Expanding on my previous post on Kubeflow, I will explore KServe, a standard Model Inference Platform on Kubernetes built for highly scalable use cases.
First KServe Endpoint
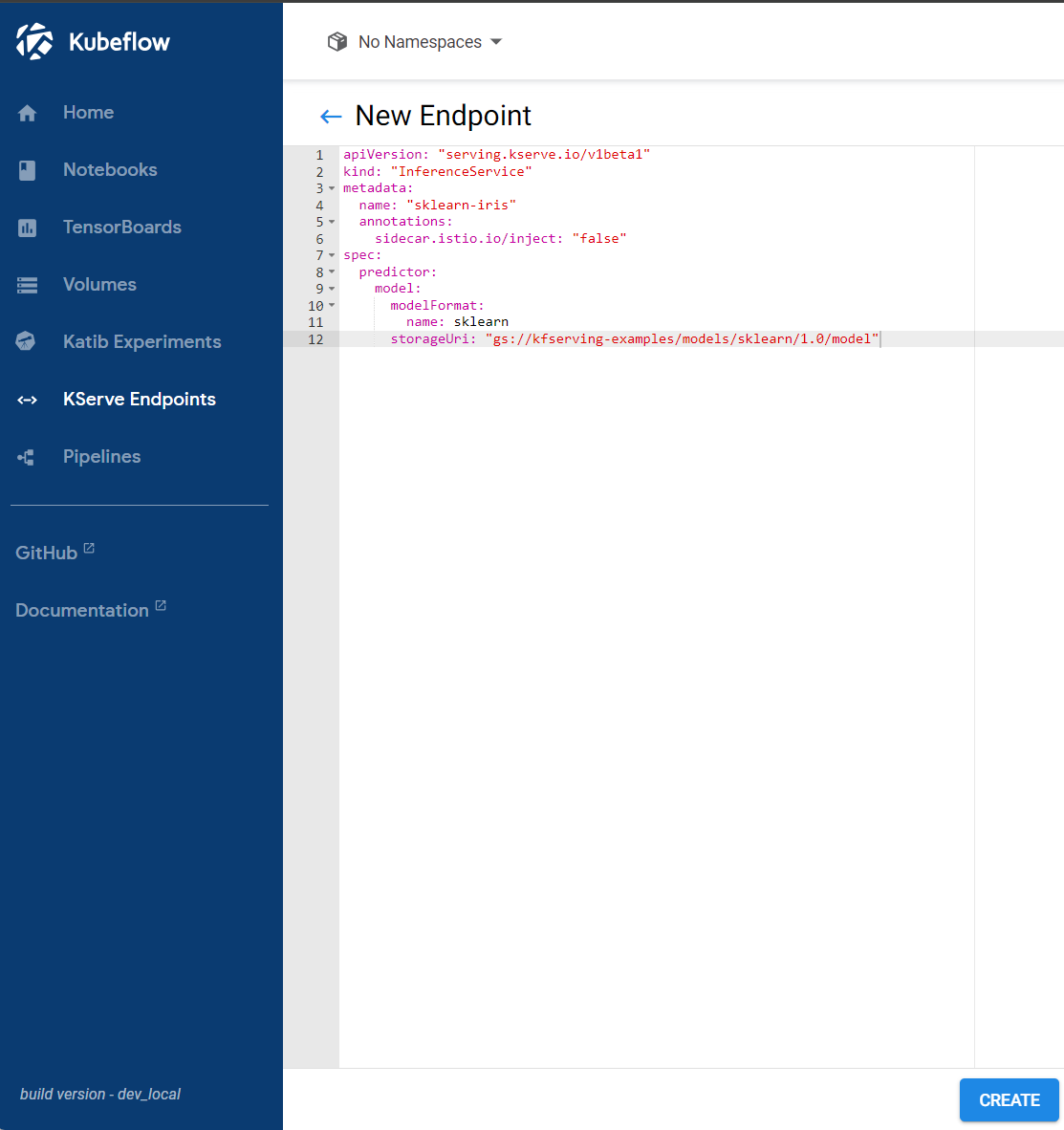
Referencing KServe on Kubeflow with Istio-Dex, below is the sklearn.yaml configuration. Note the sidecar annotation, which instructs not to inject the istio sidecar. Without this annotation, you may encounter error (refer to the troubleshooting section):
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "sklearn-iris"
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
predictor:
model:
modelFormat:
name: sklearn
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/sklearn/1.0/model"
From the Kubeflow dashboard, navigate to KServe Endpoints, click on the New Endpoint button on the top right, and input the above configuration:
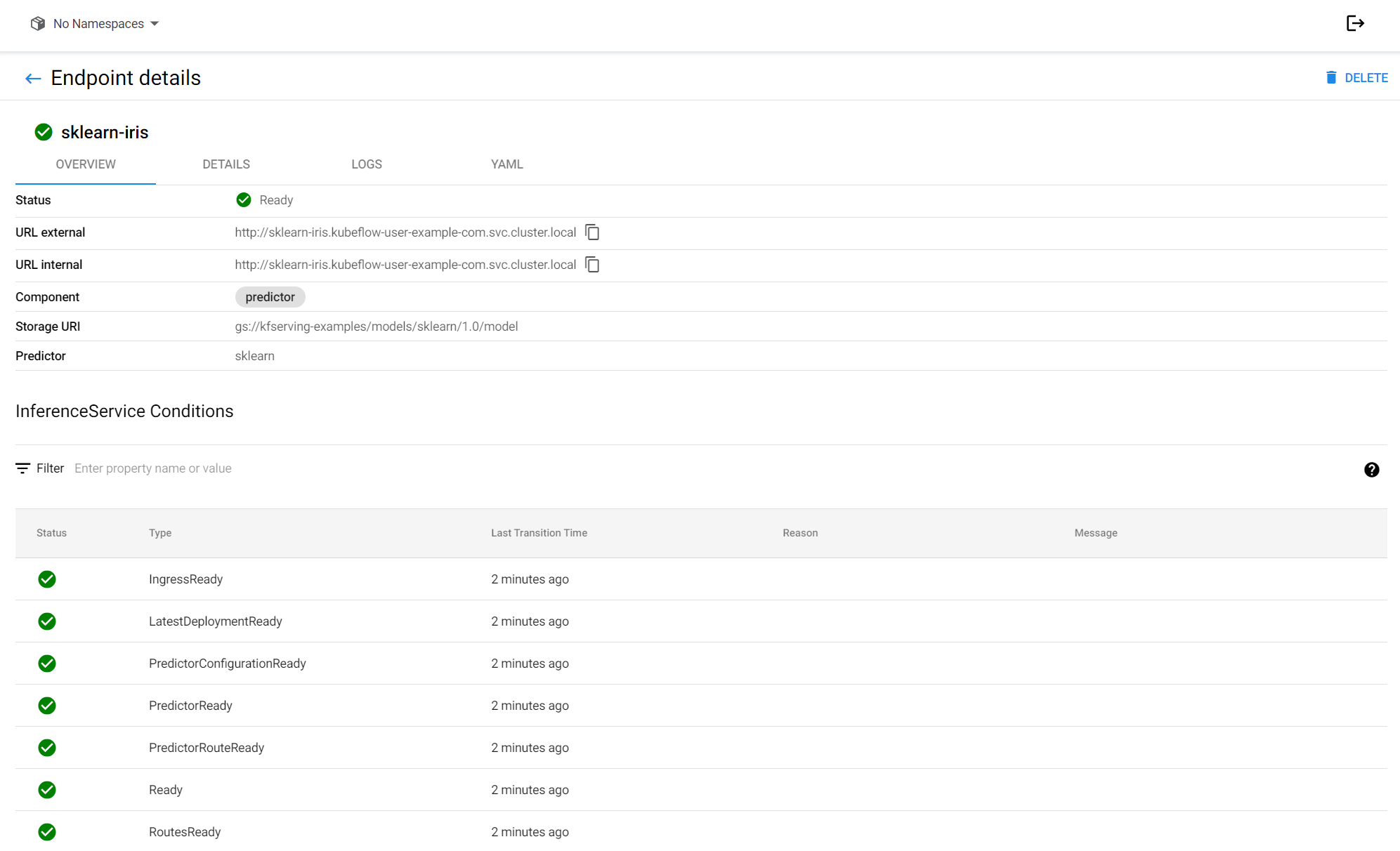
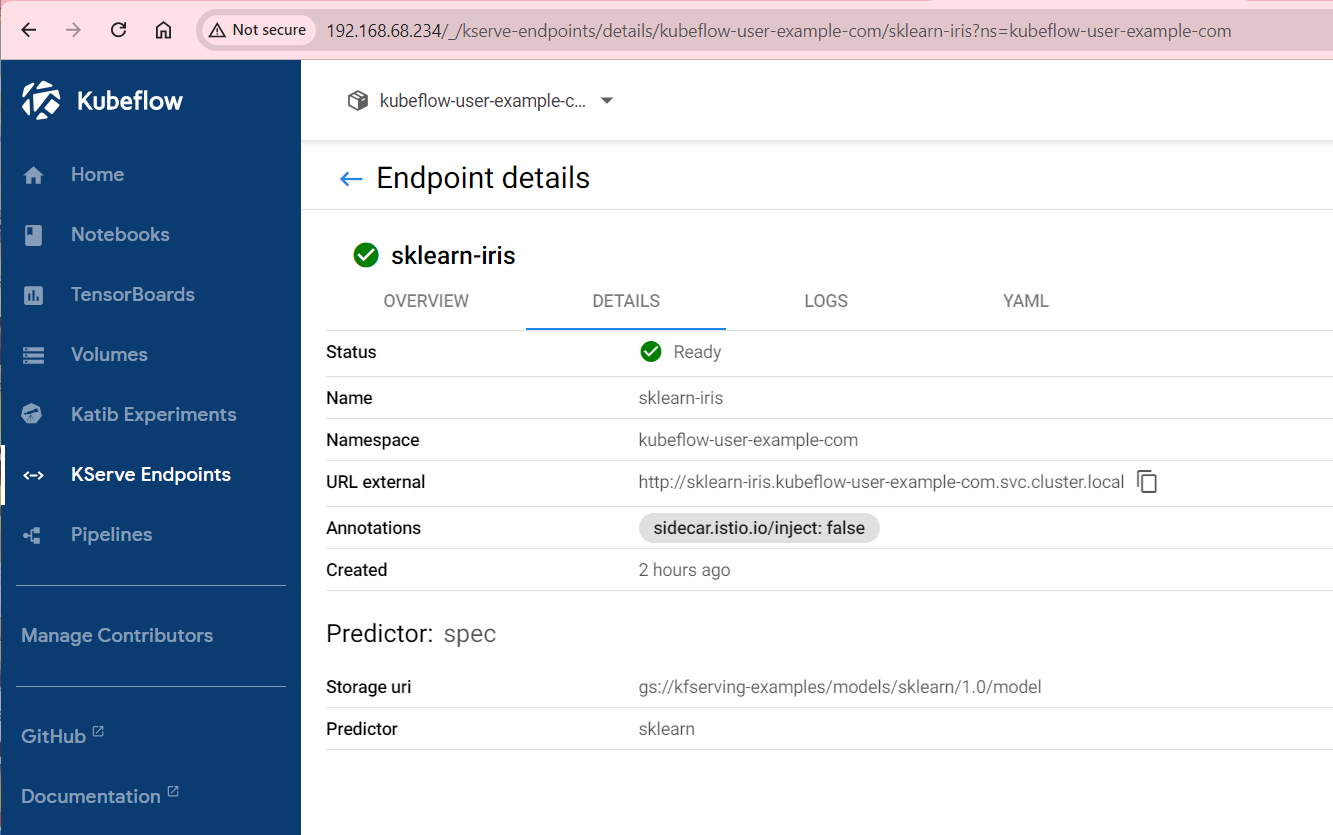
Here is the overview of the sklearn-iris endpoint:
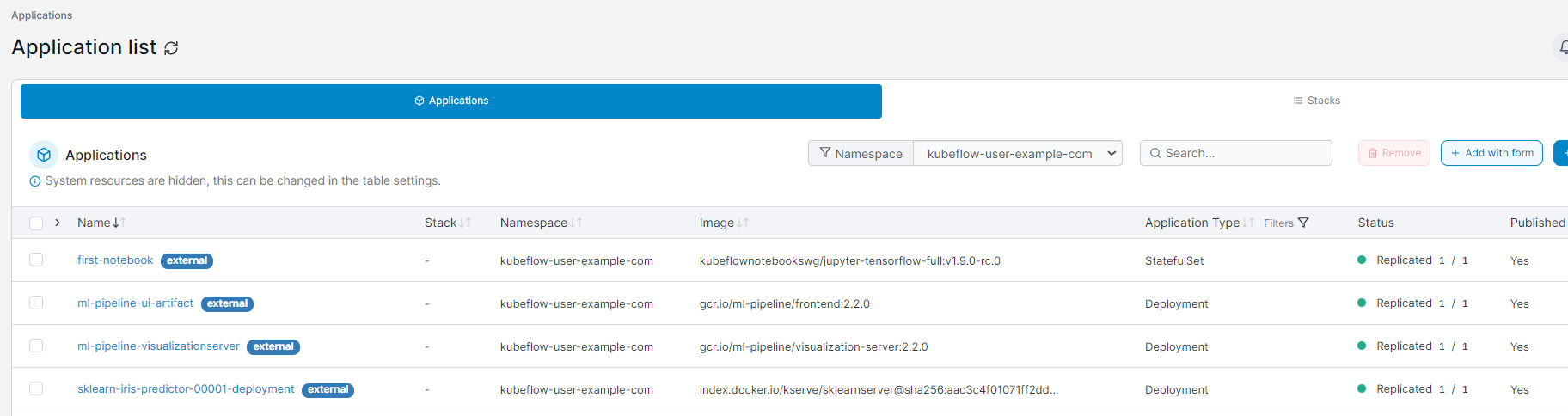
And its corresponding Kubernetes deployment:
First Prediction
Using the dex_auth.py, input the following into your first notebook:
import re
from urllib.parse import urlsplit
import requests
def get_istio_auth_session(url: str, username: str, password: str) -> dict:
"""
Determine if the specified URL is secured by Dex and try to obtain a session cookie.
WARNING: only Dex `staticPasswords` and `LDAP` authentication are currently supported
(we default to using `staticPasswords` if both are enabled)
:param url: Kubeflow server URL, including protocol
:param username: Dex `staticPasswords` or `LDAP` username
:param password: Dex `staticPasswords` or `LDAP` password
:return: auth session information
"""
# define the default return object
auth_session = {
"endpoint_url": url, # KF endpoint URL
"redirect_url": None, # KF redirect URL, if applicable
"dex_login_url": None, # Dex login URL (for POST of credentials)
"is_secured": None, # True if KF endpoint is secured
"session_cookie": None, # Resulting session cookies in the form "key1=value1; key2=value2"
}
# use a persistent session (for cookies)
with requests.Session() as s:
################
# Determine if Endpoint is Secured
################
resp = s.get(url, allow_redirects=True)
if resp.status_code != 200:
raise RuntimeError(
f"HTTP status code '{resp.status_code}' for GET against: {url}"
)
auth_session["redirect_url"] = resp.url
# if we were NOT redirected, then the endpoint is UNSECURED
if len(resp.history) == 0:
auth_session["is_secured"] = False
return auth_session
else:
auth_session["is_secured"] = True
################
# Get Dex Login URL
################
redirect_url_obj = urlsplit(auth_session["redirect_url"])
# if we are at `/auth?=xxxx` path, we need to select an auth type
if re.search(r"/auth$", redirect_url_obj.path):
#######
# TIP: choose the default auth type by including ONE of the following
#######
# OPTION 1: set "staticPasswords" as default auth type
redirect_url_obj = redirect_url_obj._replace(
path=re.sub(r"/auth$", "/auth/local", redirect_url_obj.path)
)
# OPTION 2: set "ldap" as default auth type
# redirect_url_obj = redirect_url_obj._replace(
# path=re.sub(r"/auth$", "/auth/ldap", redirect_url_obj.path)
# )
# if we are at `/auth/xxxx/login` path, then no further action is needed (we can use it for login POST)
if re.search(r"/auth/.*/login$", redirect_url_obj.path):
auth_session["dex_login_url"] = redirect_url_obj.geturl()
# else, we need to be redirected to the actual login page
else:
# this GET should redirect us to the `/auth/xxxx/login` path
resp = s.get(redirect_url_obj.geturl(), allow_redirects=True)
if resp.status_code != 200:
raise RuntimeError(
f"HTTP status code '{resp.status_code}' for GET against: {redirect_url_obj.geturl()}"
)
# set the login url
auth_session["dex_login_url"] = resp.url
################
# Attempt Dex Login
################
resp = s.post(
auth_session["dex_login_url"],
data={"login": username, "password": password},
allow_redirects=True,
)
if len(resp.history) == 0:
raise RuntimeError(
f"Login credentials were probably invalid - "
f"No redirect after POST to: {auth_session['dex_login_url']}"
)
# store the session cookies in a "key1=value1; key2=value2" string
auth_session["session_cookie"] = "; ".join(
[f"{c.name}={c.value}" for c in s.cookies]
)
auth_session["authservice_session"] = s.cookies.get("authservice_session")
return auth_session
To determine the cluster IP, use this command:
CLUSTER_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}')
echo $CLUSTER_IP

Next, in the notebook, enter the following:
import requests
KUBEFLOW_ENDPOINT = "http://10.43.239.213" # Cluster or LoadBalancer IP and port
KUBEFLOW_USERNAME = "user@example.com"
KUBEFLOW_PASSWORD = "12341234"
MODEL_NAME = "sklearn-iris"
SERVICE_HOSTNAME = "sklearn-iris.kubeflow-user-example-com.svc.cluster.local"
PREDICT_ENDPOINT = f"{KUBEFLOW_ENDPOINT}/v1/models/{MODEL_NAME}:predict"
iris_input = {"instances": [[6.8, 2.8, 4.8, 1.4], [6.0, 3.4, 4.5, 1.6]]}
_auth_session = get_istio_auth_session(
url=KUBEFLOW_ENDPOINT, username=KUBEFLOW_USERNAME, password=KUBEFLOW_PASSWORD
)
print(_auth_session)
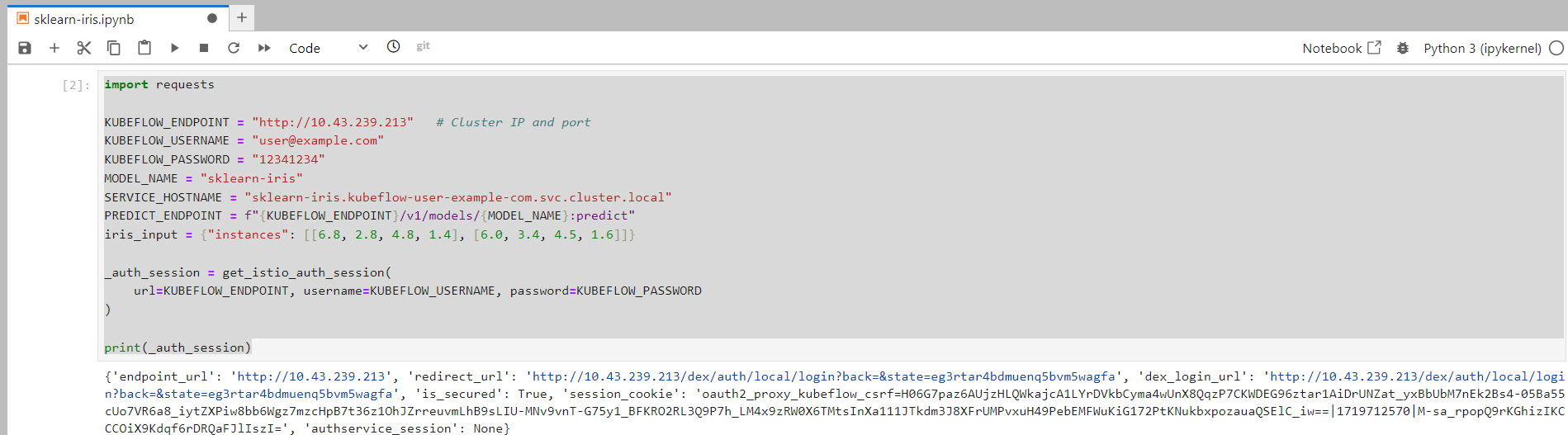
Finally, in the last cell, input the following:
cookies = {"authservice_session": _auth_session['authservice_session']}
jar = requests.cookies.cookiejar_from_dict(cookies)
res = requests.post(
url=PREDICT_ENDPOINT,
headers={"Host": SERVICE_HOSTNAME, "Content-Type": "application/json"},
cookies=jar,
json=iris_input,
timeout=200,
)
print("Status Code: ", res.status_code)
print("Response: ", res.json())

This is the log:
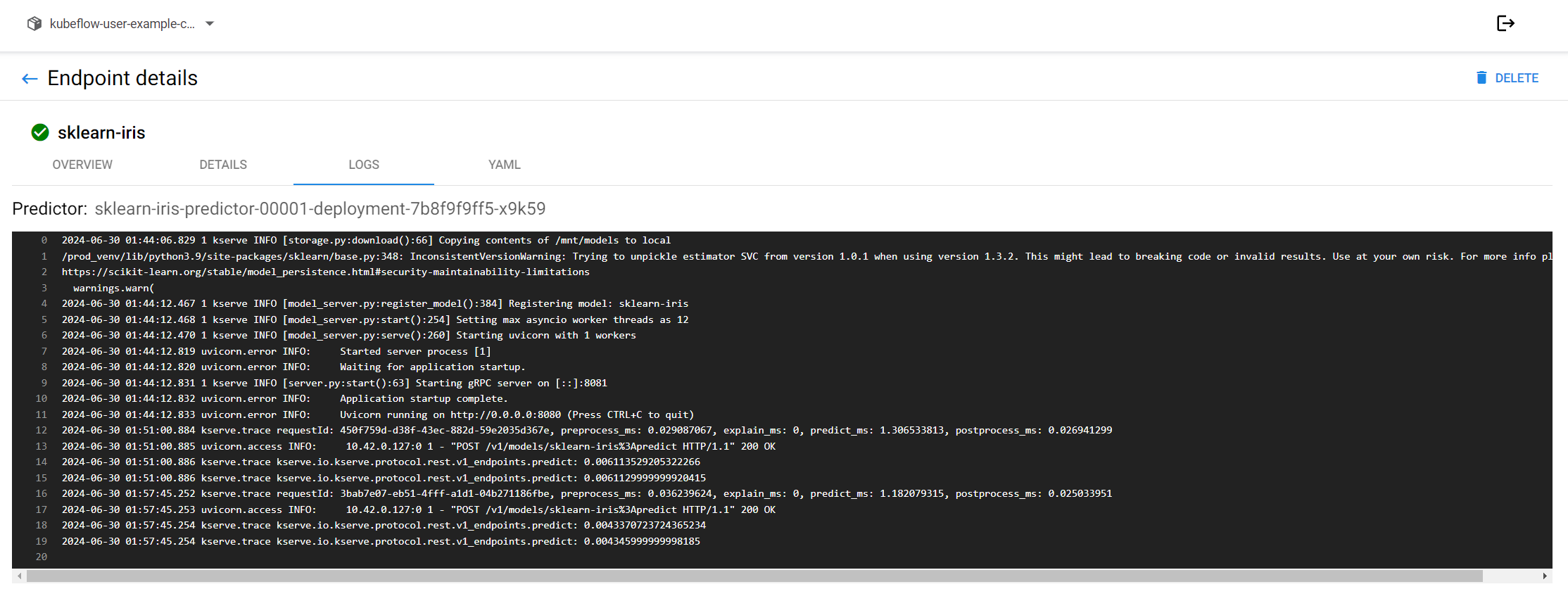
And that’s it! We see the expected two predictions returned (i.e. {“predictions”: [1, 1]}).
Optional - Load Balancer
In this section, referencing my previous post on MetalLB, we will install MetalLB.
# Apply the required MetalLB manifests
kca metallb-native.yaml
kca metallb-l2-advertisement.yaml
kca metallb-ip-address-pool.yaml
Next, change the service type from ClusterIP to LoadBalacer in the common/istio-1-22/istio-install/base/patches/service.yaml file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: istio-ingressgateway
namespace: istio-system
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
This is the istio-system namespace:
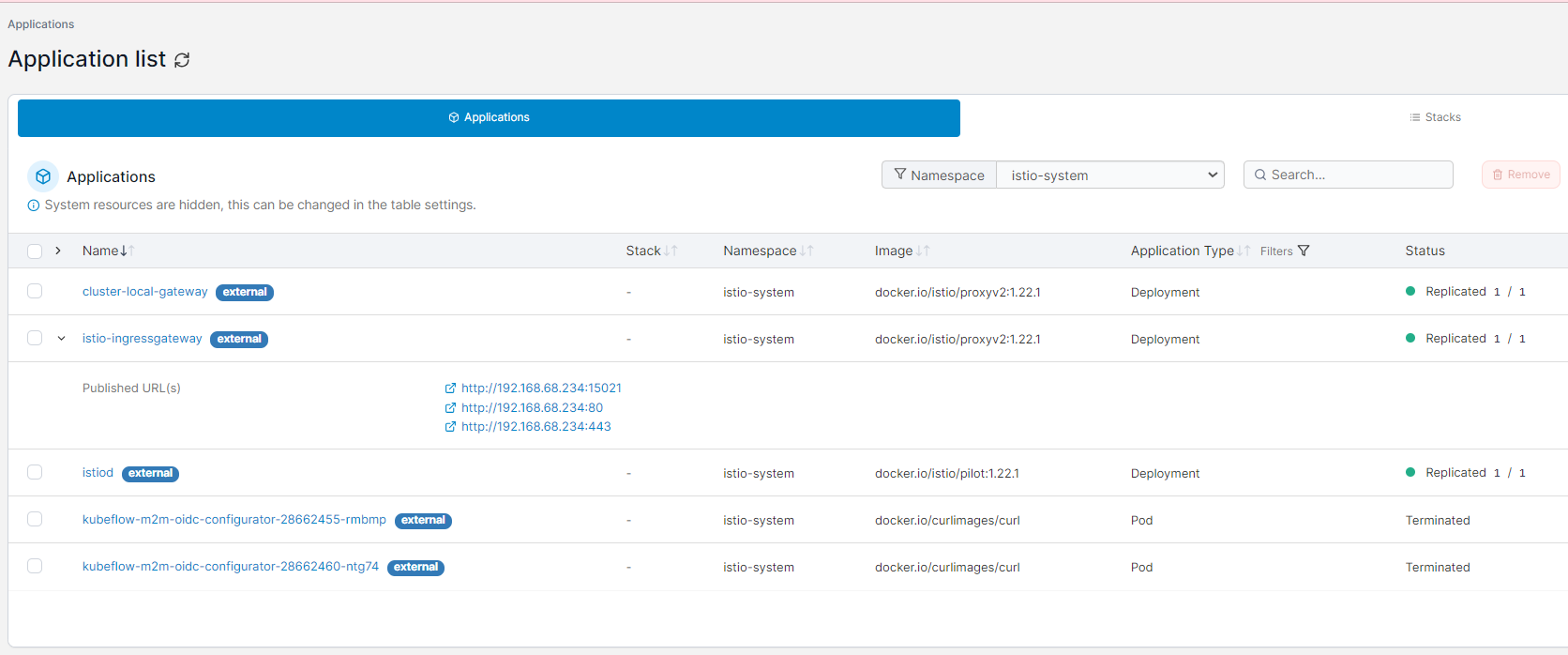
With this configuration, you can now access Kubeflow directly via http://192.168.68.234/ without using the port-forward command:
Optional - Integrate with GitLab
After organising your notebooks, such as into a first-notebook, you can commit them to GitLab by opening a terminal. Alternatively, you may use the built-in jupyterlab-git UI for a more visual approach.
Initialise Environment
Set global Git settings as follows:
git config --global --add safe.directory /home/jovyan
git config --global user.email "seehiong@xxxxxx.xxx"
git config --global user.name "seehiong.local"
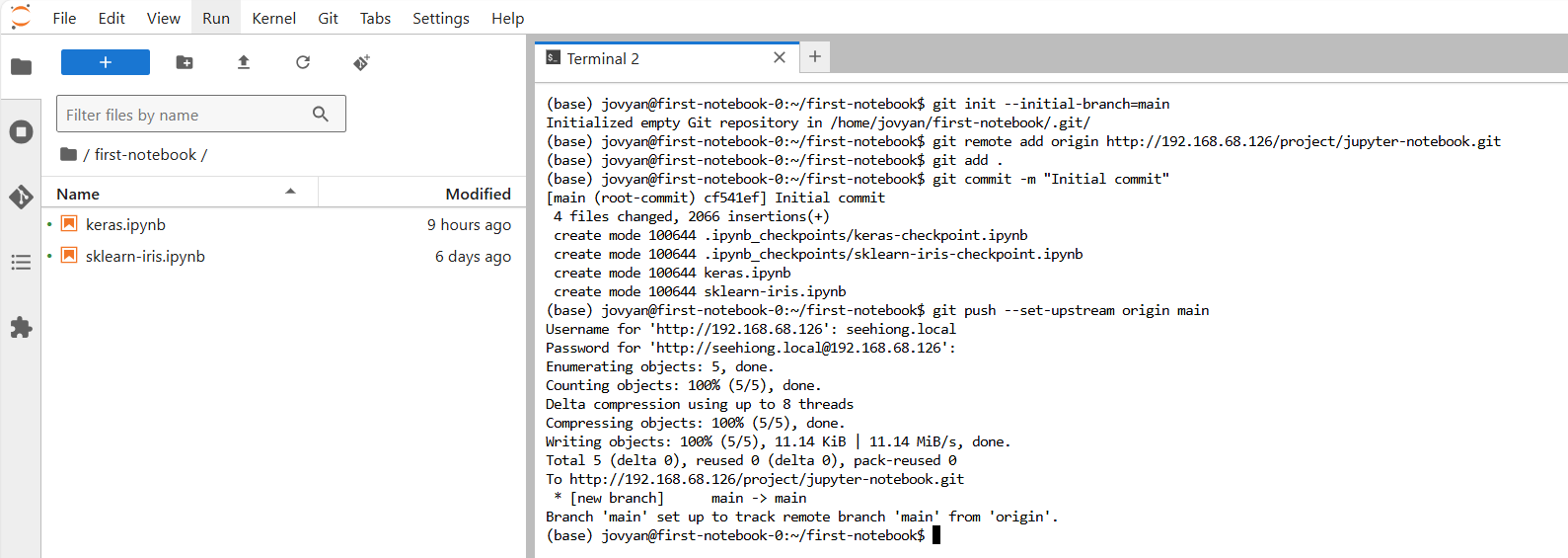
After creating the project in GitLab, commit the code:
git init --initial-branch=main
git remote add origin http://192.168.68.126/project/jupyter-notebook.git
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit"
git push --set-upstream origin main
After entering your username and password, your first commit to GitLab is complete!
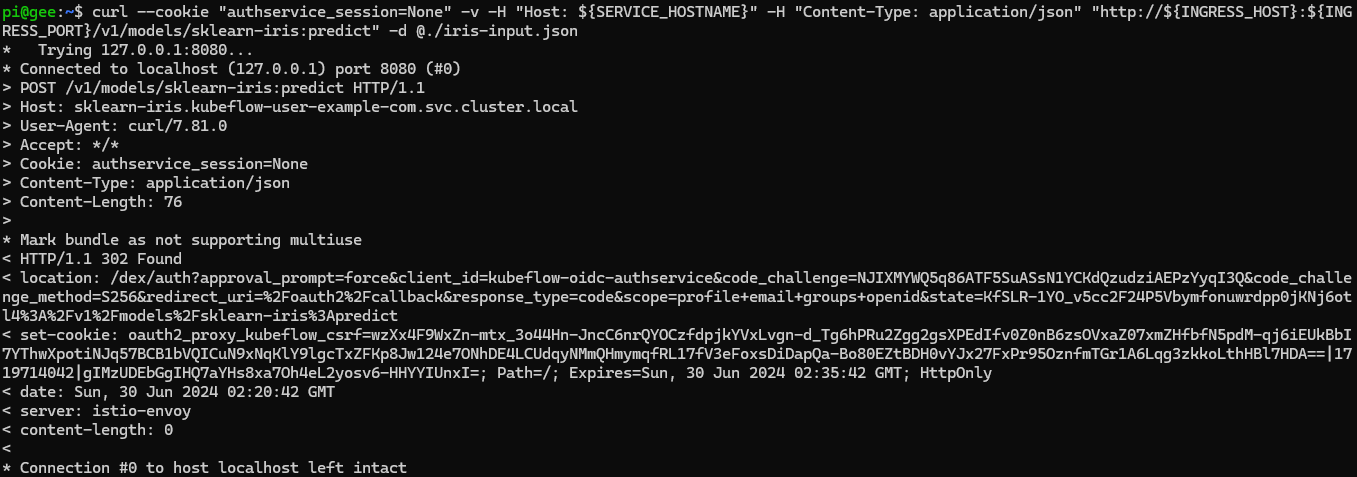
Troubleshooting
KServe sklearn-iris 302 Found issue
In my setup, if I follow the official First InferenceService, the above python scripts will not work. Below is the schema from the official link:
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "sklearn-iris"
spec:
predictor:
model:
modelFormat:
name: sklearn
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/sklearn/1.0/model"
And the iris-input.json file:
{
"instances": [
[6.8, 2.8, 4.8, 1.4],
[6.0, 3.4, 4.5, 1.6]
]
}
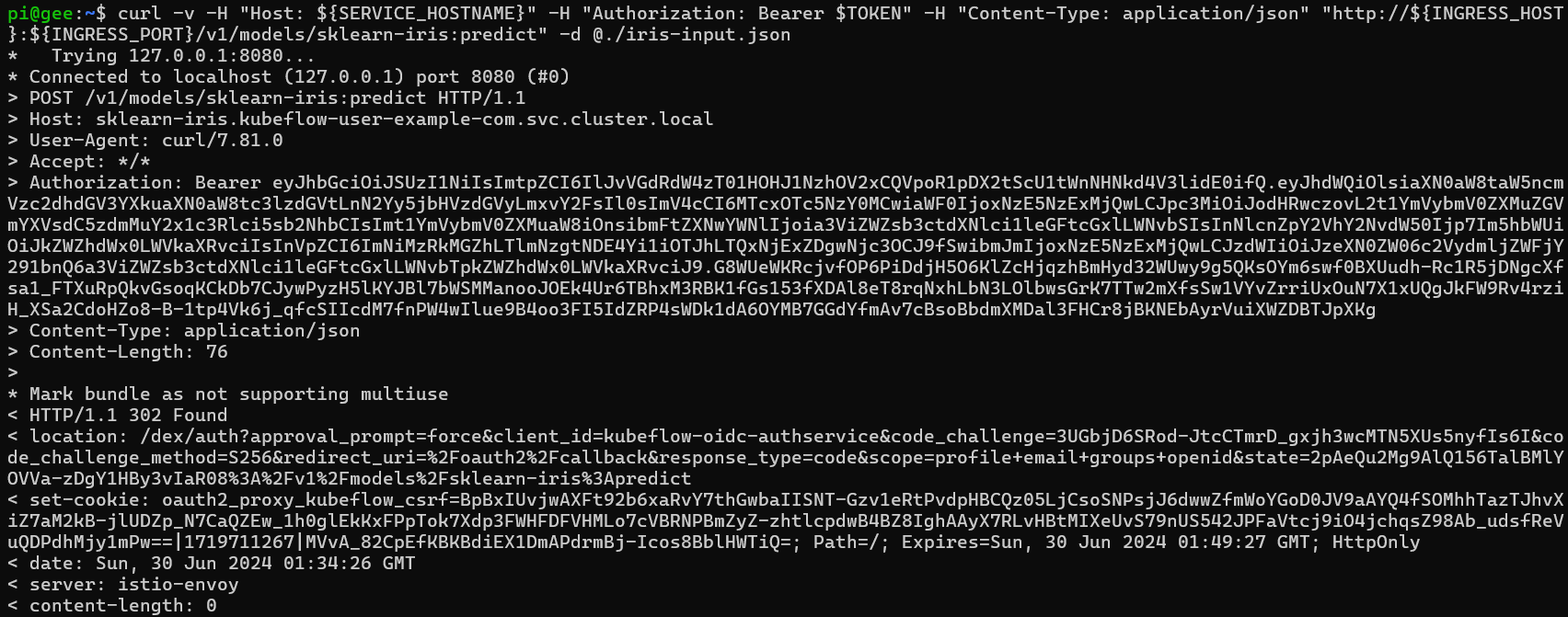
With or without the Istio sidecar for the inference service, I still see this 302 issue with these commands (authenticating through the service access token):
kubectl port-forward svc/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system 8080:80
SERVICE_HOSTNAME=$(kubectl get inferenceservice sklearn-iris -n kubeflow-user-example-com -o jsonpath='{.status.url}' | cut -d "/" -f 3)
INGRESS_HOST=localhost
INGRESS_PORT=8080
TOKEN=$(kubectl create token default-editor -n kubeflow-user-example-com --audience=istio-ingressgateway.istio-system.svc.cluster.local --duration=24h)
curl -v -H "Host: ${SERVICE_HOSTNAME}" -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -H "Content-Type: application/json" "http://${INGRESS_HOST}:${INGRESS_PORT}/v1/models/sklearn-iris:predict" -d @./iris-input.json
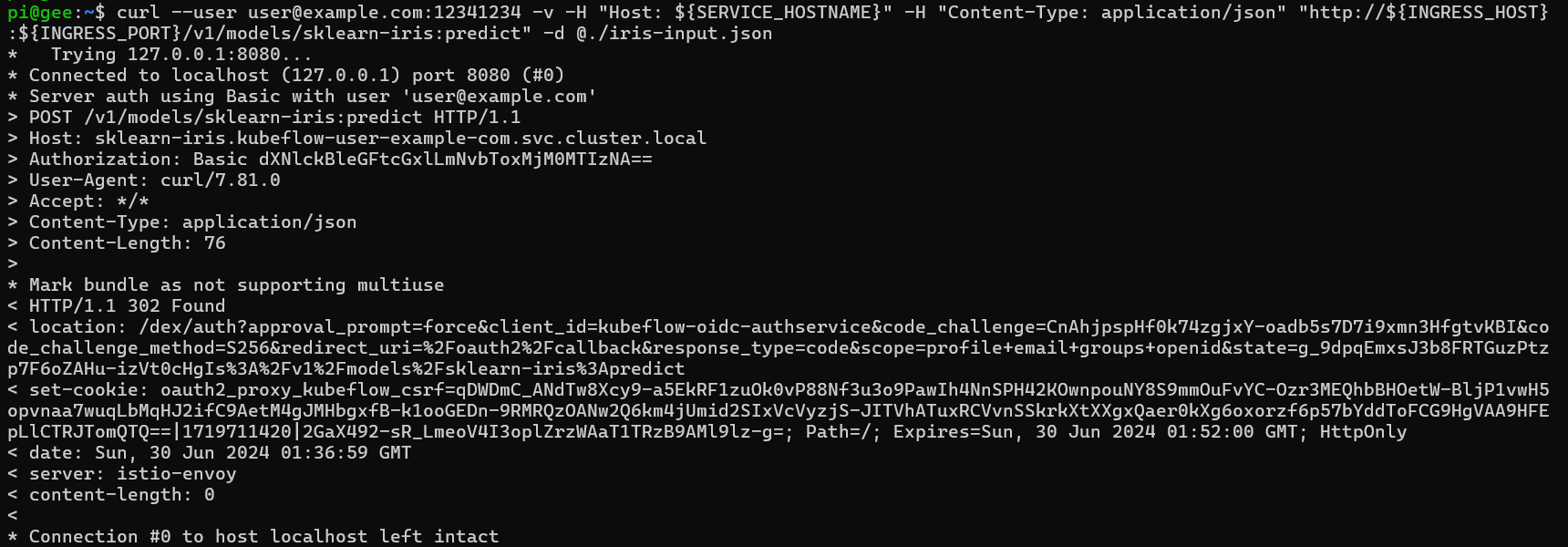
This fails too, for the basic authentication as such:
curl --user user@example.com:12341234 -v -H "Host: ${SERVICE_HOSTNAME}" -H "Content-Type: application/json" "http://${INGRESS_HOST}:${INGRESS_PORT}/v1/models/sklearn-iris:predict" -d @./iris-input.json
Using cookies also fails:
curl --cookie "authservice_session=None" -v -H "Host: ${SERVICE_HOSTNAME}" -H "Content-Type: application/json" "http://${INGRESS_HOST}:${INGRESS_PORT}/v1/models/sklearn-iris:predict" -d @./iris-input.json