Integrating NFS for Improved Scalability
If you’ve been following the previous post, you might have observed that deploying LLM may not be as scalable. In this post, we delve into the integration of NFS (Network File System) to externalize model environment variables. This approach eliminates the need to rebuild a new image each time a new LLM (Language Model) is introduced into your workflow.
Setting up NFS
Let’s start by setting up NFS to connect to my recently acquired TerraMaster NAS.
sudo apt install nfs-common
# Create an arbitrary folder for mounting
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/shared
# Mounting to the external NAS
sudo mount -t nfs 192.168.68.111:/mnt/usb/usbshare1 /mnt/shared
For a permanent mount, append the following to /etc/fstab:
192.168.68.111:/mnt/usb/usbshare1 /mnt/shared nfs auto 0 0
Verify the settings:
sudo umount /mnt/shared
sudo mount -a
df -h
Integrating NFS with K3s
Utilizing the K3s packaged components, any files dropped into /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/manifests are automatically picked up. Referring to this reference, let’s create the /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/manifests/nfs-models.yaml file with the HelmChart content:
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChart
metadata:
name: nfs-models
namespace: llm
spec:
chart: nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
repo: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
set:
nfs.server: 192.168.68.111
nfs.path: /mnt/usb/usbshare1
storageClass.name: nfs-models
storageClass.reclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClass.accessModes: ReadWriteMany
nfs.reclaimPolicy: Retain
Check the creation of the storageClass:
kc get sc

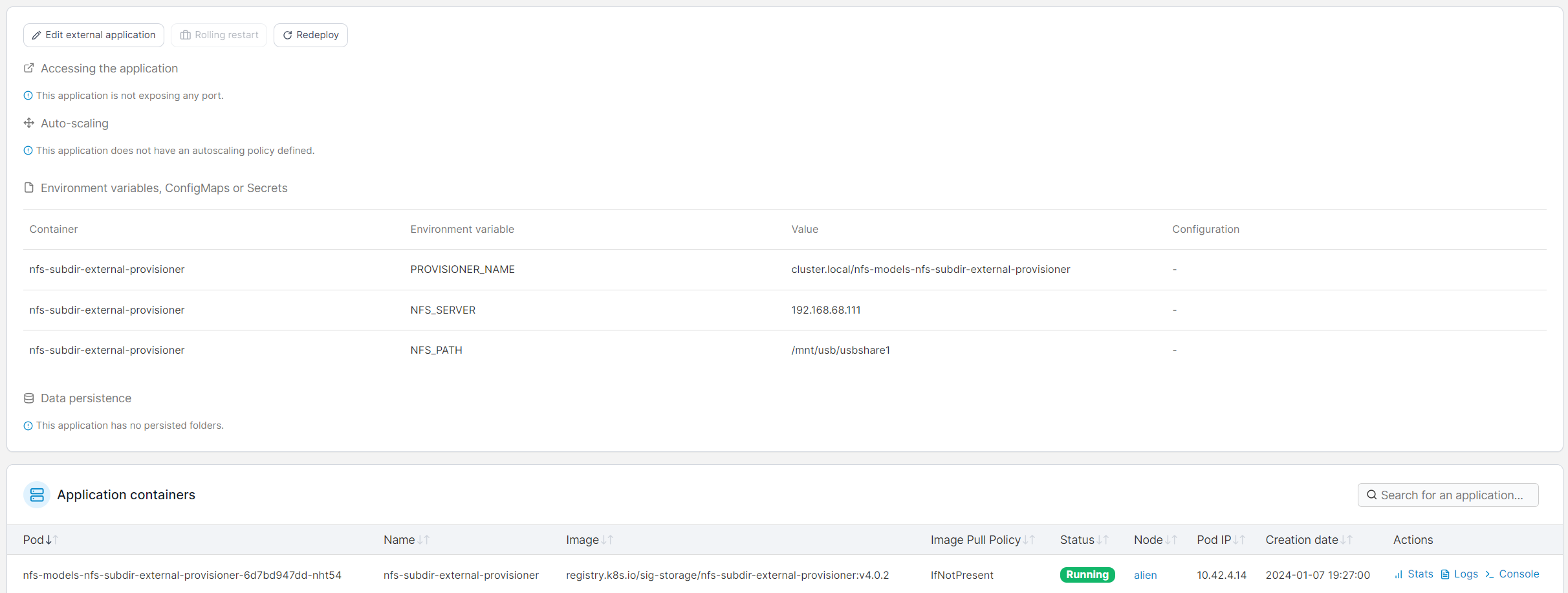
The goal is to share the PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) with all LLM pods. This is the pvc.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nfs-models
namespace: llm
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: nfs-models
resources:
requests:
storage: 200Gi
Apply the change:
kca pvc.yaml
Copy the downloaded LLM models to the shared folder, which should look something like:
$ ls /mnt/shared/
llm-nfs-models-pvc-e1dffafe-b3c0-469c-b988-cf46c57f666a
Building the llama-cpp-python image
To make the model dynamic via environment variable, modify the Dockerfile:
FROM python:3-slim-bullseye
ENV model sample_model
# We need to set the host to 0.0.0.0 to allow outside access
ENV HOST 0.0.0.0
# Install the package
RUN apt update && apt install -y libopenblas-dev ninja-build build-essential pkg-config
RUN pip install --upgrade pip
RUN python -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip pytest cmake scikit-build setuptools fastapi uvicorn sse-starlette pydantic-settings starlette-context
RUN CMAKE_ARGS="-DLLAMA_BLAS=ON -DLLAMA_BLAS_VENDOR=OpenBLAS" pip install --no-cache-dir --force-reinstall llama_cpp_python==0.2.27 --verbose
# Run the server
CMD ["sh", "-c", "python3 -m llama_cpp.server --model /models/\"$model\""]
Build the image:
# Build the image
docker build . -t llama-cpp-python:0.2.27
# Tag it
docker tag llama-cpp-python:0.2.27 192.168.68.115:30500/llama-cpp-python:0.2.27
# Push to the registry
docker push 192.168.68.115:30500/llama-cpp-python:0.2.27
Deploying llama-cpp-python image
Here is the deploy.yaml file for deploying the phi2 model:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: llama-phi2
namespace: llm
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: llama-phi2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: llama-phi2
name: llama-phi2
spec:
containers:
- name: llama-phi2
image: 192.168.68.115:30500/llama-cpp-python:0.2.27
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- IPC_LOCK
volumeMounts:
- name: models-store
mountPath: /models
env:
- name: model
value: phi-2.Q4_K_M.gguf
resources:
requests:
memory: "6Gi"
limits:
memory: "6Gi"
imagePullSecrets:
- name: regcred
volumes:
- name: models-store
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nfs-models
The corresponding svc.yaml (service) file is as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: llama-phi2-svc
namespace: llm
spec:
selector:
app: llama-phi2
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8000
These changes are applied with the following commands:
kca deploy.yaml
kca svc.yaml
Update both Kong service and route:
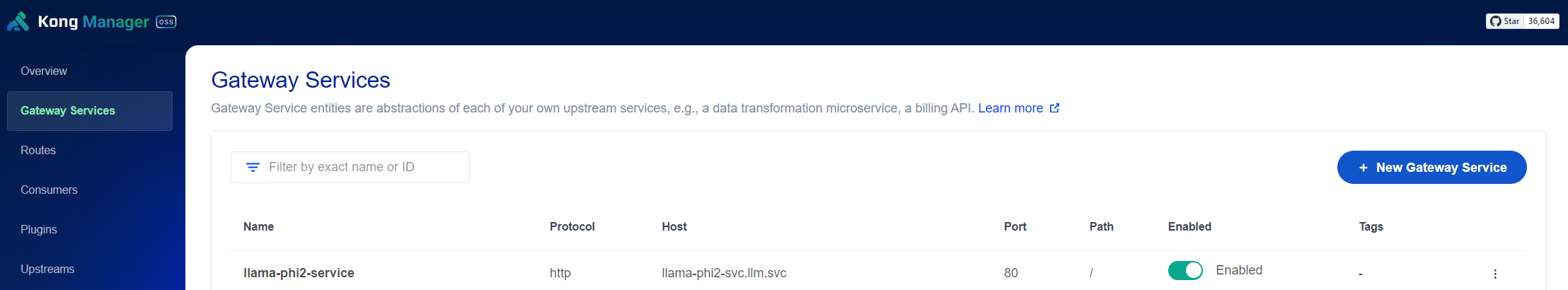
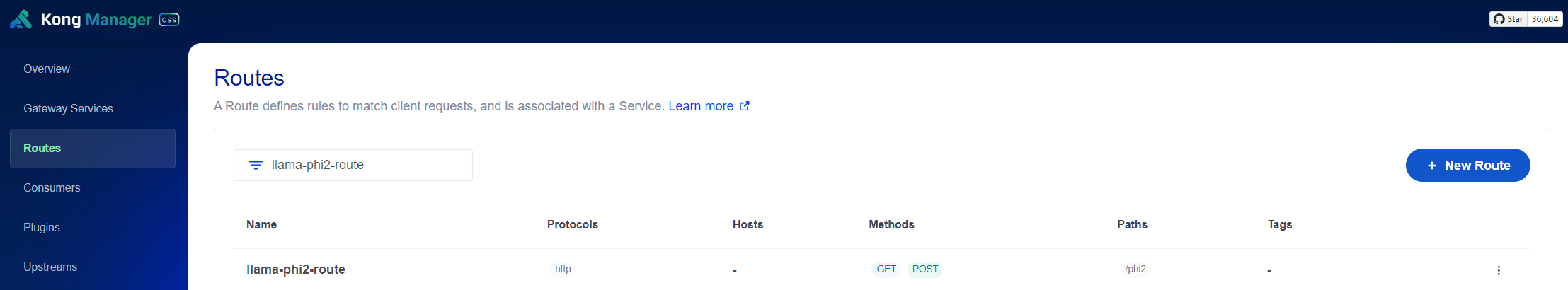
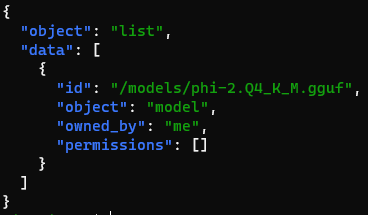
Now, you can test the connection with:
curl http://api.local/phi2/v1/models | jq
Deploying a New LLM
Let’s deploy stabelm-zephyr-3b-GGUF by:
cd /mnt/shared/llm-nfs-models-pvc-e1dffafe-b3c0-469c-b988-cf46c57f666a
# Downloads the stablelm
wget https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/stablelm-zephyr-3b-GGUF/resolve/main/stablelm-zephyr-3b.Q4_K_M.gguf
In a similar fashion, the deploy.yaml file for the stablelm-zephyr LLM is as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: llama-stablelm-zephyr
namespace: llm
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: llama-stablelm-zephyr
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: llama-stablelm-zephyr
name: llama-stablelm-zephyr
spec:
containers:
- name: llama-stablelm-zephyr
image: 192.168.68.115:30500/llama-cpp-python:0.2.27
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- IPC_LOCK
volumeMounts:
- name: models-store
mountPath: /models
env:
- name: model
value: stablelm-zephyr-3b.Q4_K_M.gguf
resources:
requests:
memory: "6Gi"
limits:
memory: "6Gi"
imagePullSecrets:
- name: regcred
volumes:
- name: models-store
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nfs-models
The svc.yaml file is similar:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: llama-stablelm-zephyr-svc
namespace: llm
spec:
selector:
app: llama-stablelm-zephyr
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8000
By applying the changes and adding the relevant Kong service and route, you can check the path:
# Assuming the path of the LLM is stablelm-zephyr
curl http://api.local/stablelm-zephyr/v1/models | jq
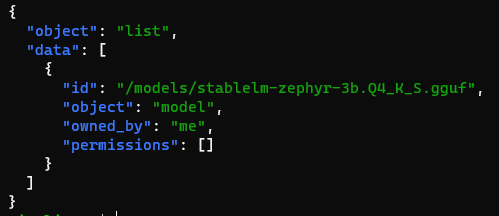
And that concludes this post! By deploying LLM in this manner, you can consolidate all models in your NAS, enabling better scalability in your home lab.