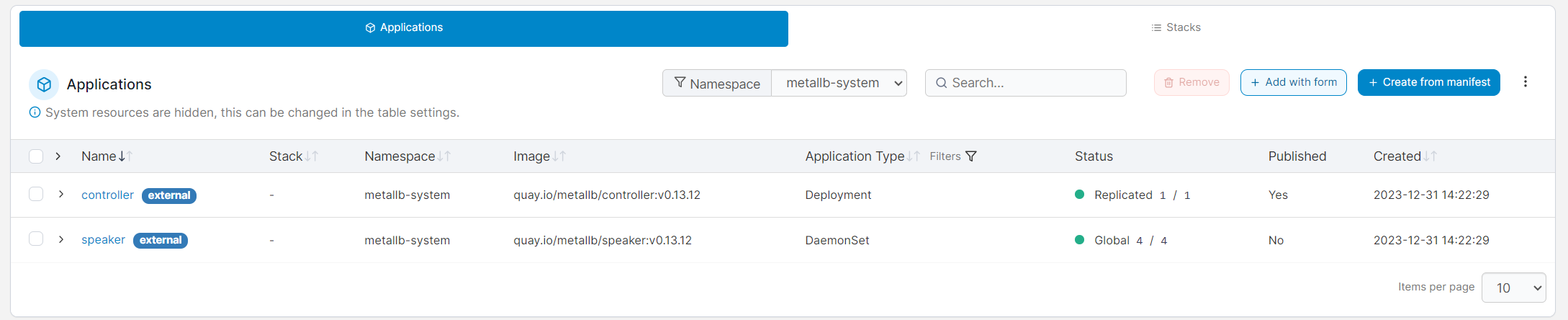
Configuring MetalLB
Let’s integrate MetalLB into our Home Lab. Follow the Metallb installation guide, start the installation process:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.13.12/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
# Apply the MetalLB manifest
kca metallb-native.yaml
To implement advanced L2 configration, add the following in metallb-l2-advertisement.yaml:
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: L2Advertisement
metadata:
name: first-advert
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
ipAddressPools:
- first-pool
For a more advanced Address Pool configuration, add the following details to metallb-ip-address-pool.yaml:
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: first-pool
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
addresses:
- 192.168.68.220-192.168.68.240
MetalLB will assign the specified IP addresses upon applying these configurations:
kca metallb-l2-advertisement.yaml
kca metallb-ip-address-pool.yaml
Configuring Kong Services and Routes
Referencing from my previous posts on deploying llama-phi2-svc and localai-server-svc, here’s how I set them up:
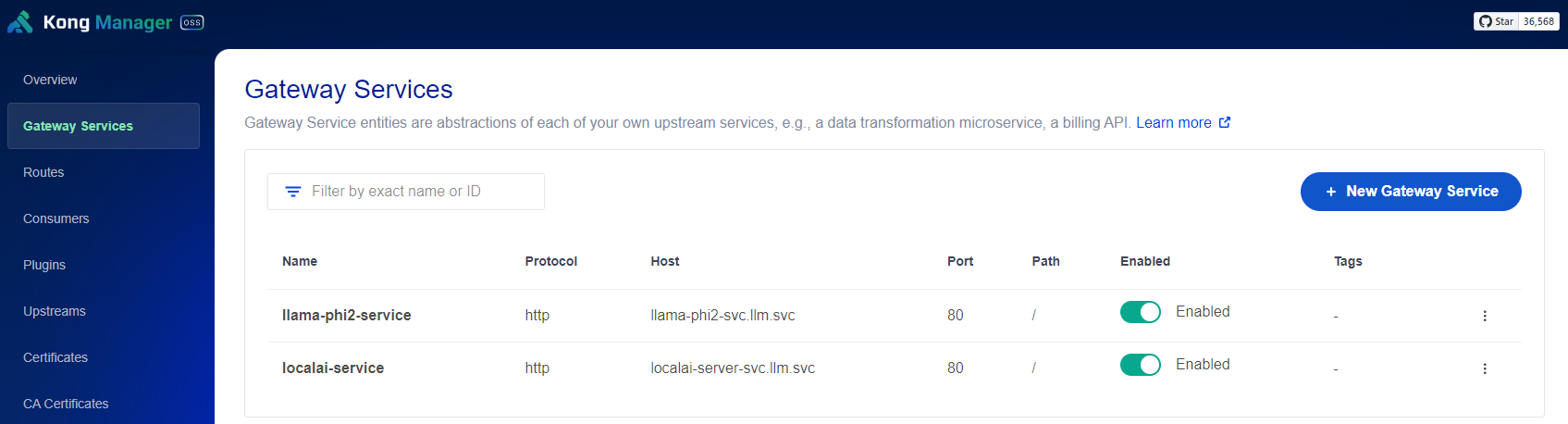
Setting up path-based routing rules:
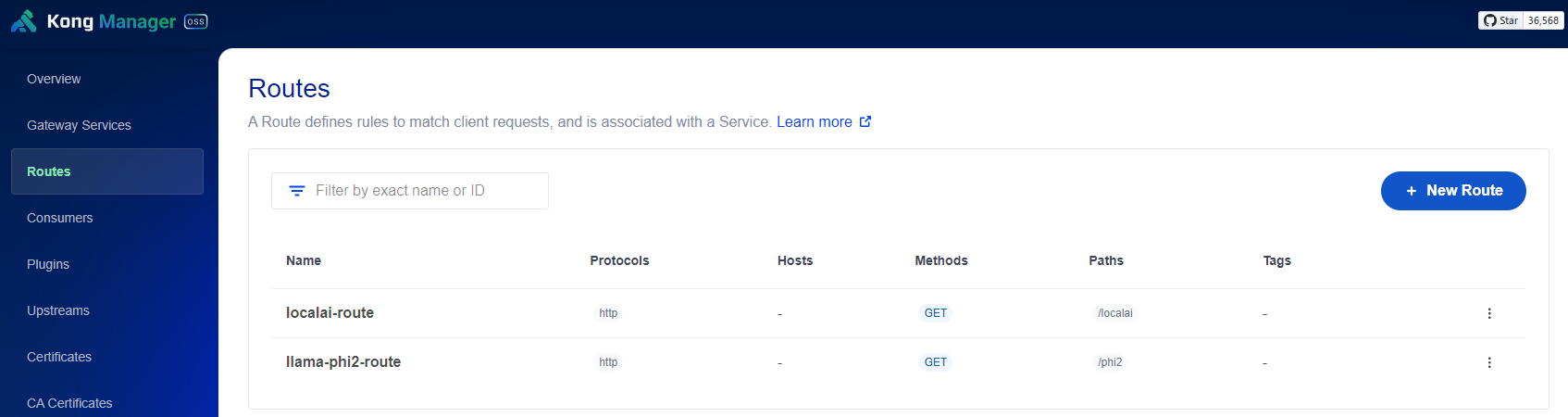
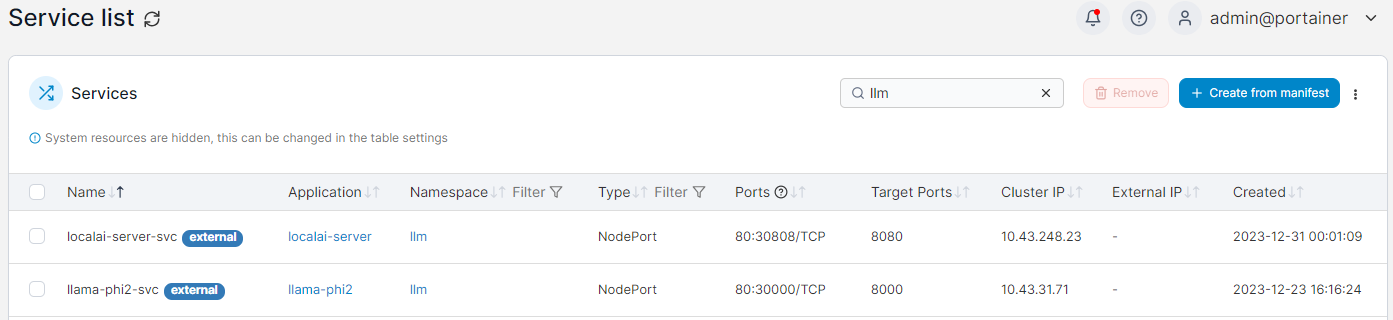
Viewing the Service list in Portainer:
Testing Path-Based Routes with Kong
For connecting to Microsoft’s Phi2 model, I configured api.local to point to 192.168.68.223:
curl http://api.local:8000/phi2/docs -i
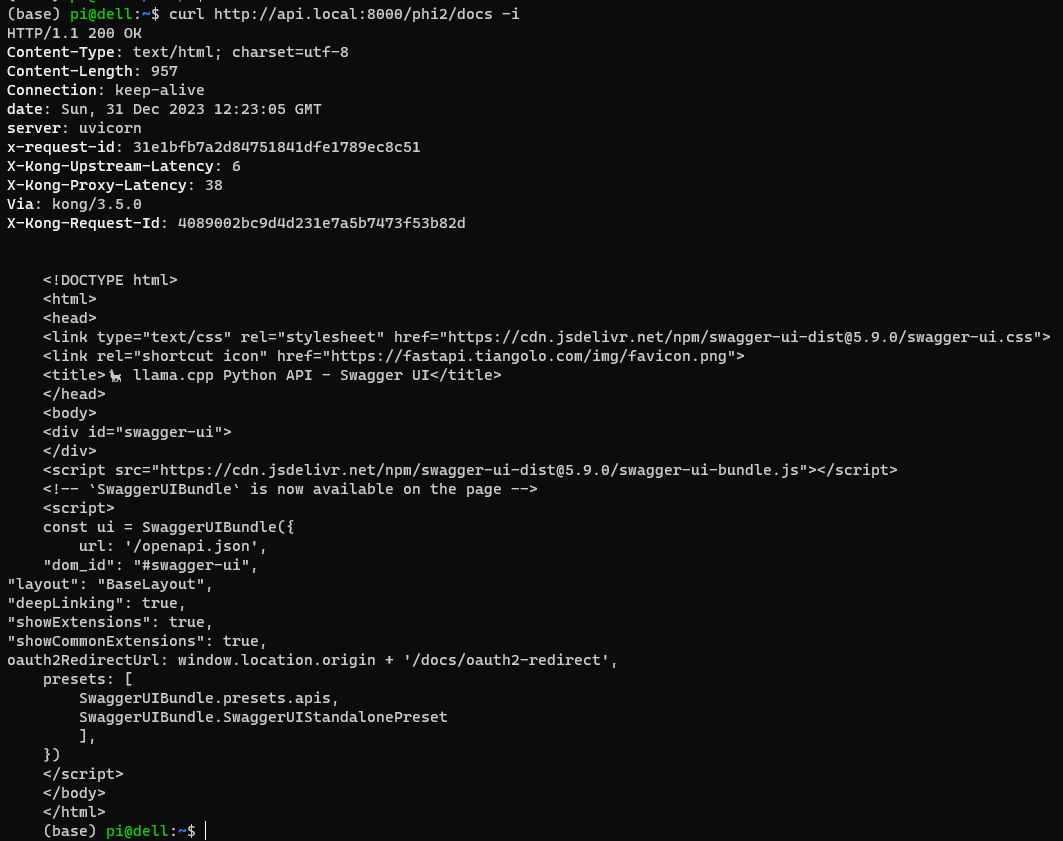
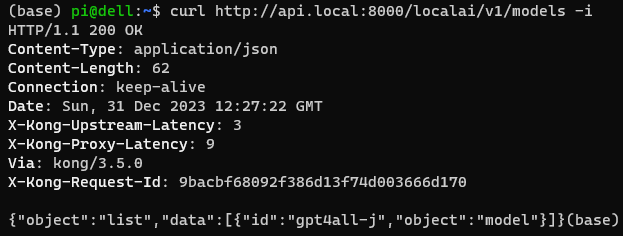
For connecting to the LocalAI bundled gpt4all-j model, use:
curl http://api.local:8000/localai/v1/models -i
Troubleshooting
If you’ve followed this post, you may have noticed the use of api.local:8000 instead. This is a result of the Kong setup configuration.

Feel free to make any adjustments according to your preferences!