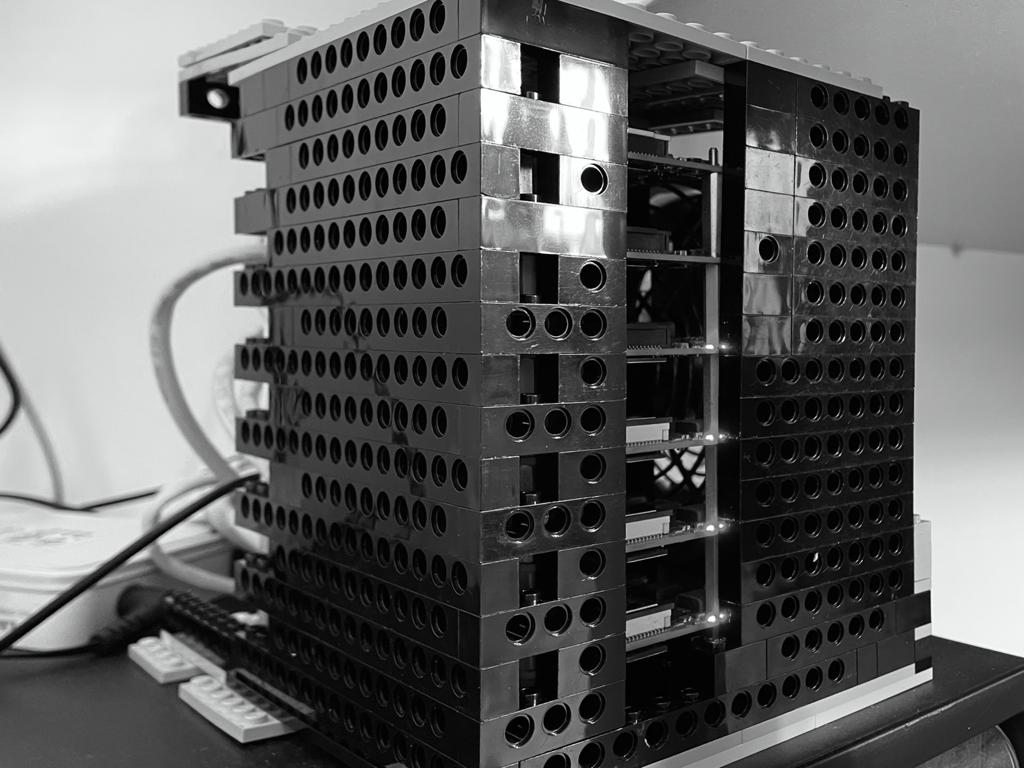

Building a CI/CD pipeline on a Raspberry PI Cluster, with 3 master and 1 worker nodes, enclosed in a custom-made LEGO structure
Building a CI/CD pipeline on a Raspberry PI Cluster (Part I)
(Total Setup Time: 40 mins)
In this series, I will build my own CI/CD pipeline, with tools that are configured to run on Raspberry PI Cluster and Longhorn, a HA Raspberry PI Cluster. By end of this guide, you will have a self-hosted Git service, working hand-in-hand with Jenkins.
Preparation
(5 mins)
Metallb is a load-balancer implementation for bare metal Kubernetes clusters. You may refer to the previous guide on Metallb. Let’s install it by with these commands:
mkdir ~/metallb
cd ~/metallb
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.9.3/manifests/namespace.yaml -O metallb-namespace.yaml
kubectl apply -f metallb-namespace.yaml
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.9.3/manifests/metallb.yaml -O metallb.yaml
kubectl apply -f metallb.yaml
kubectl create secret generic -n metallb-system memberlist --from-literal=secretkey="$(openssl rand -base64 128)"
This is my layer2 configuration, in metallb-config.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
address-pools:
- name: default
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.100.200-192.168.100.250
kubectl apply -f metallb-config.yaml
I create 4 volumes, namely mysql, gitea, jenkins and maven-agent, specific to each of the tools.
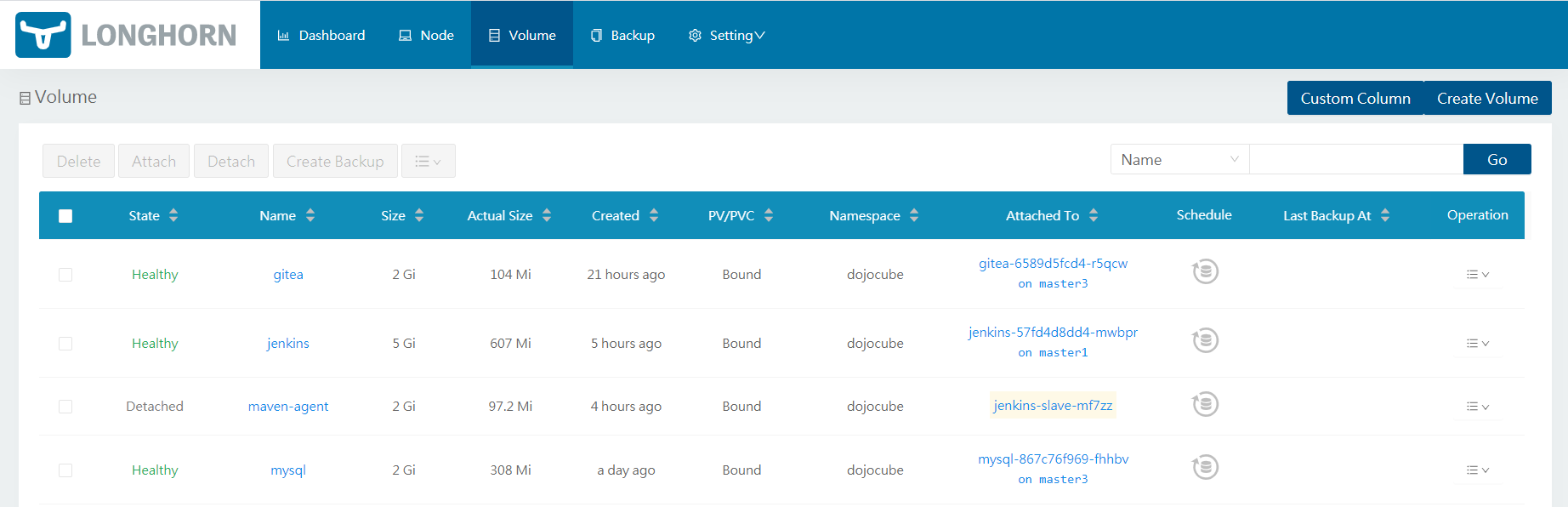
Installing Mysql
(5 mins)
Referencing Gitea for Kubernetes Cluster, these are the steps for installing Mysql.
kubectl create namespace seehiong
docker pull mysql/mysql-server:latest
mkdir ~/mysql
cd ~/mysql
vi mysql-deployment.yaml
# Insert below into mysql-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql
namespace:seehiong
spec:
ports:
- port: 3306
selector:
app: mysql
clusterIP: None
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mysql
namespace:seehiong
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mysql
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
hostname: mysql
containers:
- image: mysql/mysql-server:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: mysql
env:
# Use secret in real usage
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: password
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
name: mysql
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumes:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pvc
kubectl apply -f mysql-deployment.yaml
You may check on the pod ID and run the following scripts:
kubectl get pods -n seehiong
kubectl exec --namespace=seehiong -it mysql-6587f996b5-qrcr6 -- /bin/bash
mysql -u root -p
# Execute these within the docker prompt, with username=gitea, password=gitea, database=gitedb
CREATE USER 'gitea'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'gitea';
CREATE DATABASE giteadb;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON giteadb.* TO 'gitea';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Installing Gitea
(5 mins)
First, installs Gitea by running thse commands:
apt install docker-compose
mkdir ~/gitea
cd ~/gitea
vi docker-compose.yml
# Insert below into docker-compose.yml
version: "2"
networks:
gitea:
external: false
services:
server:
image: gitea/gitea:latest
environment:
- USER_UID=1000
- USER_GID=1000
- DB_TYPE=mysql
- DB_HOST=mysql:3306
- DB_NAME=giteadb
- DB_USER=gitea
- DB_PASSWD=gitea
restart: always
networks:
- gitea
volumes:
- ./gitea:/data
- /etc/timezone:/etc/timezone:ro
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
ports:
- "3000:3000"
- "222:22"
# Builds, starts and stops container
docker-compose up -d
docker-compose down
Second, creates the deployment file for Gitea:
vi gitea-deployment.yaml
# Insert below into gitea-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: gitea
namespace: seehiong
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip: home-net
spec:
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
nodePort: 30000
name: gitea-http
- port: 2222
targetPort: 2222
nodePort: 32222
name: gitea-ssh
selector:
app: gitea
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: 192.168.100.250
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: gitea
namespace: seehiong
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: gitea
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: gitea
spec:
hostname: gitea
containers:
- image: gitea/gitea:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: gitea
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
name: gitea-http
- containerPort: 22
name: gitea-ssh
volumeMounts:
- name: gitea-persistent-storage
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: gitea-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: gitea-pvc
kubectl apply -f gitea-deployment.yaml
kubectl get svc -n seehiong
Third, access to the configured url, i.e. 192.168.100.250:3000 and follows the gitea installation. For my case, the parameters are:
username: gitea
password: gitea
database: giteadb
Installing Jenkins
(5 mins)
By referencing Jenkins for Kuberenetes Cluster, the installation steps are:
mkdir ~/jenkins
cd ~/jenkins
vi Dockerfile
# Insert below into Dockerfile
FROM balenalib/raspberrypi4-64-debian-openjdk:11-bullseye
ENV JENKINS_HOME /var/jenkins_home
ENV JENKINS_SLAVE_AGENT_PORT 50000
RUN apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends curl git
RUN curl -fL -o /opt/jenkins.war http://updates.jenkins-ci.org/download/war/2.295/jenkins.war
VOLUME ${JENKINS_HOME}
WORKDIR ${JENKINS_HOME}
EXPOSE 8080 ${JENKINS_SLAVE_AGENT_PORT}
CMD ["/bin/bash","-c","java -jar /opt/jenkins.war"]
# Builds, tags the image
docker build -t seehiong/jenkins:1.0 .
Next, creates the Jenkins deployment file and deploys it to the cluster.
vi jenkins-deployment.yaml
# Insert below into jenkins-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: seehiong
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip: home-net
spec:
ports:
- port: 8080
name: jenkins-http
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 30080
- port: 50000
name: jenkins-slave
targetPort: 50000
selector:
app: jenkins
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: 192.168.100.250
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: seehiong
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: jenkins
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: jenkins
spec:
hostname: jenkins
containers:
- name: jenkins
image: seehiong/jenkins:1.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/jenkins_home
volumes:
- name: jenkins-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: jenkins-pvc
kubectl apply -f jenkins-deployment.yaml
kubectl get po -n seehiong
# Gets the pod ID, replace the following accordingly and retrieves the password
kubectl logs -n seehiong jenkins-6c6cb7d48c-pnnr5
Installing Maven-agent
(5 mins)
By referencing Jenkins Agent on Kubernetes Cluster, the steps to create a maven-agent are:
# Source
# https://hub.docker.com/r/jenkins/slave/dockerfile
FROM balenalib/raspberrypi4-64-debian-openjdk:11-bullseye
ARG VERSION=4.7
ARG user=jenkins
ARG group=jenkins
ARG uid=1000
ARG gid=1000
# Modified for debian-bullseye
RUN groupadd -g ${gid} ${group}
RUN useradd -d /home/${user} -u ${uid} -g ${group} -m ${user}
LABEL Description="This is a base image, which provides the Jenkins agent executable (slave.jar)" Vendor="Jenkins project" Version="${VERSION}"
ARG AGENT_WORKDIR=/home/${user}/agent
# Modified for debian-bullseye
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl bash git git-lfs openssh-client openssl procps \
&& curl --create-dirs -fsSLo /usr/share/jenkins/agent.jar https://repo.jenkins-ci.org/public/org/jenkins-ci/main/remoting/${VERSION}/remoting-${VERSION}.jar \
&& chmod 755 /usr/share/jenkins \
&& chmod 644 /usr/share/jenkins/agent.jar \
&& ln -sf /usr/share/jenkins/agent.jar /usr/share/jenkins/slave.jar \
&& apt-get remove -y curl
USER ${user}
ENV AGENT_WORKDIR=${AGENT_WORKDIR}
RUN mkdir /home/${user}/.jenkins && mkdir -p ${AGENT_WORKDIR}
VOLUME /home/${user}/.jenkins
VOLUME ${AGENT_WORKDIR}
WORKDIR /home/${user}
# Source
# https://hub.docker.com/r/jenkins/inbound-agent/dockerfile
USER ${user}
COPY jenkins-agent /usr/share/jenkins/jenkins-agent
USER root
COPY jenkins-agent /usr/local/bin/jenkins-agent
RUN chmod +x /usr/local/bin/jenkins-agent \
&& ln -s /usr/local/bin/jenkins-agent /usr/local/bin/jenkins-slave
USER ${user}
ENTRYPOINT ["jenkins-agent"]
Next, copies the content of jenkins-agent and pastes it into a file (COPY command will copy this file into the docker image).
docker build -t seehiong/jenkins-agent:1.0 .
# Checks Java version
docker run -it seehiong/jenkins-agent:1.0 /bin/bash
java -version
Configuring Jenkins - Kubernetes
(5 mins)
First, navigates to the configured url, i.e. 192.168.100.250:8080. Installs the recommended commonly used plugins.
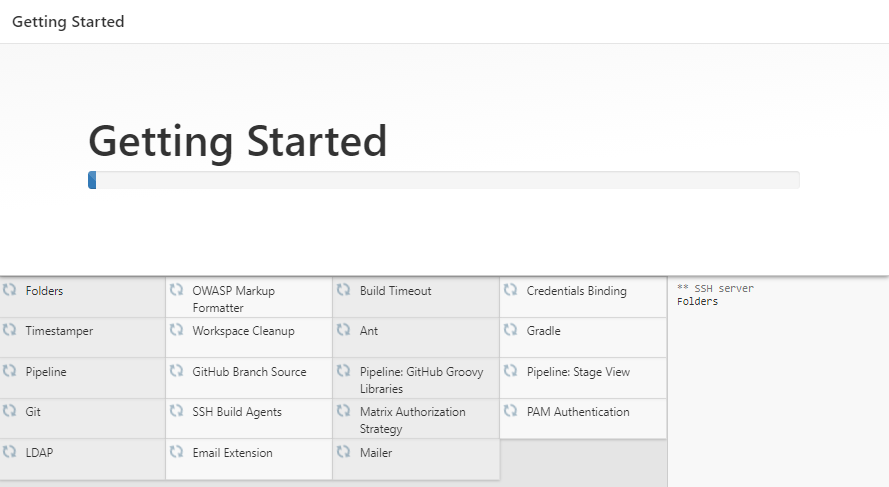
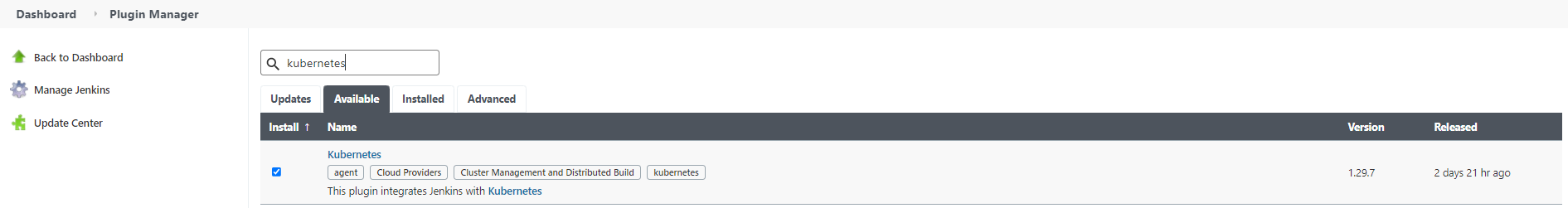
Second, installs Kuberenetes and Gitea plugin:
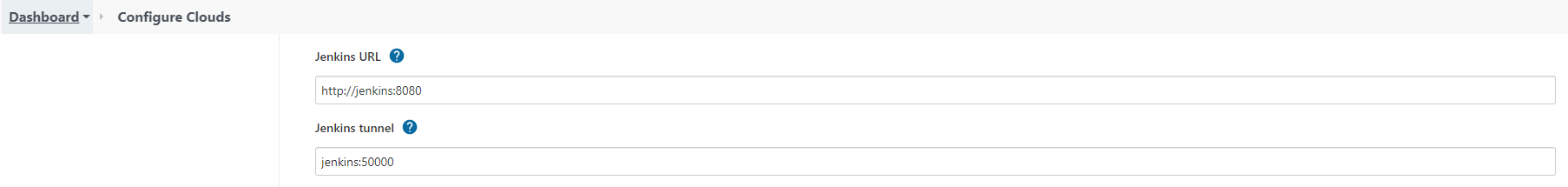
Third, navigates to Manage Jenkins > Manage Nodes and Cloud > Configure Clouds. Selects Kuberenetes, clicks on the Kuberenetes Cloud Details and tests the connection. Enters Jenkins url:
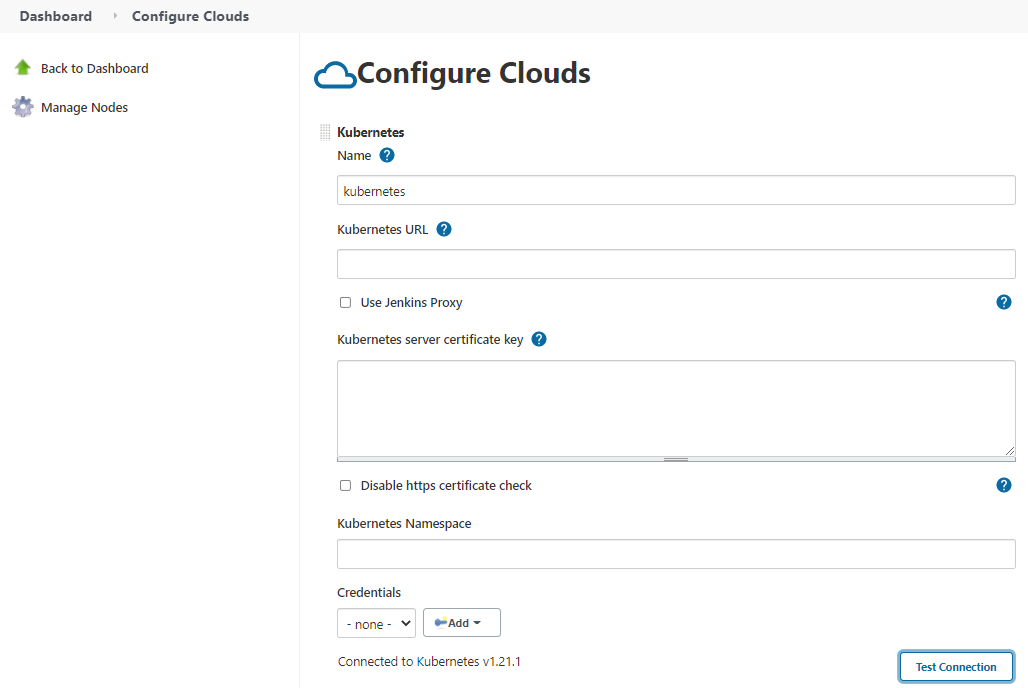
You may setup the Jenkins URL with:
Jenkins URL: http://jenkins:8080
jenkins tunnel: jenkins:50000
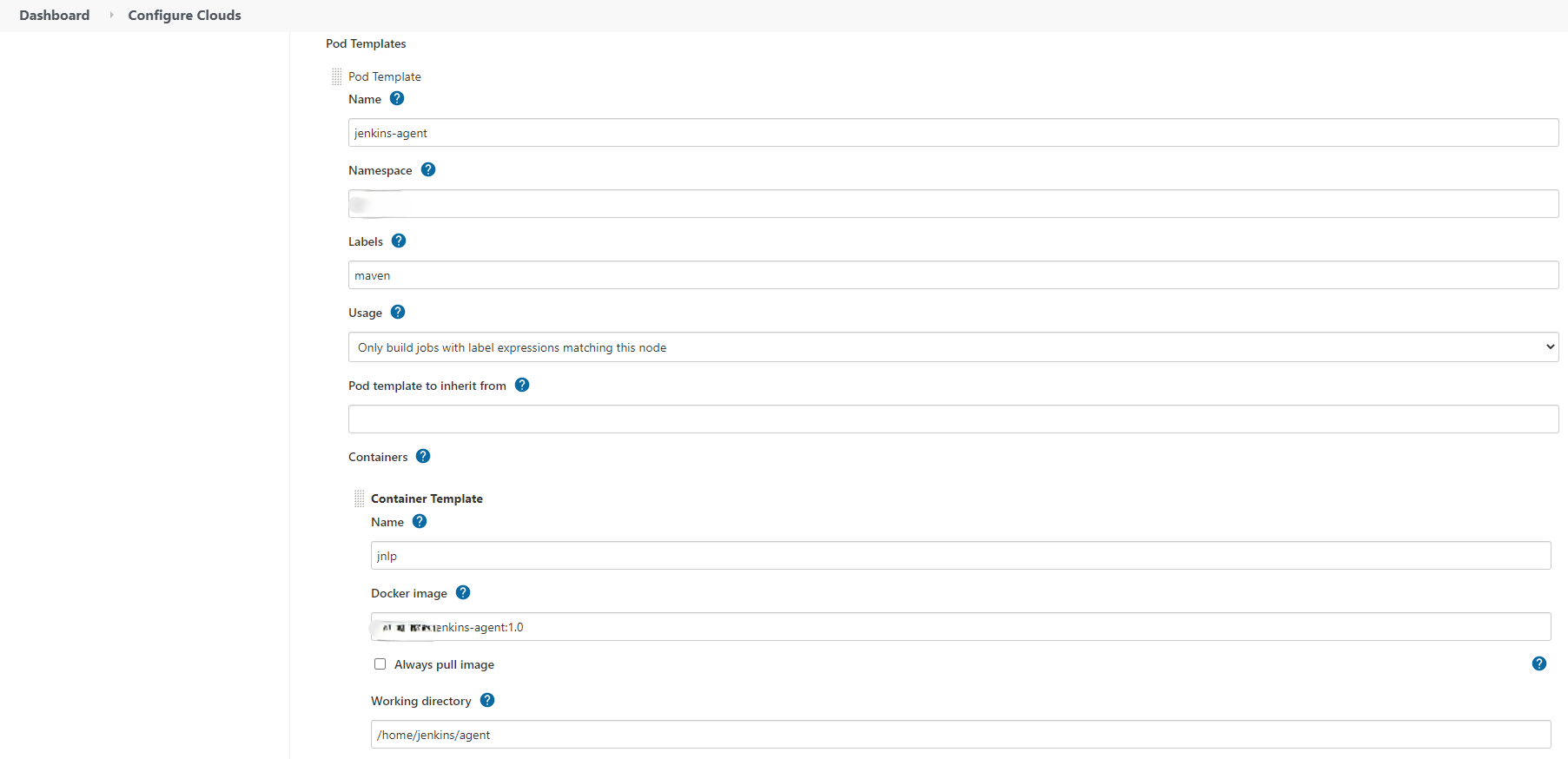
Fourth, configures the pod template:
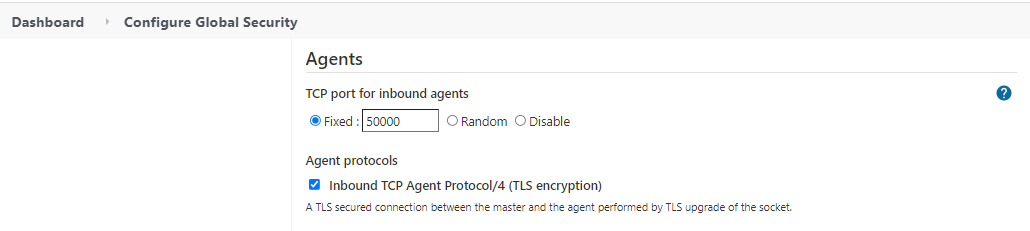
Lastly, navigates to Manage Jenkins -> Configure Global Security. Enters the Agent values:
Configuring Jenkins - Gitea
(5 mins)
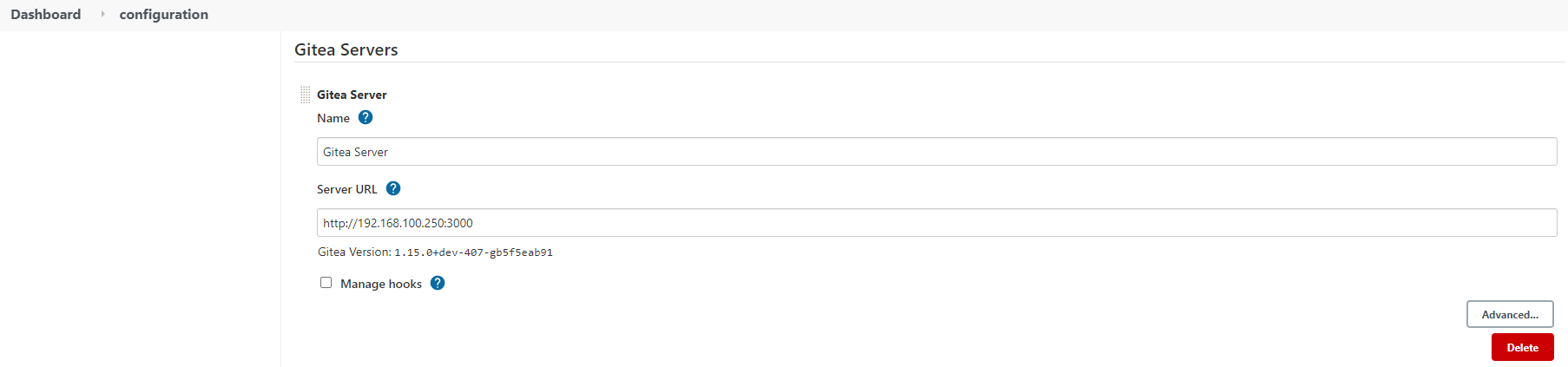
First, navigates to Manage Jenkins > Configure System. Adds Gitea erver:
Second, creates a new seehiong Gitea Organization. Configures the Jenkins Credentials and Projects under the General tab.
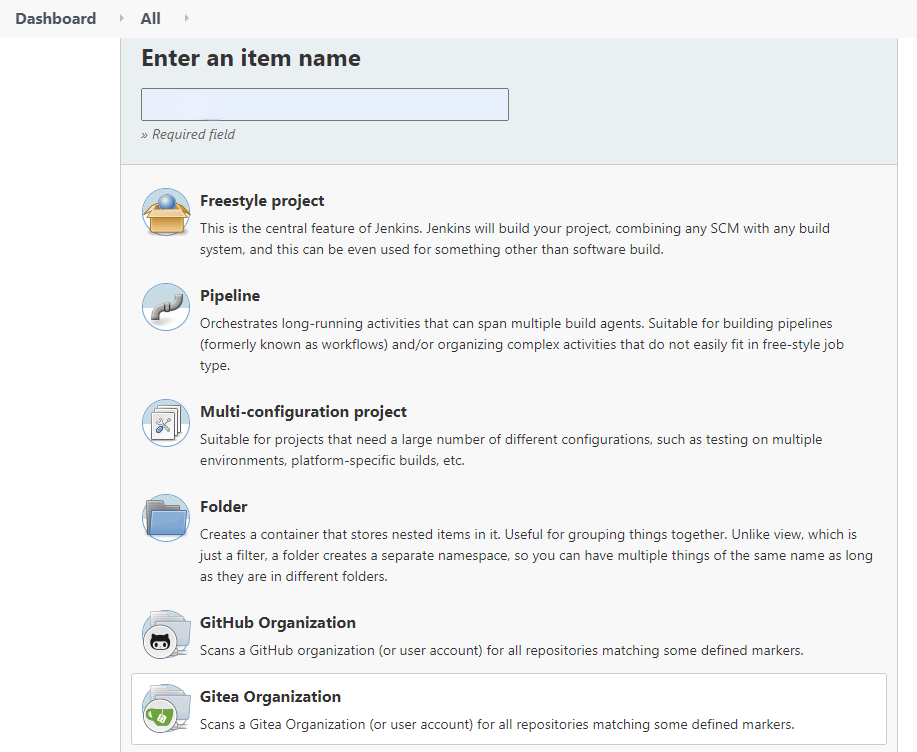
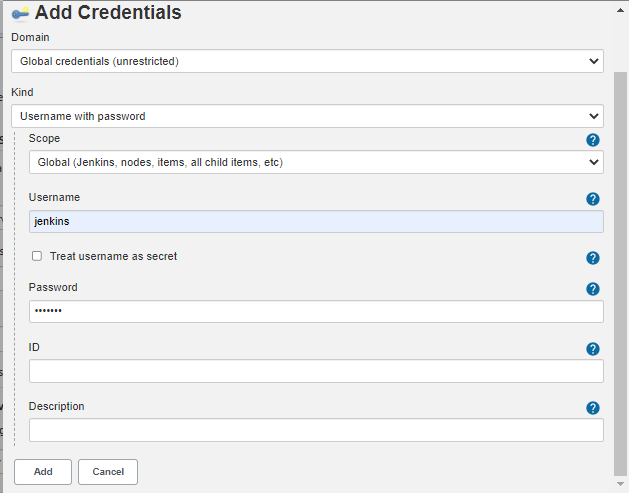
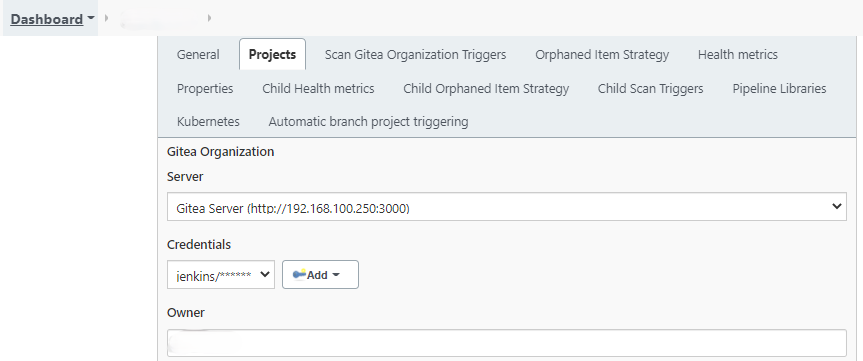
Integrating Jenkins and Gitea
(5 mins)
By referencing Integration between Jenkins and Gitea, adds a new seehiong organization. Then, creates a Jenkins user in Gitea and adds as collaborators.
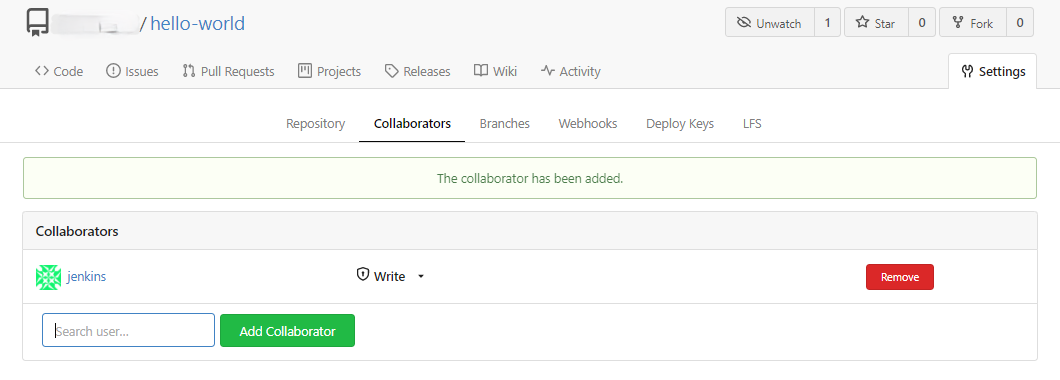
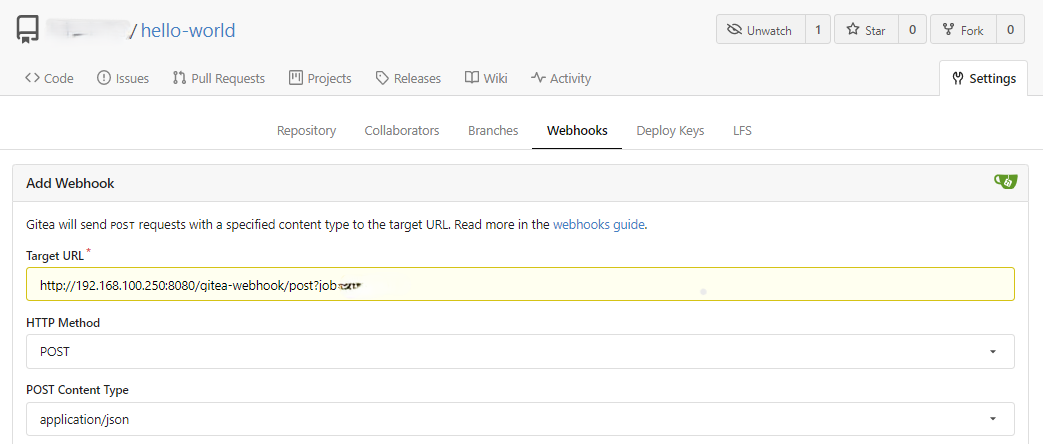
Next, adds Gitea webhooks to Jenkins and tests the delivery.
In Action
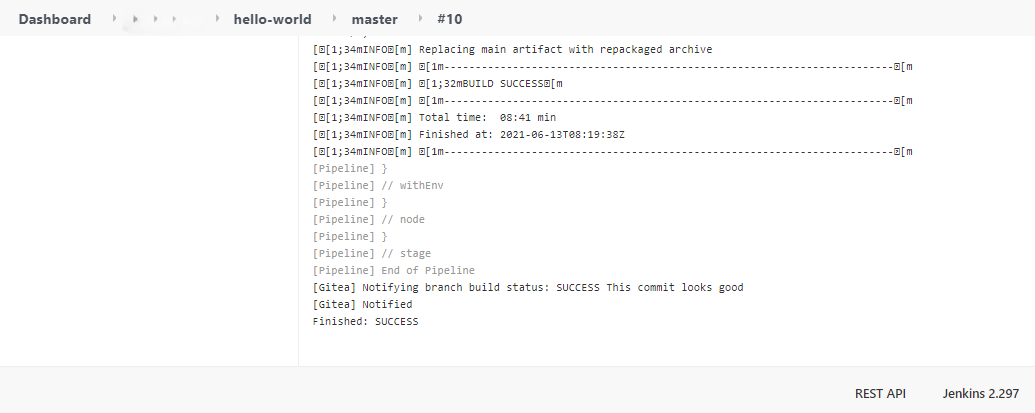
Finally, if you followed through the steps diligently, building a CI/CD pipeline on a Raspberry PI Cluster is completed. When you commit any code, it triggers the CI pipeline. Maven-agent will build and compile your code.
Troubleshooting
Error testing connection : Failure executing: GET at: https://10.96.0.1/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods. Message: Forbidden!Configured service account doesn’t have access. Service account may have been revoked.
When testing connection at Kuberenetes Cloud setting, the above error appears. You may fix by:
cd ~/jenkins
vi jenkins-rbac.yaml
# Insert below into jenkins-rbac.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: jenkins-rbac
namespace: seehiong
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: seehiong
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kubectl apply -f jenkins-rbac.yaml
Cannot find Jenkins password in /var/jenkins/home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Depending on your configuration, you may find the initialAdminPassword
docker ps
docker logs 90494de7c46d #Container ID
kubectl get po -n seehiong
kubectl logs -n seehiong jenkins-57fd4d8dd4-mwbpr #Pod Name
Upgrading Jenkins version
For upgrading Jenkins version, the permanent fix is to modify jenkins/Dockerfile
# Find the jenkins.war file and modify the version to the latest
RUN curl -fL -o /opt/jenkins.war http://updates.jenkins-ci.org/download/war/2.297/jenkins.war
docker build -t seehiong/jenkins:1.0 .
/home/jenkins/agent/workspace/seehiong_hello-world_master@tmp/durable-5d2c75ea/script.sh: 1: ./mvnw: Permission denied
You may check the mvnw file in your project and changes the file permission accordingly.
chmod +x mvnw
# Adds and pushes change to gitea
git update-index --chmod=+x mvnw